Abstract
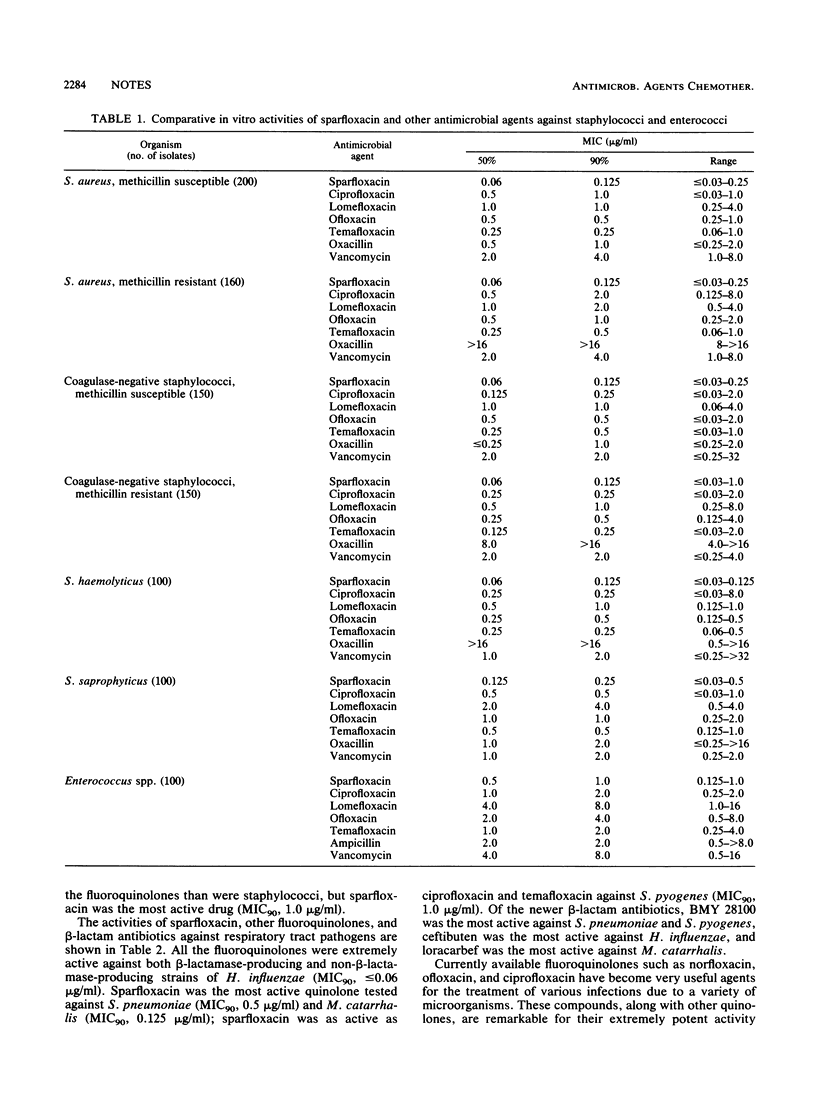
The in vitro activity of sparfloxacin (CI-978; AT-4140) was compared with those of other antimicrobial agents against isolates of staphylococci, enterococci, and various respiratory tract pathogens. Sparfloxacin was the most active drug tested against staphylococci (MIC for 90% of the strains tested [MIC90], 0.125 micrograms/ml) and enterococci (MIC90, 1.0 microgram/ml). It was also active against Haemophilus influenzae (MIC90, less than or equal to 0.06 microgram/ml), Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis (MIC90, 0.125 microgram/ml), Streptococcus pneumoniae (MIC90, 0.5 microgram/ml), and Streptococcus pyogenes (MIC90, 1.0 microgram/ml).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auckenthaler R., Michéa-Hamzehpour M., Pechère J. C. In-vitro activity of newer quinolones against aerobic bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17 (Suppl B):29–39. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.suppl_b.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper B., Lawlor M. Pneumococcal bacteremia during ciprofloxacin therapy for pneumococcal pneumonia. Am J Med. 1989 Oct;87(4):475–475. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(89)80838-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J. Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections with oral ciprofloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):153–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_d.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlando F., Rietiker S., Täuber M. G., Flepp M., Meier B., Lüthy R. Single-dose ciprofloxacin at 100 versus 250 mg for treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infections in women. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):354–356. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R. N., Kennedy D. J., Reilly P. M., Luppen K. L., Weinandt W. J., Bollinger M. R., Aguirre F., Kodesch F., Saeed A. M. Treatment of bone, joint, and soft-tissue infections with oral ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):151–155. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S. The fluoroquinolones: pharmacology, clinical uses, and toxicities in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):716–721. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Barry A. L. In vitro evaluation of WIN 57273, a new broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):306–313. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A., Phillips I. The comparative in-vitro activity of eight newer quinolones and nalidixic acid. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):1–20. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_d.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima T., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro activity of AT-4140 against clinical bacterial isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1980–1988. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzulli T., Simor A. E., Jaeger R., Fuller S., Low D. E. Comparative in vitro activities of several new fluoroquinolones and beta-lactam antimicrobial agents against community isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Mar;34(3):467–469. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Ruane P. J., Johnston L., Wong P., Wheelock J. P., MacDonald K., Reinhardt J. F., Johnson C. C., Statner B., Blomquist I. Ciprofloxacin for eradication of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Kurobe N., Ohue T., Hashimoto M., Shimizu M. Pharmacokinetics of a novel quinolone, AT-4140, in animals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):89–93. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Minami A., Nakata K., Kurobe N., Kouno K., Sakaguchi Y., Kashimoto S., Yoshida H., Kojima T., Ohue T. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of AT-4140, a new broad-spectrum quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1167–1173. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Novelli A., Chin N. X. Comparative in vitro activity of a new quinolone, AM-1091. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jul;33(7):1036–1041. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.7.1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piercy E. A., Barbaro D., Luby J. P., Mackowiak P. A. Ciprofloxacin for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):128–130. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. M., Leyland M. J., Farrell I. D., Geddes A. M. Preliminary evaluation of ciprofloxacin, a new 4-quinolone antibiotic, in the treatment of febrile neutropenic patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):165–174. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_d.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. P., Baltch A. L., Hammer M. C., Conroy J. V. In vitro activities of PD 117,596 and reference antibiotics against 448 clinical bacterial strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Sep;32(9):1450–1455. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.9.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. Fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agents. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Oct;2(4):378–424. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.4.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. The fluoroquinolones: structures, mechanisms of action and resistance, and spectra of activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):581–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


