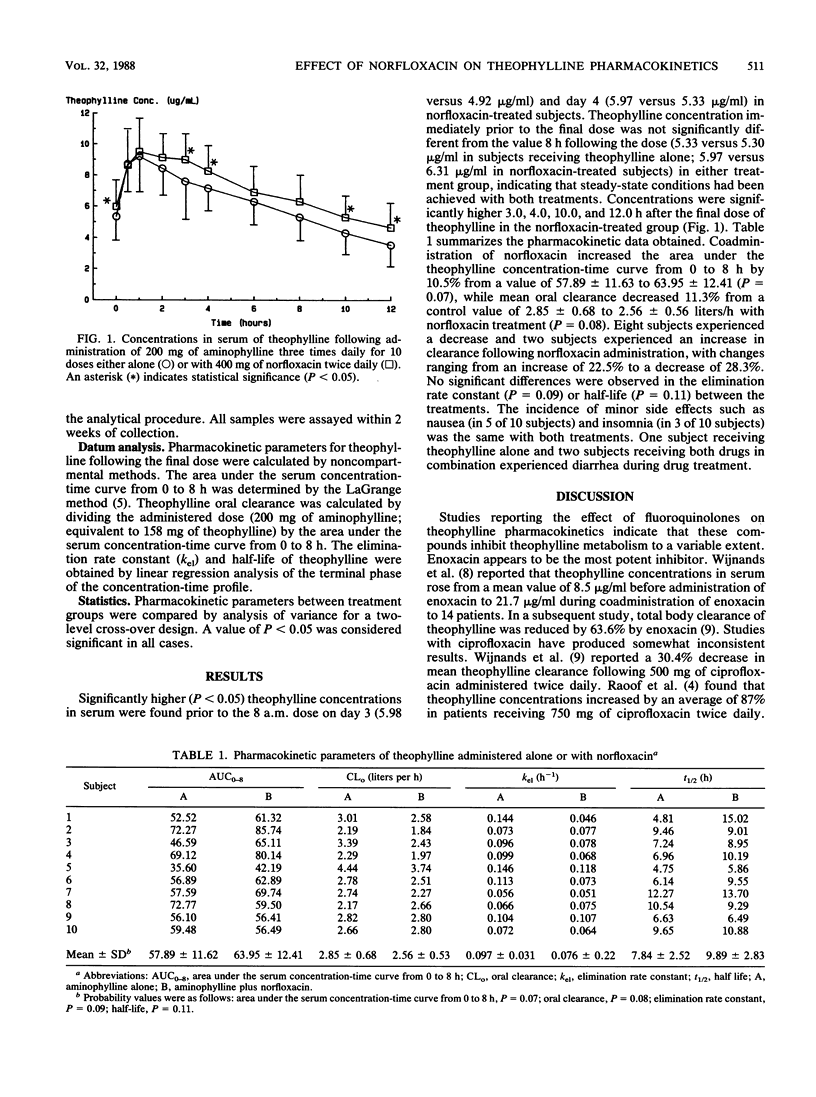
Abstract
Norfloxacin is a currently marketed fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Other quinolones which are structurally similar to norfloxacin, particularly enoxacin, inhibit theophylline clearance. Since norfloxacin may be administered to patients also receiving theophylline, we studied the effect of norfloxacin on the pharmacokinetics of theophylline in 10 healthy male volunteers. A randomized, crossover study design with a 2-week washout period between treatments was used. Subjects received oral theophylline (200 mg of aminophylline [theophylline ethylenediamine]) three times daily for 4 days either alone or with 400 mg of norfloxacin (orally) twice daily for the same period. Theophylline concentrations in serum were significantly higher (P less than 0.05) at 0, 3, 4, 10, and 12 h following the final dose in the norfloxacin treatment group than in the group receiving only theophylline. However, mean theophylline oral clearance was not significantly different between the two treatments (2.85 +/- 0.68 liters/h without norfloxacin versus 2.56 +/- 0.53 liters/h with norfloxacin [P = 0.08]). Similarly, no significant differences were observed in theophylline half-life (P = 0.11). We conclude that norfloxacin is unlikely to have a clinically significant effect on theophylline disposition in most patients.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gregoire S. L., Grasela T. H., Jr, Freer J. P., Tack K. J., Schentag J. J. Inhibition of theophylline clearance by coadministered ofloxacin without alteration of theophylline effects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Mar;31(3):375–378. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.3.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nix D. E., DeVito J. M., Whitbread M. A., Schentag J. J. Effect of multiple dose oral ciprofloxacin on the pharmacokinetics of theophylline and indocyanine green. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Feb;19(2):263–269. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoof S., Wollschlager C., Khan F. A. Ciprofloxacin increases serum levels of theophylline. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):115–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocci M. L., Jr, Jusko W. J. LAGRAN program for area and moments in pharmacokinetic analysis. Comput Programs Biomed. 1983 Jun;16(3):203–216. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(83)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybak M. J., Bowles S. K., Chandrasekar P. H., Edwards D. J. Increased theophylline concentrations secondary to ciprofloxacin. Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1987 Nov;21(11):879–881. doi: 10.1177/106002808702101106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano M., Yamamoto I., Ueda J., Yoshikawa E., Yamashina H., Goto M. Comparative pharmacokinetics of theophylline following two fluoroquinolones co-administration. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1987;32(4):431–432. doi: 10.1007/BF00543982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijnands W. J., Vree T. B., Van Herwaarden C. L. Enoxacin decreases the clearance of theophylline in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1985 Dec;20(6):583–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1985.tb05115.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijnands W. J., Vree T. B., van Herwaarden C. L. The influence of quinolone derivatives on theophylline clearance. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Dec;22(6):677–683. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb02957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. The fluoroquinolones: structures, mechanisms of action and resistance, and spectra of activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):581–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


