Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (135.0 KB).
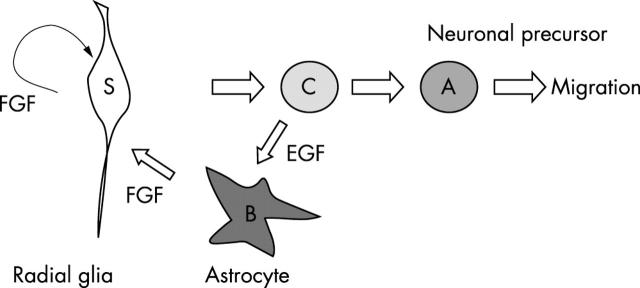
Figure 1 .
Cells of the astrocyte lineage give rise to neurones in the postnatal subventricular zone (SVZ). In the normal SVZ, there is a steady state equilibrium in which stem cells (S) generate transit amplifying cells (C cells) and neuronal progenitor cells (A cells). C cells also generate astrocytes (B cells), and this can be increased by exogenous epidermal growth factor (EGF). Astrocytes are normally quiescent. The C and A cells divide with a cell cycle of 13 h. Stem cells, estimated to be about 1% of the rapidly dividing cells, may lineally derive from astrocytes through a dedifferentiation process, a process that may be enhanced by fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman J., Das G. D. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol. 1965 Jun;124(3):319–335. doi: 10.1002/cne.901240303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Buylla A., Herrera D. G., Wichterle H. The subventricular zone: source of neuronal precursors for brain repair. Prog Brain Res. 2000;127:1–11. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(00)27002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvidsson Andreas, Collin Tove, Kirik Deniz, Kokaia Zaal, Lindvall Olle. Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Nat Med. 2002 Aug 5;8(9):963–970. doi: 10.1038/nm747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curristin Sheila M., Cao Anjun, Stewart William B., Zhang Heping, Madri Joseph A., Morrow Jon S., Ment Laura R. Disrupted synaptic development in the hypoxic newborn brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Nov 15;99(24):15729–15734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.232568799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbing J. Undernutrition and the developing brain: the use of animal models ot elucidate the human problem. Psychiatr Neurol Neurochir. 1971 Nov-Dec;74(6):433–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetsch F., Caillé I., Lim D. A., García-Verdugo J. M., Alvarez-Buylla A. Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain. Cell. 1999 Jun 11;97(6):703–716. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80783-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetsch F., García-Verdugo J. M., Alvarez-Buylla A. Regeneration of a germinal layer in the adult mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Sep 28;96(20):11619–11624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.20.11619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson P. S., Perfilieva E., Björk-Eriksson T., Alborn A. M., Nordborg C., Peterson D. A., Gage F. H. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med. 1998 Nov;4(11):1313–1317. doi: 10.1038/3305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganat Y., Soni S., Chacon M., Schwartz M. L., Vaccarino F. M. Chronic hypoxia up-regulates fibroblast growth factor ligands in the perinatal brain and induces fibroblast growth factor-responsive radial glial cells in the sub-ependymal zone. Neuroscience. 2002;112(4):977–991. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould E., Tanapat P., McEwen B. S., Flügge G., Fuchs E. Proliferation of granule cell precursors in the dentate gyrus of adult monkeys is diminished by stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Mar 17;95(6):3168–3171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.6.3168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack M., Wright L. L., Shankaran S., Tyson J. E., Horbar J. D., Bauer C. R., Younes N. Very-low-birth-weight outcomes of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Network, November 1989 to October 1990. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995 Feb;172(2 Pt 1):457–464. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(95)90557-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitoshi Seiji, Tropepe Vincent, Ekker Marc, van der Kooy Derek. Neural stem cell lineages are regionally specified, but not committed, within distinct compartments of the developing brain. Development. 2002 Jan;129(1):233–244. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.1.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempermann G., Kuhn H. G., Gage F. H. Experience-induced neurogenesis in the senescent dentate gyrus. J Neurosci. 1998 May 1;18(9):3206–3212. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-09-03206.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa K., Matsumoto M., Hori M. Protective and regenerative response endogenously induced in the ischemic brain. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2001 Mar;79(3):262–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laroia N., McBride L., Baggs R., Guillet R. Dextromethorphan ameliorates effects of neonatal hypoxia on brain morphology and seizure threshold in rats. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1997 May 20;100(1):29–34. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(97)00018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magavi Sanjay S., Macklis Jeffrey D. Induction of neuronal type-specific neurogenesis in the cerebral cortex of adult mice: manipulation of neural precursors in situ. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2002 Mar 31;134(1-2):57–76. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(01)00316-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ment L. R., Schwartz M., Makuch R. W., Stewart W. B. Association of chronic sublethal hypoxia with ventriculomegaly in the developing rat brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1998 Dec 7;111(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(98)00139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatomi Hirofumi, Kuriu Toshihiko, Okabe Shigeo, Yamamoto Shin-ichi, Hatano Osamu, Kawahara Nobutaka, Tamura Akira, Kirino Takaaki, Nakafuku Masato. Regeneration of hippocampal pyramidal neurons after ischemic brain injury by recruitment of endogenous neural progenitors. Cell. 2002 Aug 23;110(4):429–441. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00862-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyakas C., Buwalda B., Luiten P. G. Hypoxia and brain development. Prog Neurobiol. 1996 May;49(1):1–51. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(96)00007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peretto P., Merighi A., Fasolo A., Bonfanti L. The subependymal layer in rodents: a site of structural plasticity and cell migration in the adult mammalian brain. Brain Res Bull. 1999 Jul 1;49(4):221–243. doi: 10.1016/s0361-9230(99)00037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song Hong-jun, Stevens Charles F., Gage Fred H. Neural stem cells from adult hippocampus develop essential properties of functional CNS neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2002 May;5(5):438–445. doi: 10.1038/nn844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaccarino F. M., Schwartz M. L., Hartigan D., Leckman J. F. Basic fibroblast growth factor increases the number of excitatory neurons containing glutamate in the cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 1995 Jan-Feb;5(1):64–78. doi: 10.1093/cercor/5.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vexler Z. S., Ferriero D. M. Molecular and biochemical mechanisms of perinatal brain injury. Semin Neonatol. 2001 Apr;6(2):99–108. doi: 10.1053/siny.2001.0041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J. Perinatal brain injury: from pathogenesis to neuroprotection. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2001;7(1):56–64. doi: 10.1002/1098-2779(200102)7:1<56::AID-MRDD1008>3.0.CO;2-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Sheen V. L., Macklis J. D. Cortical interneurons upregulate neurotrophins in vivo in response to targeted apoptotic degeneration of neighboring pyramidal neurons. Exp Neurol. 1998 Dec;154(2):389–402. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1998.6965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., Lawlor P. A., Leone P., Dragunow M., During M. J. Environmental enrichment inhibits spontaneous apoptosis, prevents seizures and is neuroprotective. Nat Med. 1999 Apr;5(4):448–453. doi: 10.1038/7449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Praag H., Kempermann G., Gage F. H. Neural consequences of environmental enrichment. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2000 Dec;1(3):191–198. doi: 10.1038/35044558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]