Abstract
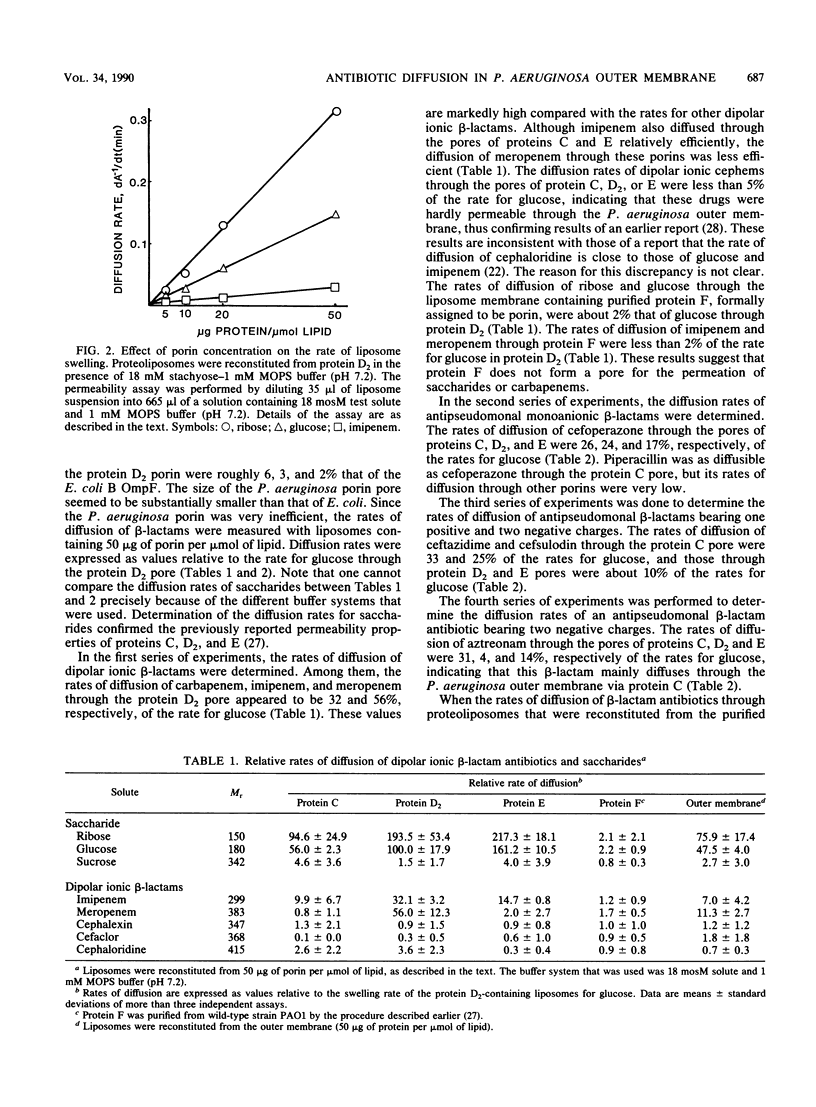
Determination of the rates of diffusion of beta-lactam antibiotics through purified Pseudomonas aeruginosa porins C, D2, and E in liposomes yielded the following results. (i) The rates of carbapenem (imipenem and meropenem) diffusion through the protein D2 pore were roughly 2 to 70 times higher than those through other porin pores. It is not clear why the protein D2 pore allowed rapid diffusion of carbapenems. The rates of diffusion of glucosamine and triglycine through the protein D2 pore were about 14 and 4 times higher, respectively, than that of an uncharged test solute with a similar Mr, glucose. (ii) The rates of diffusion of antipseudomonal anionic beta-lactams such as piperacillin, ceftazidime, cefsulodin, and aztreonam through the protein C pore were higher than those through other porin pores. This was probably due to the slightly larger pore size and the slight anion selectivity of protein C, since the apparent exclusion limit of the protein C pore for uncharged saccharides is higher than that of other porins and the rate of diffusion of gluconic acid through the protein C pore is about double that for glucose. (iii) The rates of diffusion of cefoperazone through all three species of porin were relatively high. These results indicate that the antipseudomonal beta-lactams permeate the P. aeruginosa outer membrane via newly identified porins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angus B. L., Carey A. M., Caron D. A., Kropinski A. M., Hancock R. E. Outer membrane permeability in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of a wild-type with an antibiotic-supersusceptible mutant. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):299–309. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Hancock R. E. Properties of the large ion-permeable pores formed from protein F of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 20;646(2):298–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey A. J., Bryan L. E. Penetration of beta-lactams through Pseudomonas aeruginosa porin channels. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Aug;31(8):1216–1221. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.8.1216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh N., Wakebe H., Yoshihara E., Nakae T., Nishino T. Role of protein F in maintaining structural integrity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):983–990. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.983-990.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Decad G. M., Nikaido H. Identification of the protein producing transmembrane diffusion pores in the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 5;554(2):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90373-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Nikaido H. Outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria. XIX. Isolation from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and use in reconstitution and definition of the permeability barrier. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):381–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.381-390.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii J., Nakae T. Size of diffusion pore of Alcaligenes faecalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Mar;32(3):378–384. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.3.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M., Yang Y. J. Beta-lactamase lability and inducer power of newer beta-lactam antibiotics in relation to their activity against beta-lactamase-inducibility mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch M. J., Drusano G. L., Mobley H. L. Emergence of resistance to imipenem in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1892–1896. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Kageyama M. Separation and characterization of the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biochem. 1978 Jul;84(1):179–191. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T., Ishii J., Ferenci T. The role of the maltodextrin-binding site in determining the transport properties of the LamB protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):622–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Rosenberg E. Y. Porin channels in Escherichia coli: studies with liposomes reconstituted from purified proteins. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):241–252. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.241-252.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen M. M., Marso E., Pickett M. J. Nonfermentative bacilli associated with man. 3. Pathogenicity and antibiotic susceptibility. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Aug;54(2):178–192. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/54.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., Dudek E. J., DiVincenzo C. A., Lucks D. A., Lerner S. A. Emergence of resistance to imipenem during therapy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):289–294. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Kamio Y., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: chemical analysis and freeze-fracture studies with lipopolysaccharide mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):942–958. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.942-958.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studemeister A. E., Quinn J. P. Selective imipenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with diminished outer membrane permeability. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1267–1268. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga H., Tokunaga M., Nakae T. Characterization of porins from the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. 1. Chemical analysis. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):433–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama H., Akatsuka A., Nakae T. The outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a barrier against the penetration of disaccharides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 14;134(1):106–112. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90533-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama H., Nakae T. A small diffusion pore in the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 15;157(1):33–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihara E., Gotoh N., Nakae T. In vitro demonstration by the rate assay of the presence of small pore in the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):470–476. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80865-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihara E., Nakae T. Identification of porins in the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that form small diffusion pores. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6297–6301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Nikaido H. Diffusion of beta-lactam antibiotics through the porin channels of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):84–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Nikaido H. Permeability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane to hydrophilic solutes. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):636–642. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.636-642.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Zalman L. S., Nikaido H. Purification and properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa porin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2308–2314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]