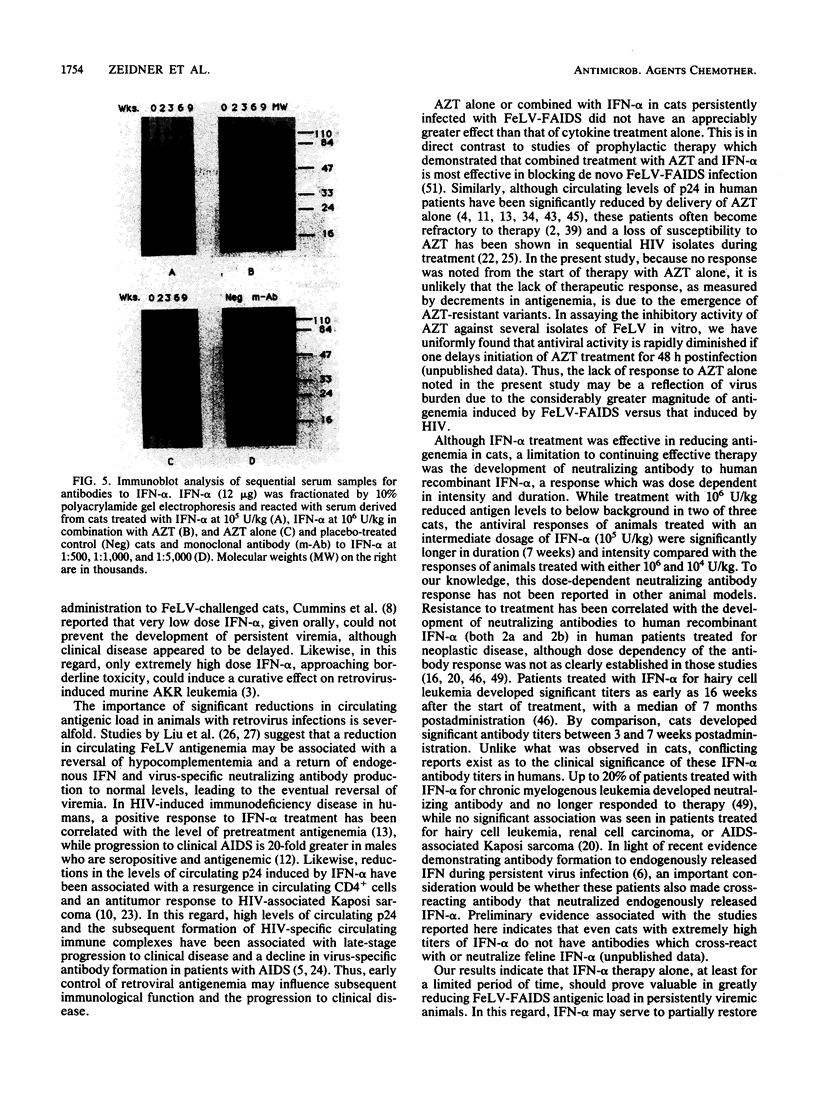
Abstract
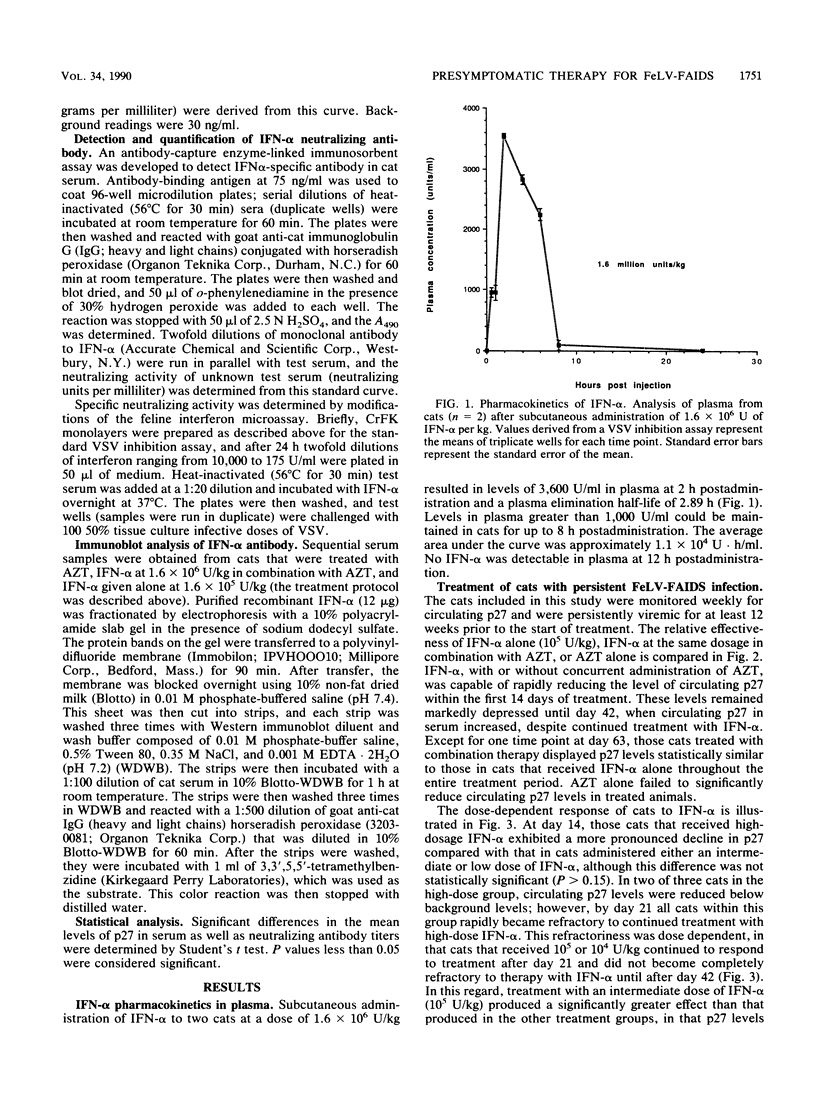
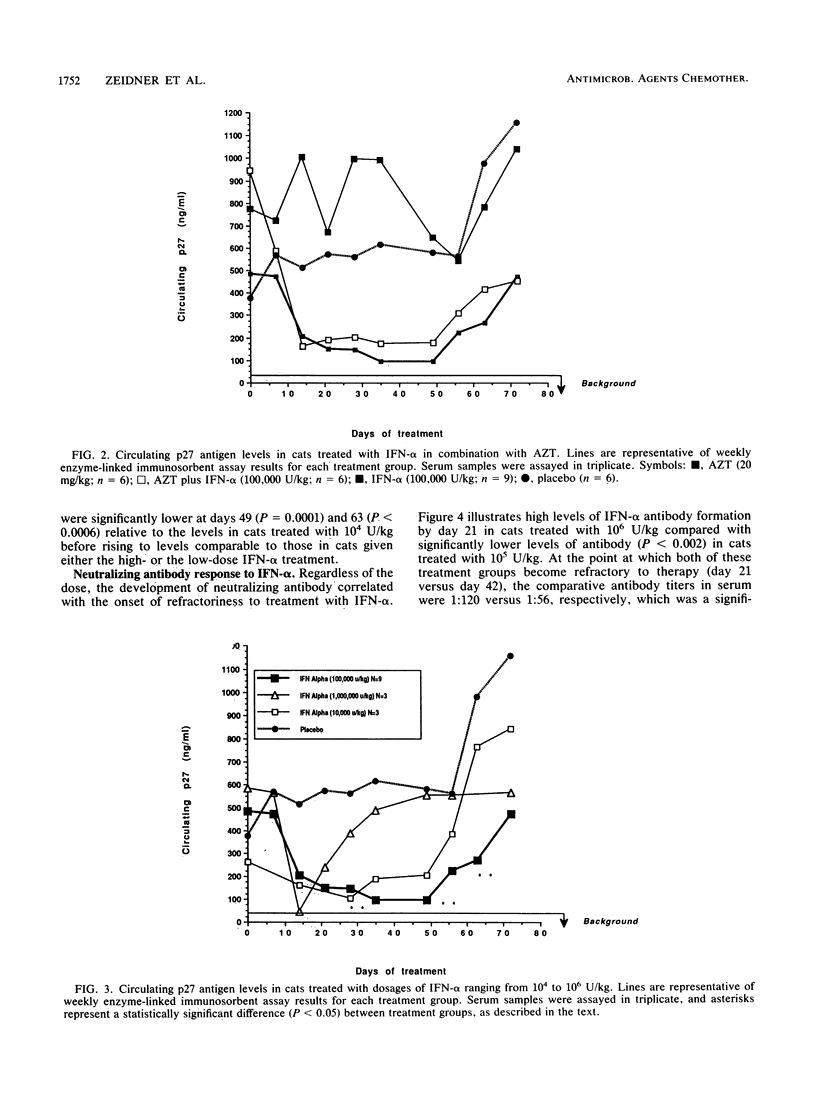
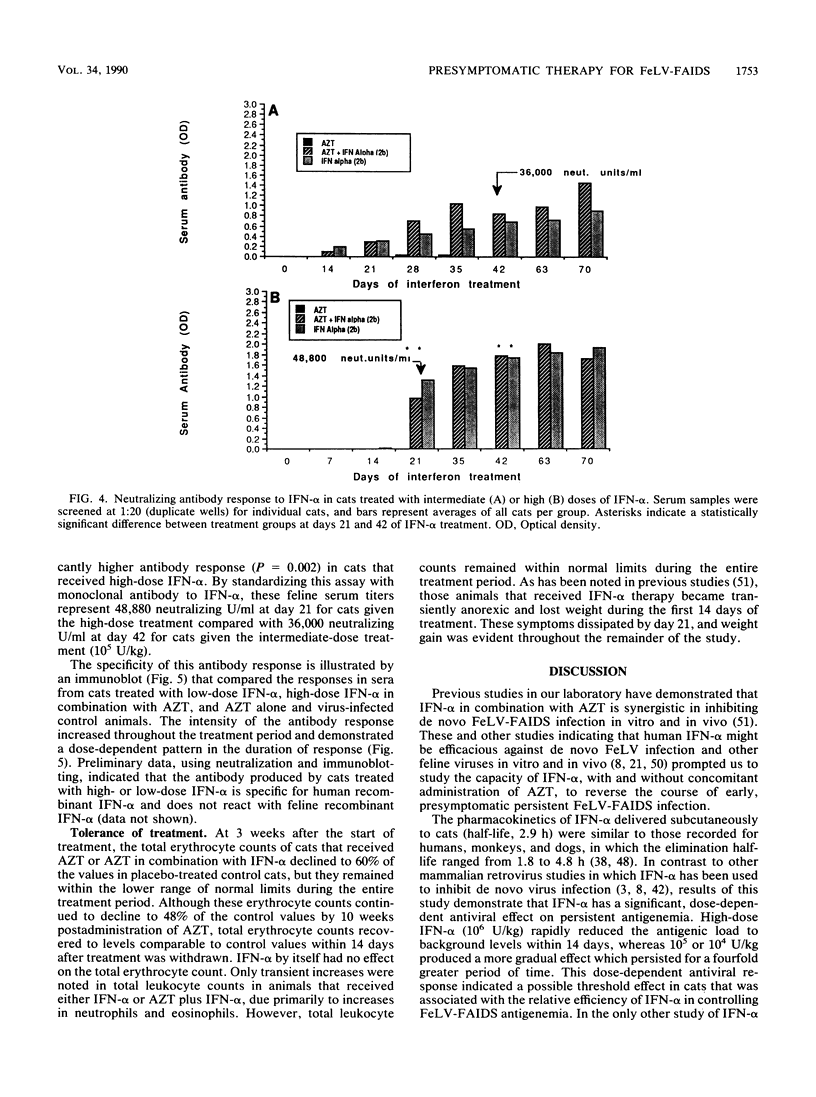
The therapeutic efficacies of human recombinant alpha interferon (IFN-alpha), IFN-alpha plus zidovudine (AZT), and AZT alone were evaluated in presymptomatic cats with established feline leukemia virus (FeLV)-acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (FAIDS) infection and high levels of persistent antigenemia. Subcutaneous injection of 1.6 x 10(6) U of human recombinant IFN-alpha 2b per kg delivered peak concentrations in plasma of 3,600 U/ml at 2 h postadministration with a half-life of elimination of 2.9 h. This dosage of IFN-alpha could be delivered to cats for up to 12 weeks without significant clinical toxicity. Oral administration of AZT (20 mg/kg three times daily) resulted in peak concentrations in plasma of 3 micrograms/ml at 2 h with a half-life of elimination of approximately 1.60 h. Treatment of FeLV-FAIDS-infected cats with IFN-alpha, either alone or in combination with orally administered AZT, resulted in significant decreases in circulating p27 core antigen beginning 2 weeks after the initiation of therapy. AZT alone had no effect on circulating virus antigen. Depending upon whether high (1.6 x 10(6) U/kg)- or low (1.6 x 10(4) to 1.6 x 10(5) U/kg)-dosage IFN-alpha was used, cats became refractory to therapy 3 or 7 weeks after the beginning of treatment. At these times, IFN-alpha-treated animals developed antibodies to IFN-alpha that were neutralizing, specific for human recombinant IFN-alpha, and dose dependent in magnitude. The results of this study indicate that human recombinant IFN-alpha is effective in reducing circulating virus antigenic load in cats persistently infected with FeLV-FAIDS. However, the continued efficacy of IFN-alpha therapy appeared to be limited by the formation of cytokine-specific neutralizing antibodies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A. Semi-micro, dye-binding assay for rabbit interferon. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):723–725. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.723-725.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. C. Failure of zidovudine to maintain remission in patients with AIDS. N Engl J Med. 1989 Mar 2;320(9):594–595. doi: 10.1056/nejm198903023200913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook M. G., Gor D., Forster S. M., Harris W., Jeffries D. J., Thomas H. C. Suppression of HIV p24 antigen and induction of HIV anti-p24 antibody by alpha interferon in patients with chronic hepatitis B. AIDS. 1988 Oct;2(5):391–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carini C., Mezzaroma I., Scano G., D'Amelio R., Matricardi P., Aiuti F. Characterization of specific immune complexes in HIV-related disorders. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Jul;26(1):21–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruso A., Bonfanti C., Colombrita D., De Francesco M., De Rango C., Foresti I., Gargiulo F., Gonzales R., Gribaudo G., Landolfo S. Natural antibodies to IFN-gamma in man and their increase during viral infection. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):685–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Seto D., Tateno M., Levy J. A. Biologic features of HIV-1 that correlate with virulence in the host. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.2832945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins J. M., Tompkins M. B., Olsen R. G., Tompkins W. A., Lewis M. G. Oral use of human alpha interferon in cats. J Biol Response Mod. 1988 Oct;7(5):513–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J. W., Morgan W. M., Hardy A. M., Jaffe H. W., Darrow W. W., Dowdle W. R. The epidemiology of AIDS: current status and future prospects. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1352–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.2994217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dournon E., Matheron S., Rozenbaum W., Gharakhanian S., Michon C., Girard P. M., Perronne C., Salmon D., De Truchis P., Leport C. Effects of zidovudine in 365 consecutive patients with AIDS or AIDS-related complex. Lancet. 1988 Dec 3;2(8623):1297–1302. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92903-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenyö E. M., Morfeldt-Månson L., Chiodi F., Lind B., von Gegerfelt A., Albert J., Olausson E., Asjö B. Distinct replicative and cytopathic characteristics of human immunodeficiency virus isolates. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4414–4419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4414-4419.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., Fyfe J. A., St Clair M. H., Weinhold K., Rideout J. L., Freeman G. A., Lehrman S. N., Bolognesi D. P., Broder S., Mitsuya H. Phosphorylation of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine and selective interaction of the 5'-triphosphate with human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8333–8337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galton J. E., Bedford P., Scott J. E., Brand C. M., Nethersell A. B. Antibodies to lymphoblastoid interferon. Lancet. 1989 Sep 2;2(8662):572–573. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90703-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy W. D., Jr, McClelland A. J. Feline leukemia virus. Its related diseases and control. Vet Clin North Am. 1977 Feb;7(1):93–103. doi: 10.1016/s0091-0279(77)50008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorn K. L., Vogt M. W., Chou T. C., Blumberg R. S., Byington R., Schooley R. T., Hirsch M. S. Synergistic inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus in vitro by azidothymidine and recombinant alpha A interferon. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):168–172. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover E. A., Mullins J. I., Quackenbush S. L., Gasper P. W. Experimental transmission and pathogenesis of immunodeficiency syndrome in cats. Blood. 1987 Dec;70(6):1880–1892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itri L. M., Campion M., Dennin R. A., Palleroni A. V., Gutterman J. U., Groopman J. E., Trown P. W. Incidence and clinical significance of neutralizing antibodies in patients receiving recombinant interferon alfa-2a by intramuscular injection. Cancer. 1987 Feb 1;59(3 Suppl):668–674. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870201)59:3+<668::aid-cncr2820591317>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson P., Essex M. Inhibition of feline leukemia virus replication by human leukocyte interferon. Antiviral Res. 1983 Aug;3(2):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(83)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land S., Terloar G., McPhee D., Birch C., Doherty R., Cooper D., Gust I. Decreased in vitro susceptibility to zidovudine of HIV isolates obtained from patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):326–329. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Kovacs J. A., Feinberg J., Herpin B., Davey V., Walker R., Deyton L., Metcalf J. A., Baseler M., Salzman N. Anti-retroviral effects of interferon-alpha in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Lancet. 1988 Nov 26;2(8622):1218–1222. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90811-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange J. M., Paul D. A., Huisman H. G., de Wolf F., van den Berg H., Coutinho R. A., Danner S. A., van der Noordaa J., Goudsmit J. Persistent HIV antigenaemia and decline of HIV core antibodies associated with transition to AIDS. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Dec 6;293(6560):1459–1462. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6560.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G., Richman D. D. HIV with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine (AZT) isolated during prolonged therapy. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.2467383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu W. T., Engelman R. W., Trang L. Q., Hau K., Good R. A., Day N. K. Appearance of cytotoxic antibody to viral gp70 on feline lymphoma cells (FL-74) in cats during ex vivo immunoadsorption therapy: quantitation, characterization, and association with remission of disease and disappearance of viremia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3516–3520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu W. T., Good R. A., Trang L. Q., Engelman R. W., Day N. K. Remission of leukemia and loss of feline leukemia virus in cats injected with Staphylococcus protein A: association with increased circulating interferon and complement-dependent cytotoxic antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6471–6475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz H., Pedersen N. C., Durbin R., Theilen G. H. Monoclonal antibodies to three epitopic regions of feline leukemia virus p27 and their use in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of p27. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jan 28;56(2):209–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90413-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya H., Broder S. Inhibition of infectivity and replication of HIV-2 and SIV in helper T-cells by 2',3'-dideoxynucleosides in vitro. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Apr;4(2):107–113. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya H., Weinhold K. J., Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Lehrman S. N., Gallo R. C., Bolognesi D., Barry D. W., Broder S. 3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine (BW A509U): an antiviral agent that inhibits the infectivity and cytopathic effect of human T-lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7096–7100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. I., Chen C. S., Hoover E. A. Disease-specific and tissue-specific production of unintegrated feline leukaemia virus variant DNA in feline AIDS. Nature. 1986 Jan 23;319(6051):333–336. doi: 10.1038/319333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbaugh J., Donahue P. R., Quackenbush S. L., Hoover E. A., Mullins J. I. Molecular cloning of a feline leukemia virus that induces fatal immunodeficiency disease in cats. Science. 1988 Feb 19;239(4842):906–910. doi: 10.1126/science.2893454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks W. P., Parks E. S., Fischl M. A., Leuther M. D., Allain J. P., Nusinoff-Lehrman S., Barry D. W., Makuch R. W. HIV-1 inhibition by azidothymidine in a concurrently randomized placebo-controlled trail. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1988;1(2):125–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perno C. F., Yarchoan R., Cooney D. A., Hartman N. R., Gartner S., Popovic M., Hao Z., Gerrard T. L., Wilson Y. A., Johns D. G. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1/HTLV-IIIBa-L) replication in fresh and cultured human peripheral blood monocytes/macrophages by azidothymidine and related 2',3'-dideoxynucleosides. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):1111–1125. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Orenstein J. M., Kinter A., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S. Interferon-alpha but not AZT suppresses HIV expression in chronically infected cell lines. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):575–577. doi: 10.1126/science.2470148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quackenbush S. L., Mullins J. I., Hoover E. A. Colony forming T lymphocyte deficit in the development of feline retrovirus induced immunodeficiency syndrome. Blood. 1989 Feb;73(2):509–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss P., Lange J. M., Boucher C. A., Danner S. A., Goudsmit J. Resumption of HIV antigen production during continuous zidovudine treatment. Lancet. 1988 Feb 20;1(8582):421–421. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein S., Familletti P. C., Pestka S. Convenient assay for interferons. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):755–758. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.755-758.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruprecht R. M., Gama-Sosa M. A., Rosas H. D. Combination therapy after retroviral inoculation. Lancet. 1988 Jan 30;1(8579):239–240. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rübsamen-Waigmann H., Becker W. B., Helm E. B., Brodt R., Fischer H., Henco K., Brede H. D. Isolation of variants of lymphocytopathic retroviruses from the peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with ARC or AIDS. J Med Virol. 1986 Aug;19(4):335–344. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890190406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette P., Narciso P., Tozzi V., Camporiondo M. P., Galgani S., Leoni G. C., Tossini G., Visco G. Low-dose zidovudine for AIDS. Lancet. 1989 May 20;1(8647):1136–1137. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92410-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. S., Brian E. L., Pagano J. S. Resumption of virus production after human immunodeficiency virus infection of T lymphocytes in the presence of azidothymidine. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3769–3773. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3769-3773.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. A., Kennedy C., McCutchan J. A., Bozzette S. A., Straube R. G., Connor J. D., Richman D. D. The antiviral effect of zidovudine and ribavirin in clinical trials and the use of p24 antigen levels as a virologic marker. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):822–828. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steis R. G., Smith J. W., 2nd, Urba W. J., Clark J. W., Itri L. M., Evans L. M., Schoenberger C., Longo D. L. Resistance to recombinant interferon alfa-2a in hairy-cell leukemia associated with neutralizing anti-interferon antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 2;318(22):1409–1413. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806023182201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tersmette M., Gruters R. A., de Wolf F., de Goede R. E., Lange J. M., Schellekens P. T., Goudsmit J., Huisman H. G., Miedema F. Evidence for a role of virulent human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) variants in the pathogenesis of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: studies on sequential HIV isolates. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2118–2125. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2118-2125.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trown P. W., Wills R. J., Kamm J. J. The preclinical development of Roferon-A. Cancer. 1986 Apr 15;57(8 Suppl):1648–1656. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19860415)57:8+<1648::aid-cncr2820571303>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. C. Synergistic antiviral activities of acyclovir and recombinant human leukocyte (alpha) interferon on feline herpesvirus replication. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Oct;50(10):1672–1677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidner N. S., Rose L. M., Mathiason-DuBard C. K., Myles M. H., Hill D. L., Mullins J. I., Hoover E. A. Zidovudine in combination with alpha interferon and interleukin-2 as prophylactic therapy for FeLV-induced immunodeficiency syndrome (FeLV-FAIDS). J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(8):787–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wolf F., Goudsmit J., Paul D. A., Lange J. M., Hooijkaas C., Schellekens P., Coutinho R. A., van der Noordaa J. Risk of AIDS related complex and AIDS in homosexual men with persistent HIV antigenaemia. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Sep 5;295(6598):569–572. doi: 10.1136/bmj.295.6598.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wolf F., Lange J. M., Goudsmit J., Cload P., de Gans J., Schellekens P. T., Coutinho R. A., Fiddian A. P., van der Noordaa J. Effect of zidovudine on serum human immunodeficiency virus antigen levels in symptom-free subjects. Lancet. 1988 Feb 20;1(8582):373–376. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91179-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wussow P., Freund M., Block B., Diedrich H., Poliwoda H., Deicher H. Clinical significance of anti-IFN-alpha antibody titres during interferon therapy. Lancet. 1987 Sep 12;2(8559):635–636. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)93034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]