Abstract
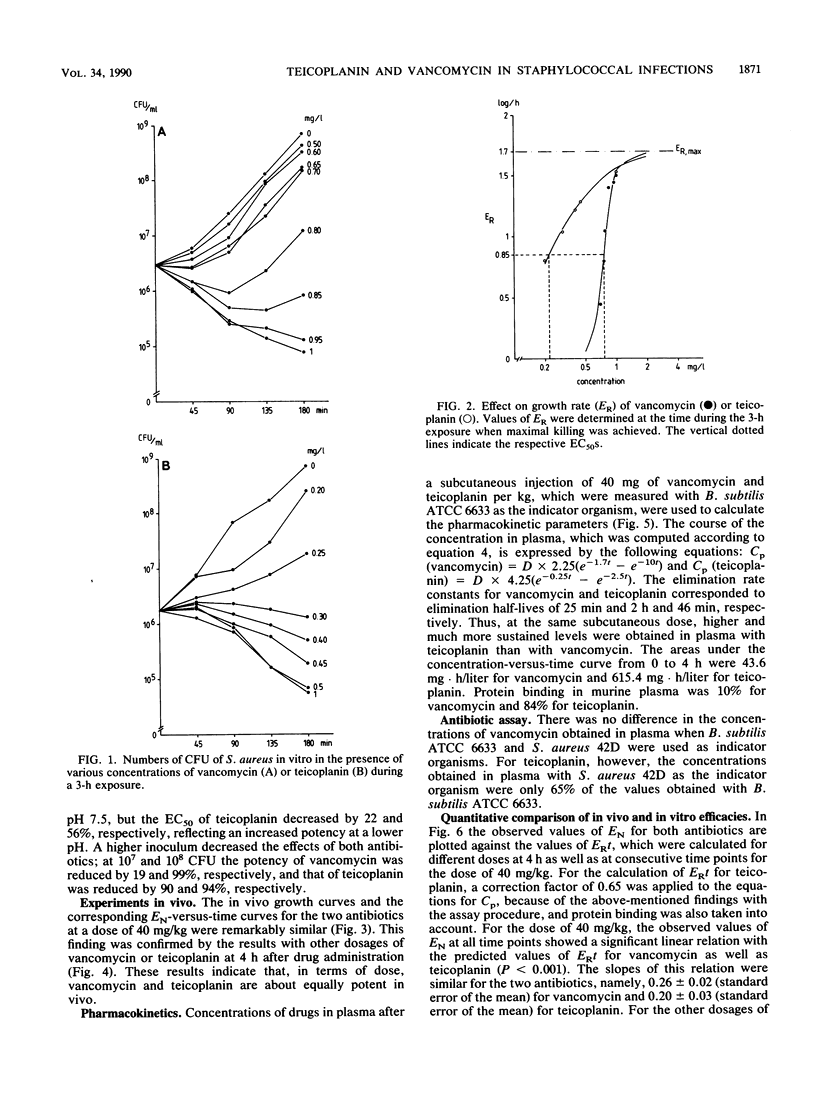
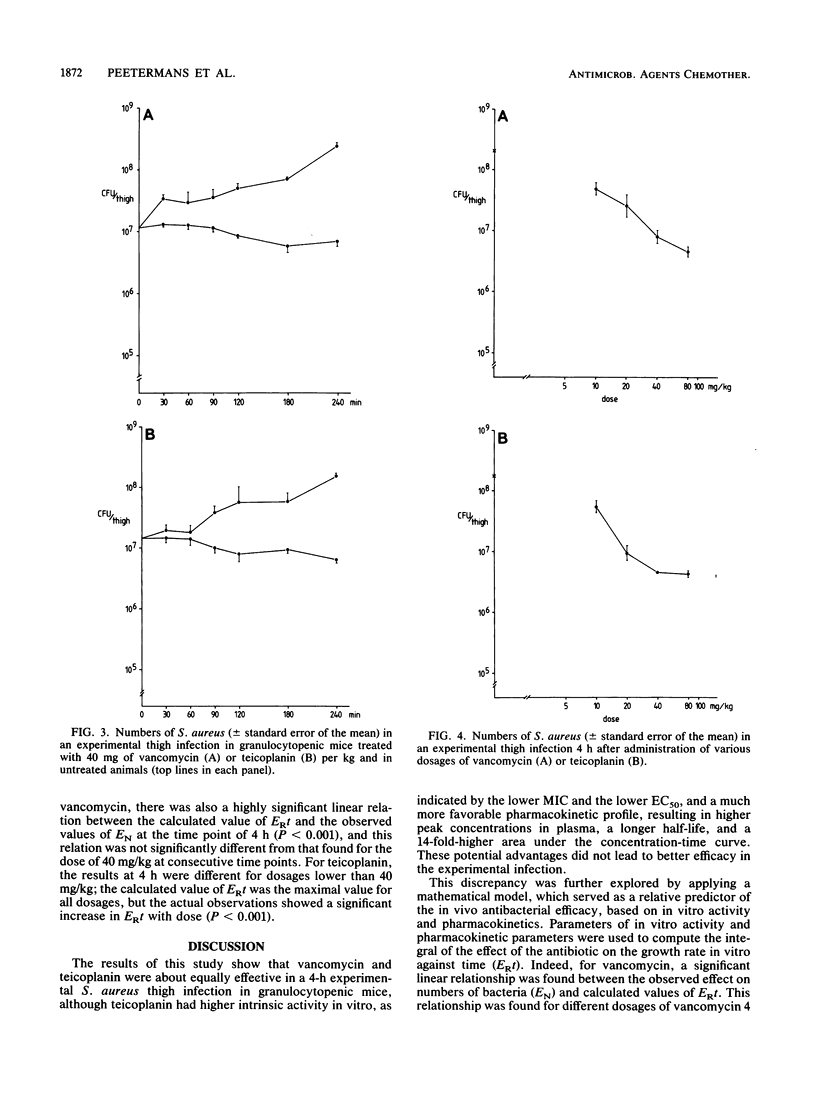
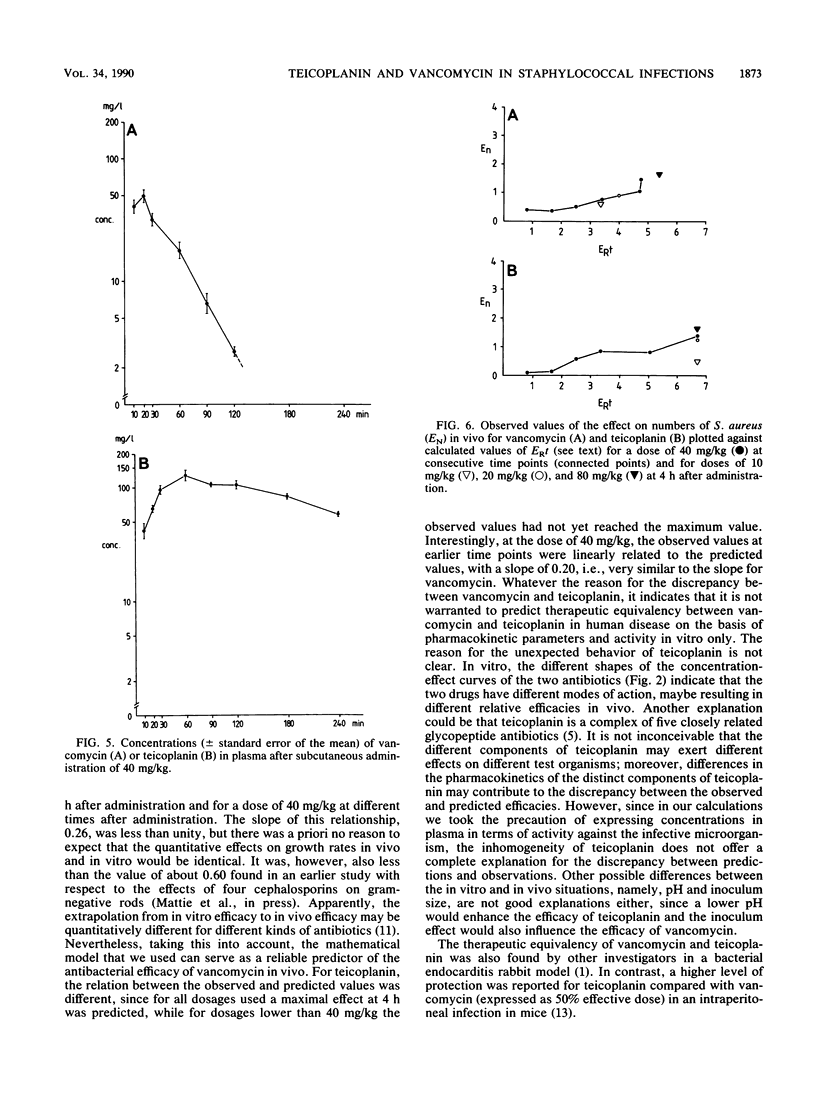
The efficacies of vancomycin and teicoplanin in an experimental Staphylococcus aureus infection in granulocytopenic mice were related to their activities in vitro and their pharmacokinetic profiles. In vitro teicoplanin had a higher intrinsic activity than vancomycin did; and it also had a more favorable pharmacokinetic profile, resulting in higher peak concentrations in plasma, a longer elimination half-life, and a larger area under the concentration-time curve than those of vancomycin. To predict the antibacterial efficacies of the drugs in vivo on the basis of their activities in vitro and pharmacokinetics, a mathematical model was applied. In the model the in vitro effect was expressed as the difference in growth rate between control cultures and those in the presence of the antibiotic (ER), and the in vivo effect was expressed as the difference between numbers of CFU in control and antibiotic-treated animals (EN). The integral of ER against time, ERt, was calculated by using the concentrations found in vivo. A significant linear relationship was found between EN and ERt for different dosages at the same times (4 h) after drug administration as well as for the same doses at consecutive times, although at the lowest doses of teicoplanin the observed effect was less than the predicted effect.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chambers H. F., Sande M. A. Teicoplanin versus nafcillin and vancomycin in the treatment of experimental endocarditis caused by methicillin-susceptible or -resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):61–64. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cynamon M. H., Granato P. A. Comparison of the in vitro activities of teichomycin A2 and vancomycin against staphylococci and enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Mar;21(3):504–505. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.3.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainstein V., LeBlanc B., Bodey G. P. Comparative in vitro study of teichomycin A2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Mar;23(3):497–499. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.3.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D. Microbiological properties of teicoplanin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jan;21 (Suppl A):1–13. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_a.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holford N. H., Sheiner L. B. Understanding the dose-effect relationship: clinical application of pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic models. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1981 Nov-Dec;6(6):429–453. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198106060-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogeterp J. J., Mattie H., Krul A. M., van Furth R. Quantitative effect of granulocytes on antibiotic treatment of experimental staphylococcal infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jun;31(6):930–934. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.6.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagast H., Dodion P., Klastersky J. Comparison of pharmacokinetics and bactericidal activity of teicoplanin and vancomycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Oct;18(4):513–520. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.4.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattie H., Goslings W. R., Noach E. L. Cloxacillin and nafcillin: serum binding and its relationship to antibacterial effect in mice. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):170–177. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattie H. Kinetics of antimicrobial action. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallanza R., Berti M., Goldstein B. P., Mapelli E., Randisi E., Scotti R., Arioli V. Teichomycin: in-vitro and in-vivo evaluation in comparison with other antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 May;11(5):419–425. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.5.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiner L. B., Stanski D. R., Vozeh S., Miller R. D., Ham J. Simultaneous modeling of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: application to d-tubocurarine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Mar;25(3):358–371. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979253358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L., Tjandramaga B., Hendrickx B., Van Hecken A., Van Melle P., Verbesselt R., Verhaegen J., De Schepper P. J. In vitro activity and human pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):881–886. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


