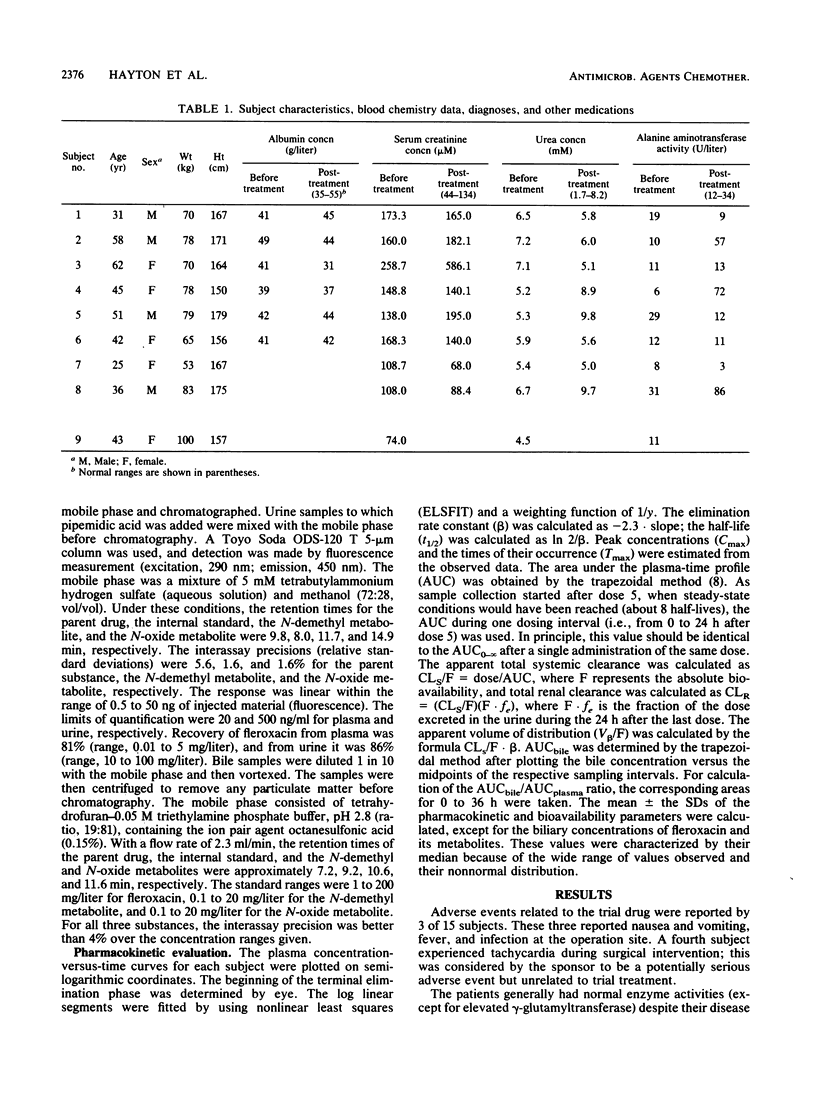
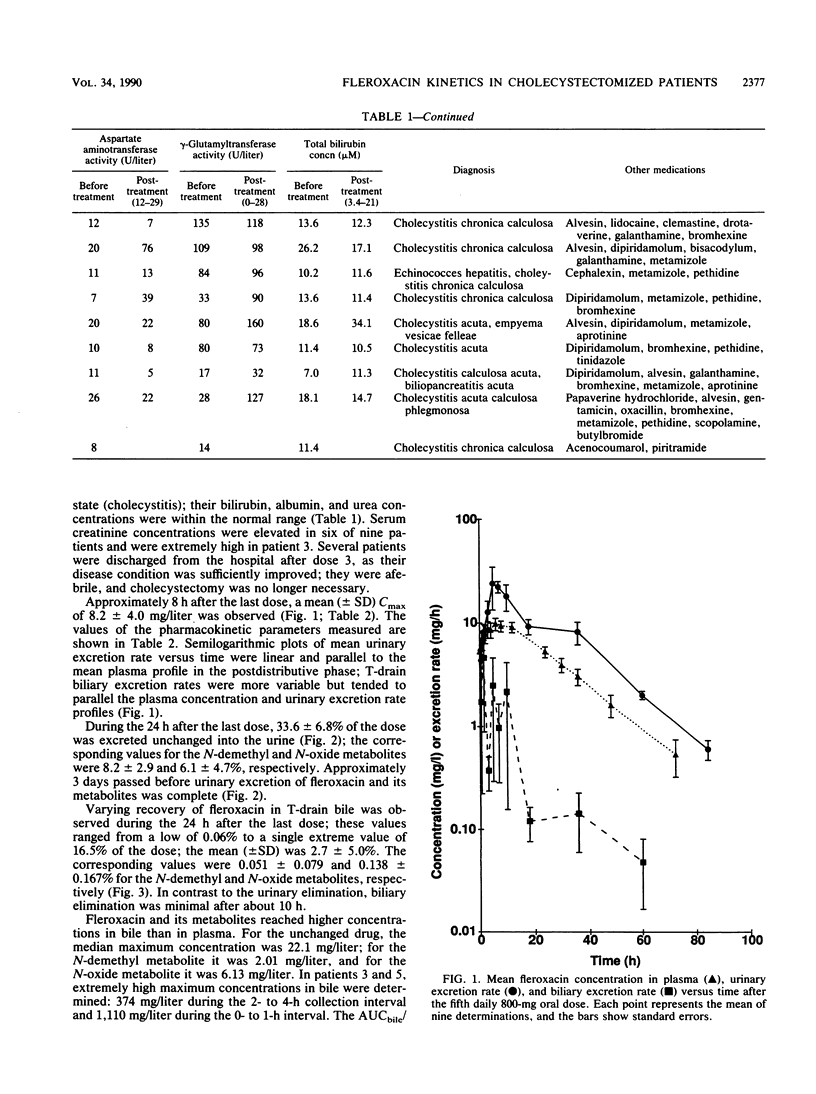
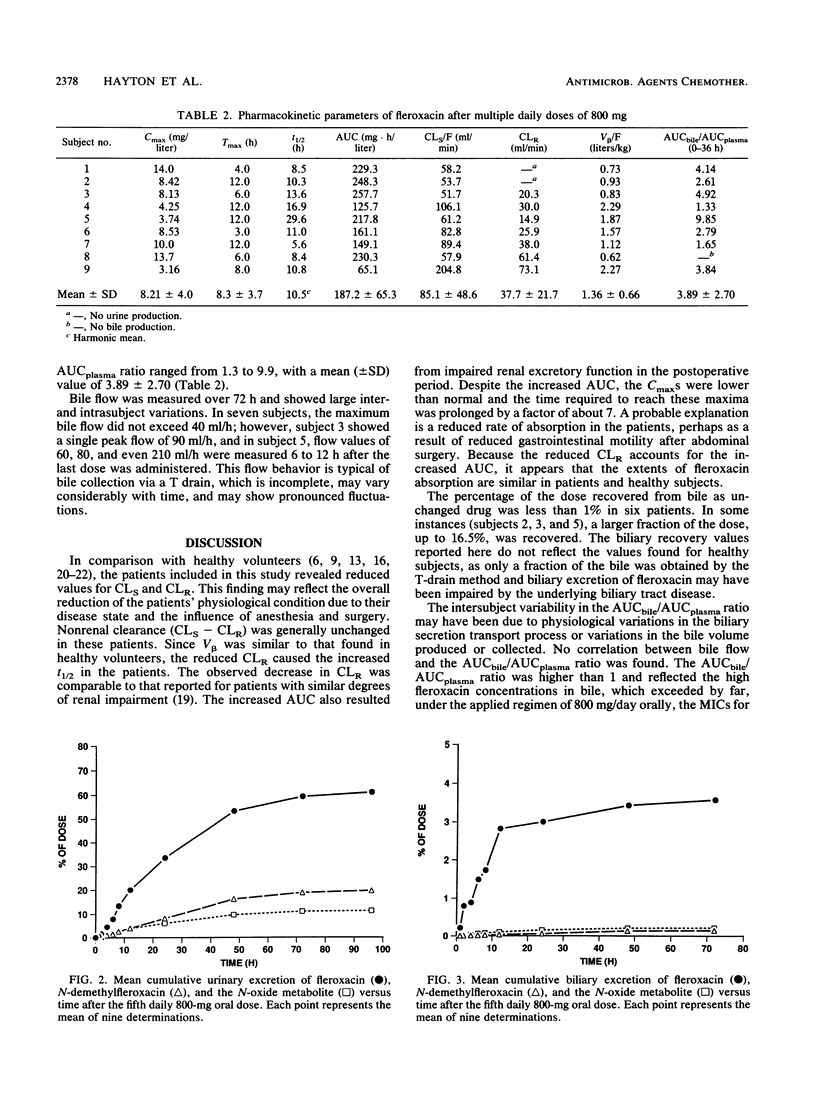
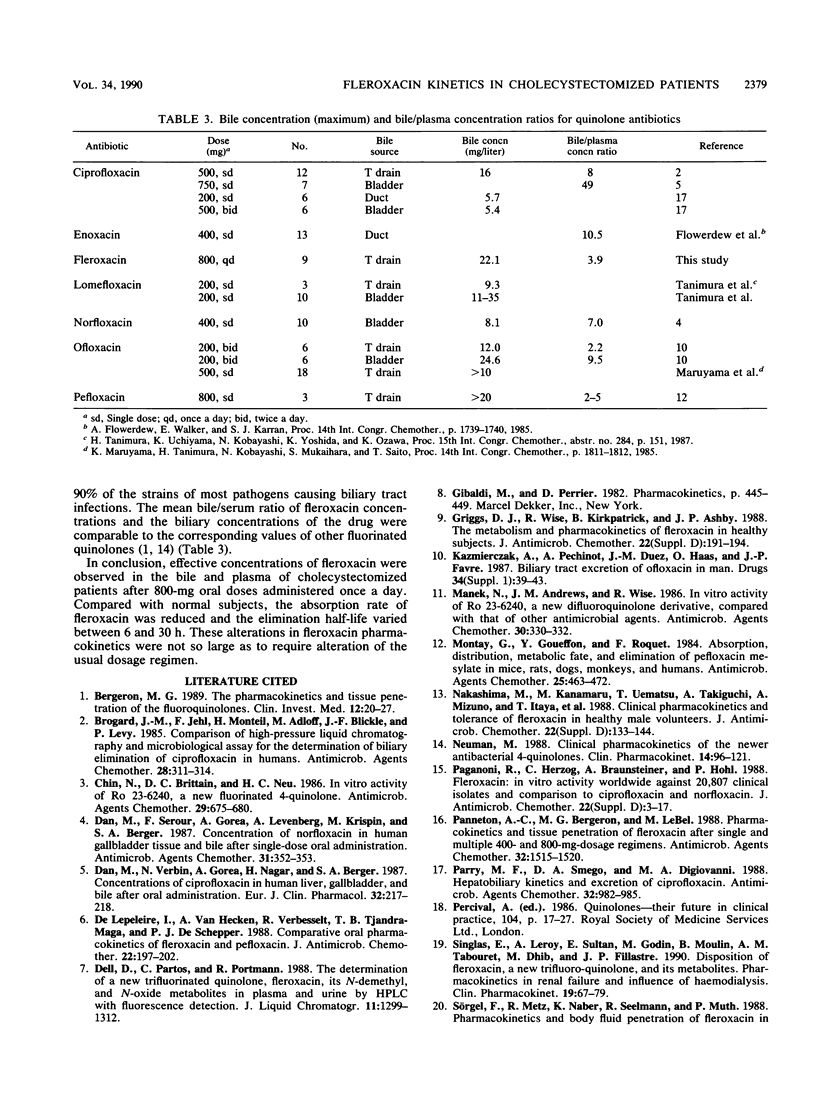
Abstract
Patients with biliary tract infections received 800 mg of fleroxacin orally once daily on five consecutive days; cholecystectomy was on day 3. Starting on the day when dose 5 was administered, serial blood and T-drain bile samples were taken for 72 h and urine was collected for 96 h. The mean (+/- the standard deviation) peak concentration in plasma was 8.2 +/- 4.0 mg/liter at 8.3 h. The harmonic mean elimination half-life was 10.5 h, which is comparable to that reported for healthy volunteers. This increase resulted from reduced renal clearance (mean [+/- standard deviation], 38 +/- 22 ml/min), as the volume of distribution in the patients (1.4 +/- 0.7 liter/kg) did not differ from that reported for healthy subjects. Maximum concentrations in T-drain bile were high (median, 22.1 mg/liter) and exceeded those measured in plasma by a factor of 2 to 3; the individual ratios of the area under the curve for bile divided by that for plasma ranged from 1.3 to 9.9. As observed in healthy volunteers, the major pathway for elimination of fleroxacin was via the kidneys. The fraction of dose 5 eliminated in the 0- to 24-h urine was reduced, however, and the fraction of the dose in the urine as the N-demethyl and N-oxide metabolites was elevated. At the dose regimen used in this study, the MICs for most pathogens that cause biliary tract infections were surpassed in plasma and bile for more than 24 h.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergeron M. G. The pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of the fluoroquinolones. Clin Invest Med. 1989 Feb;12(1):20–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogard J. M., Jehl F., Monteil H., Adloff M., Blickle J. F., Levy P. Comparison of high-pressure liquid chromatography and microbiological assay for the determination of biliary elimination of ciprofloxacin in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):311–314. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin N. X., Brittain D. C., Neu H. C. In vitro activity of Ro 23-6240, a new fluorinated 4-quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):675–680. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dan M., Serour F., Gorea A., Levenberg A., Krispin M., Berger S. A. Concentration of norfloxacin in human gallbladder tissue and bile after single-dose oral administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):352–353. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dan M., Verbin N., Gorea A., Nagar H., Berger S. A. Concentrations of ciprofloxacin in human liver, gallbladder, and bile after oral administration. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1987;32(2):217–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00542200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lepeleire I., Van Hecken A., Verbesselt R., Tjandra-Maga T. B., De Schepper P. J. Comparative oral pharmacokinetics of fleroxacin and pefloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Aug;22(2):197–202. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs D. J., Wise R., Kirkpatrick B., Ashby J. P. The metabolism and pharmacokinetics of fleroxacin in healthy subjects. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Oct;22 (Suppl 500):191–194. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_d.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazmierczak A., Pechinot A., Duez J. M., Haas O., Favre J. P. Biliary tract excretion of ofloxacin in man. Drugs. 1987;34 (Suppl 1):39–43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198700341-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manek N., Andrews J. M., Wise R. In vitro activity of Ro 23-6240, a new difluoroquinolone derivative, compared with that of other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):330–332. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montay G., Goueffon Y., Roquet F. Absorption, distribution, metabolic fate, and elimination of pefloxacin mesylate in mice, rats, dogs, monkeys, and humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):463–472. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima M., Kanamaru M., Uematsu T., Takiguchi A., Mizuno A., Itaya T., Kawahara F., Ooie T., Saito S., Uchida H. Clinical pharmacokinetics and tolerance of fleroxacin in healthy male volunteers. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Oct;22 (Suppl 500):133–144. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_d.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuman M. Clinical pharmacokinetics of the newer antibacterial 4-quinolones. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1988 Feb;14(2):96–121. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198814020-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paganoni R., Herzog C., Braunsteiner A., Hohl P. Fleroxacin: in-vitro activity worldwide against 20,807 clinical isolates and comparison to ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Oct;22 (Suppl 500):3–17. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_d.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panneton A. C., Bergeron M. G., LeBel M. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of fleroxacin after single and multiple 400- and 800-mg-dosage regimens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Oct;32(10):1515–1520. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.10.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry M. F., Smego D. A., Digiovanni M. A. Hepatobiliary kinetics and excretion of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jul;32(7):982–985. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.7.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singlas E., Leroy A., Sultan E., Godin M., Moulin B., Taburet A. M., Dhib M., Fillastre J. P. Disposition of fleroxacin, a new trifluoroquinolone, and its metabolites. Pharmacokinetics in renal failure and influence of haemodialysis. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1990 Jul;19(1):67–79. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199019010-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidekamm E., Portmann R., Suter K., Partos C., Dell D., Lücker P. W. Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of fleroxacin, a trifluorinated quinolone, in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1909–1914. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


