Abstract
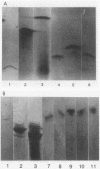
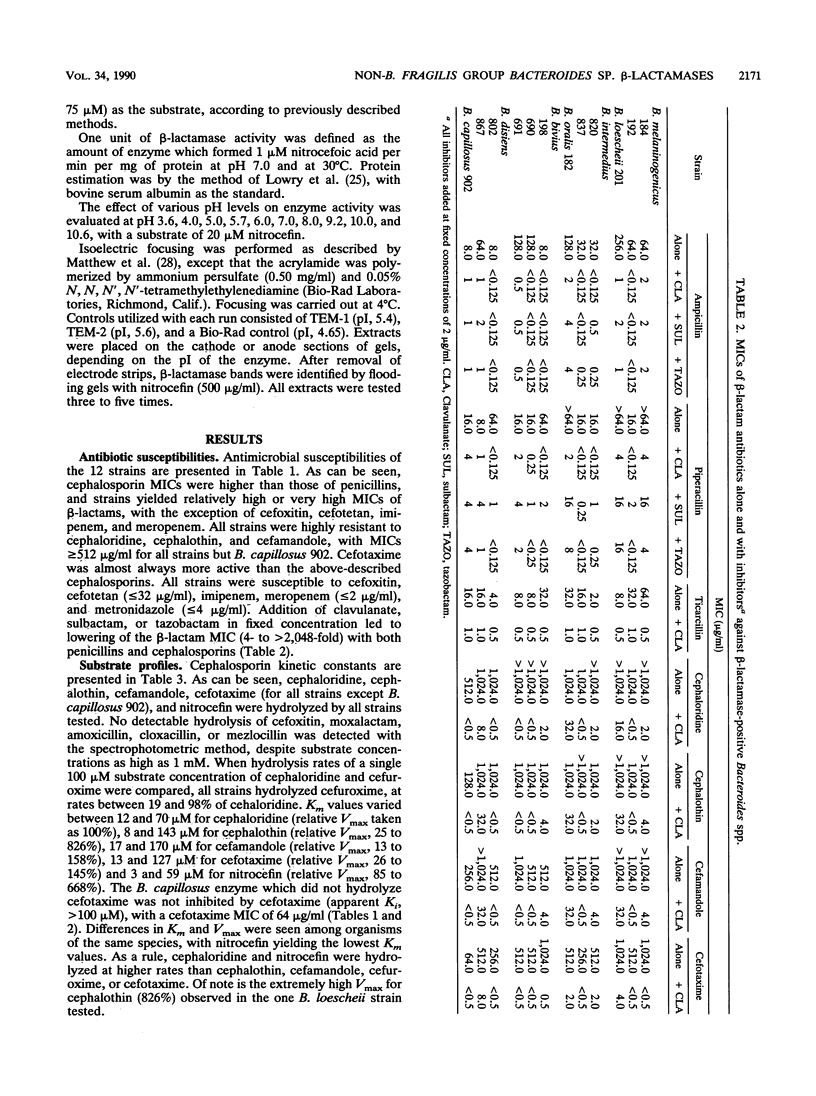
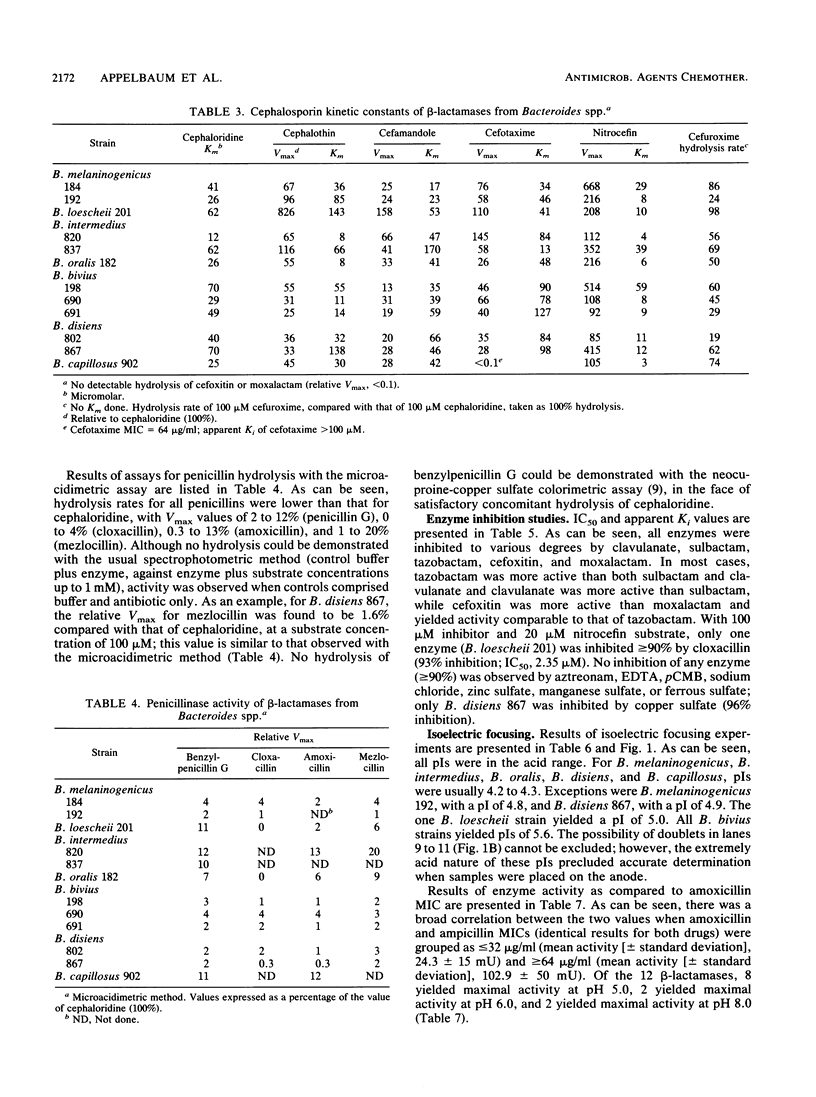
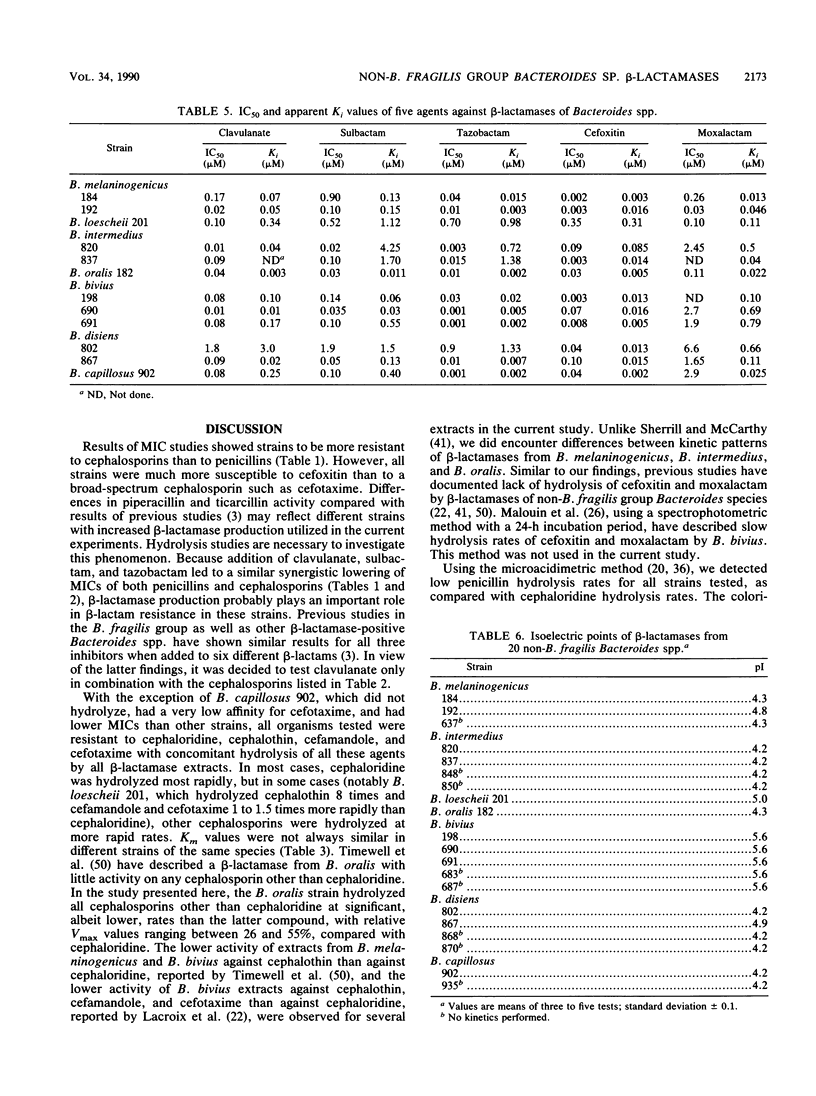
Twelve beta-lactamase-positive non-Bacteroides fragilis group Bacteroides spp. belonging to seven different species were examined by MIC determination and enzyme characterization. MICs of most beta-lactams except cefoxitin, cefotetan, imipenem, and meropenem were relatively high or very high. All enzymes hydrolyzed cephaloridine (Vmax, 100%; Km, 12 to 70 microM), cephalothin (Vmax, 25 to 826%; Km, 8 to 143 microM), cefamandole (Vmax, 13 to 158%; Km, 17 to 170 microM), and cefuroxime (hydrolysis rate, 19 to 98%), and 11 of 12 hydrolyzed cefotaxime (Vmax, 26 to 145%; Km, 13 to 127 microM); no hydrolysis of cefoxitin or moxalactam was observed. Penicillins were hydrolyzed at lower rates, with Vmax values less than or equal to 20% of that obtained with cephaloridine. Addition of clavulanate, sulbactam, or tazobactam led to a 4- to 2,048-fold lowering of MICs of penicillins as well as cephalosporins. All enzymes were inhibited by clavulanate (50% inhibitory concentration [IC50], 0.01 to 1.8 microM), sulbactam (IC50, 0.02 to 1.9 microM), tazobactam (IC50, 0.001 to 0.9 microM), cefoxitin (IC50, 0.002 to 0.35 microM), and moxalactam (IC50, 0.03 to 6.6 microM). No enzymes were inhibited by 100 microM EDTA or p-chloromercuribenzoic acid; an enzyme of one strain of B. loescheii was inhibited by 100 microM cloxacillin (IC50, 2.35 microM). Ten enzymes had optimal activity at pH 5.0 to 6.0, and two had optimal activity at pH 8.0. Isoelectric focusing revealed pIs between 4.2 and 5.6. These enzymes seem to belong to a previously unclassified group of beta-lactamases, related (but not identical) to beta-lactamases of the B. fragilis group.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew J. H., Greenwood D. Susceptibility of cefotetan and Sch 34343 to beta-lactamases produced by strains of Bacteroides that hydrolyse cefoxitin or imipenem. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 May;19(5):591–595. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.5.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelbaum P. C., Jacobs M. R., Spangler S. K., Yamabe S. Comparative activity of beta-lactamase inhibitors YTR 830, clavulanate, and sulbactam combined with beta-lactams against beta-lactamase-producing anaerobes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):789–791. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asahi Y., Watanabe K., Ueno K. Biochemical properties of beta-lactamase produced by Bacteroides distasonis. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1989 Jun;42(6):960–967. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.42.960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook I., Calhoun L., Yocum P. Beta-lactamase-producing isolates of Bacteroides species from children. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):164–166. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K. Characterization of beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):259–263. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K. Classification of beta-lactamases: groups 1, 2a, 2b, and 2b'. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):264–270. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K. Classification of beta-lactamases: groups 2c, 2d, 2e, 3, and 4. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):271–276. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohenford M. A., Abraham J., Medeiros A. A. A colorimetric procedure for measuring beta-lactamase activity. Anal Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;168(2):252–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90315-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuchural G. J., Jr, Malamy M. H., Tally F. P. Beta-lactamase-mediated imipenem resistance in Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):645–648. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuchural G. J., Jr, Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Aldridge K., Cleary T., Finegold S. M., Hill G., Iannini P., O'Keefe J. P., Pierson C. Susceptibility of the Bacteroides fragilis group in the United States: analysis by site of isolation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):717–722. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuchural G. J., Jr, Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Marsh P. K., Mayhew J. W. Cefoxitin inactivation by Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Dec;24(6):936–940. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.6.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornbusch K., Olsson-Lijequist B., Nord C. E. Antibacterial activity of new beta-lactam antibiotics on cefoxitin-resistant strains of Bacteroides fragilis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Mar;6(2):207–216. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eley A., Greenwood D. Beta-lactamases of type culture strains of the Bacteroides fragilis group and of strains that hydrolyse cefoxitin, latamoxef and imipenem. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Feb;21(1):49–57. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eley A., Greenwood D. Characterization of beta-lactamases in clinical isolates of Bacteroides. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Sep;18(3):325–333. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. Antibacteroides and beta-lactamase inhibitory activities of moxalactam. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Oct;8(4):337–341. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.4.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace M. E., Gregory F. J., Hung P. P., Fu K. P. Purification and properties of a beta-lactamase from Proteus penneri. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1986 Jul;39(7):938–942. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.39.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimdahl A., von Konow L., Nord C. E. Beta-lactamase-producing Bacteroides species in the oral cavity in relation to penicillin therapy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Sep;8(3):225–229. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.3.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Iyobe S., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of a new beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas cepacia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):355–358. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazmierczak A., Philippon A., Chardon H., Labia R., Le Goffic F. Constantes enzymatiques (Km et Vmax) des beta-lactamases mesurées par une méthode micro-acidimétrique couplée a l'ordinateur. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1973 Oct;124(3):259–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitzis M. D., Billot-Klein D., Goldstein F. W., Williamson R., Tran Van Nhieu G., Carlet J., Acar J. F., Gutmann L. Dissemination of the novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase CTX-1, which confers resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins, and its inhibition by beta-lactamase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):9–14. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix J. M., Lamothe F., Malouin F. Role of Bacteroides bivius beta-lactamase in beta-lactam susceptibility. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Nov;26(5):694–698. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.5.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung T., Williams J. D. beta-Lactamases of subspecies of Bacteroides fragilis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Jul;4(B):47–54. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.suppl_b.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M., Moosdeen F., Lindridge M. A., Kho P., Williams J. D. Behaviour of TEM-1 beta-lactamase as a resistance mechanism to ampicillin, mezlocillin and azlocillin in Escherichia coli. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Feb;17(2):139–146. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malouin F., Fijalkowski C., Lamothe F., Lacroix J. M. Inactivation of cefoxitin and moxalactam by Bacteroides bivius beta-lactamase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):749–755. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew A., Harris A. M., Marshall M. J., Ross G. W. The use of analytical isoelectric focusing for detection and identification of beta-lactamases. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):169–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara N., Yotsuji A., Kumano K., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and some properties of a cephalosporinase from Proteus vulgaris. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):185–187. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Rosenblatt J. E. Penicillin resistance and penicillinase production in clinical isolates of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):605–608. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord C. E. Mechanisms of beta-lactam resistance in anaerobic bacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8 (Suppl 5):S543–S548. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.supplement_5.s543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord C. E., Olsson-Liljequist B. Resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Bacteroides species. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl 500):33–42. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_d.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson-Liljequist B., Dornbusch K., Nord C. E. Characterization of three different beta-lactamases from the Bacteroides fragilis group. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Aug;18(2):220–225. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.2.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson B., Dornbusch K., Nord C. E. Factors contributing to resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Feb;15(2):263–268. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.2.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson B., Dornbusch K., Nord C. E. Susceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics and production of beta-lactamase in Bacteroides fragilis. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1977 Oct 7;163(3):183–194. doi: 10.1007/BF02126677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson B., Nord C. E., Wadström T. Formation of beta-lactamase in Bacteroides fragilis: cell-bound and extracellular activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):727–735. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon A. M., Paul G. C., Jacoby G. A. Properties of PSE-2 beta-lactamase and genetic basis for its production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Sep;24(3):362–369. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.3.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Wong J., Wilkins T. D. Beta-Lactamase activity in strains of Bacteroides melaninogenicus and Bacteroides oralis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):142–146. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Matsuura Y., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Properties of a new penicillinase type produced by Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):579–584. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Matsuura Y., Miyata K., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Characterization of cephalosporinases from Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron and Bacteroides vulgatus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1983 Jan;36(1):76–85. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.36.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg A. H., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Chromosomal beta-lactamases of Enterobacter cloacae are responsible for resistance to third-generation cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):918–925. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. N., Page C. D., Harper P. B. The contribution of beta-lactamases to beta-lactam resistance in Bacteroides fragilis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Jan;9(1):29–45. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Nordström K. Microiodometric determination of beta-lactamase activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Feb;1(2):94–99. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.2.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima M., Sawa K., Watanabe K., Ueno K. The beta-lactamases of genus Bacteroides. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1983 Apr;36(4):423–428. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.36.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Cuchural G. J., Jr Antibiotic resistance in anaerobic bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jul;22 (Suppl A):63–71. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_a.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Cuchural G. J., Jr, Malamy M. H. Mechanisms of resistance and resistance transfer in anaerobic bacteria: factors influencing antimicrobial therapy. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;6 (Suppl 1):S260–S269. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_1.s260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., O'Keefe J. P., Sullivan N. M., Gorbach S. L. Inactivation of cephalosporins by Bacteroides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):565–571. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timewell R. M., Phillips I., Söderholm J., Nord C. E. Isoelectric focusing of Bacteroides melaninogenicus group beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):700–704. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timewell R., Taylor E., Phillips I. The beta-lactamases of Bacteroides species. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Feb;7(2):137–146. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.2.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waley S. G. A spectrophotometric assay of beta-lactamase action on penicillins. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):789–790. doi: 10.1042/bj1390789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler H. M., Finegold S. M. Antimicrobial resistance in Bacteroides. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Feb;19(2):143–146. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.2.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yotsuji A., Minami S., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Properties of novel beta-lactamase produced by Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Dec;24(6):925–929. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.6.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yotsuji A., Minami S., Kakizawa H., Yasuda T., Takai A., Saikawa I., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Cephamycin inactivation due to enzymatic hydrolysis by beta-lactamase from Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Dec;28(6):773–777. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.6.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yotsuji A., Minami S., Okamoto S., Yasuda T., Takai A., Saikawa I., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Immunological properties of a novel beta-lactamase produced by Bacteroides fragilis. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1984 Nov;37(11):1483–1485. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.37.1483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]