Abstract
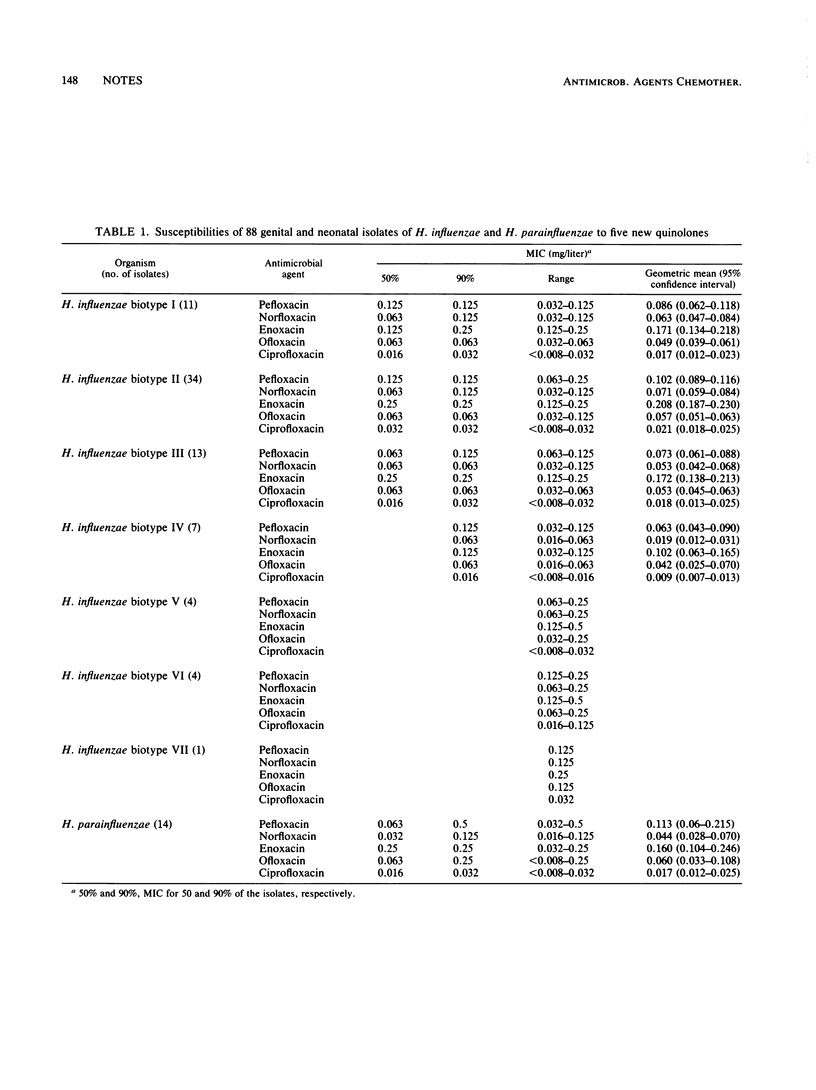
In vitro activities of five new quinolones against 88 strains of Haemophilus influenzae and H. parainfluenzae isolated from genitourinary or neonatal infections were studied. All strains were susceptible, and MICs were similar to those for respiratory tract isolates. However, H. influenzae biotype IV appeared to be more susceptible to norfloxacin, enoxacin, and ciprofloxacin than the other biotypes were.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton W. L., Brunton J. L., Meier M., Bowman M. N., Slaney L. A. Haemophilus influenzae: comparison of respiratory tract isolates with genitourinary tract isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):826–831. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.826-831.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Jones R. N., Thornsberry C., Ayers L. W., Gerlach E. H., Sommers H. M. Antibacterial activities of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, oxolinic acid, cinoxacin, and nalidixic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):633–637. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campognone P., Singer D. B. Neonatal sepsis due to nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Am J Dis Child. 1986 Feb;140(2):117–121. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1986.02140160035025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabernat H., Delmas C., Lareng M. B. Activité de l'ofloxacine sur Haemophilus influenzae, streptococcus pneumoniae et Neisseria meningitidis. Comparaison avec des molécules voisines. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1985 May;33(5):385–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. L., DeFranco L. M., Otto M. Novel method of biotyping Haemophilus influenzae that uses API 20e. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1150–1152. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1150-1152.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemmerich B., Borner K., Pennington J. E. Comparative evaluation of enoxacin, ofloxacin, ampicillin, and chloramphenicol for treatment of experimental Haemophilus influenzae pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Mar;31(3):417–420. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.3.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Heine-Jensen J., Bülow P. Haemophilus in the upper respiratory tract of children. A bacteriological, serological and clinical investigation. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(4):571–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. New antibiotics: areas of appropriate use. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):403–417. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quentin R., Goudeau A., Burfin E., Pinon G., Berger C., Laugier J., Soutoul J. H. Infections materno-foetales à Haemophilus influenzae. Presse Med. 1987 Jun 20;16(24):1181–1184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway G. L., O'Hare M. D., Felmingham D., Grüneberg R. N. The comparative activity of twelve 4-quinolone antimicrobials against Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1985;11(4):259–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Baker C. J., Quinones F. J., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Wiss K. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae (biotype 4) as a neonatal, maternal, and genital pathogen. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jan-Feb;5(1):123–136. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


