Abstract
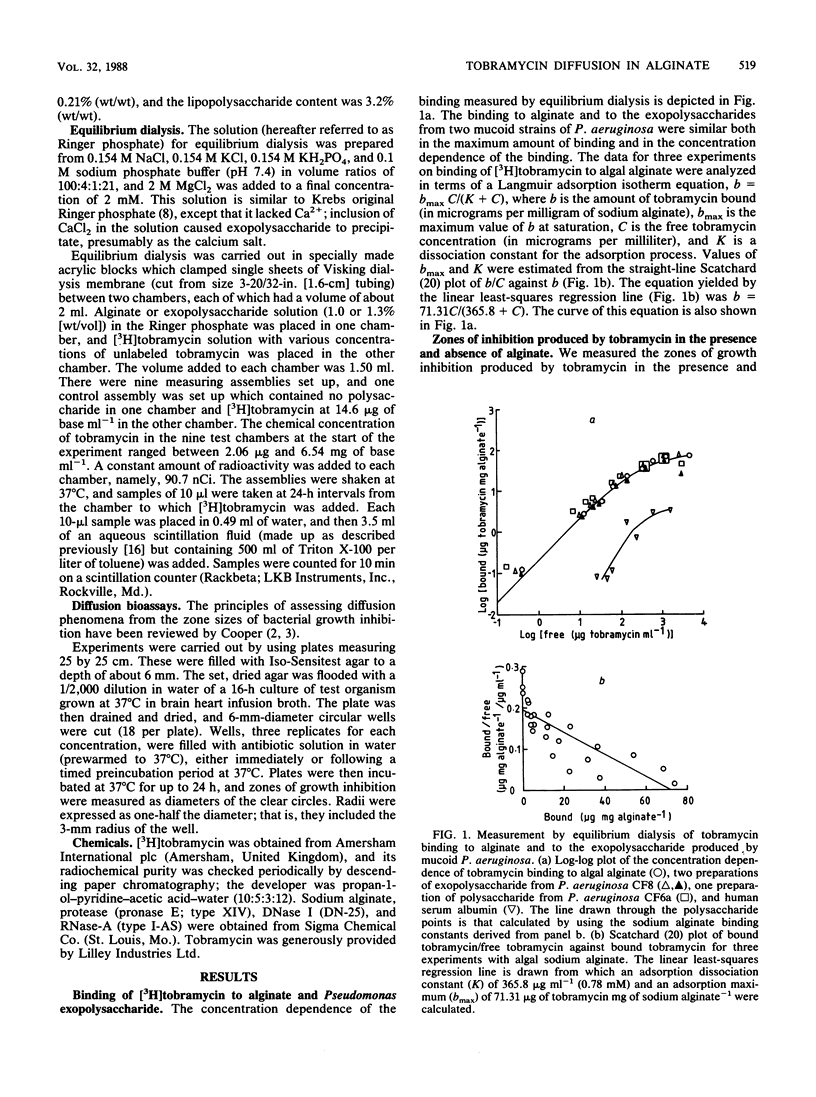
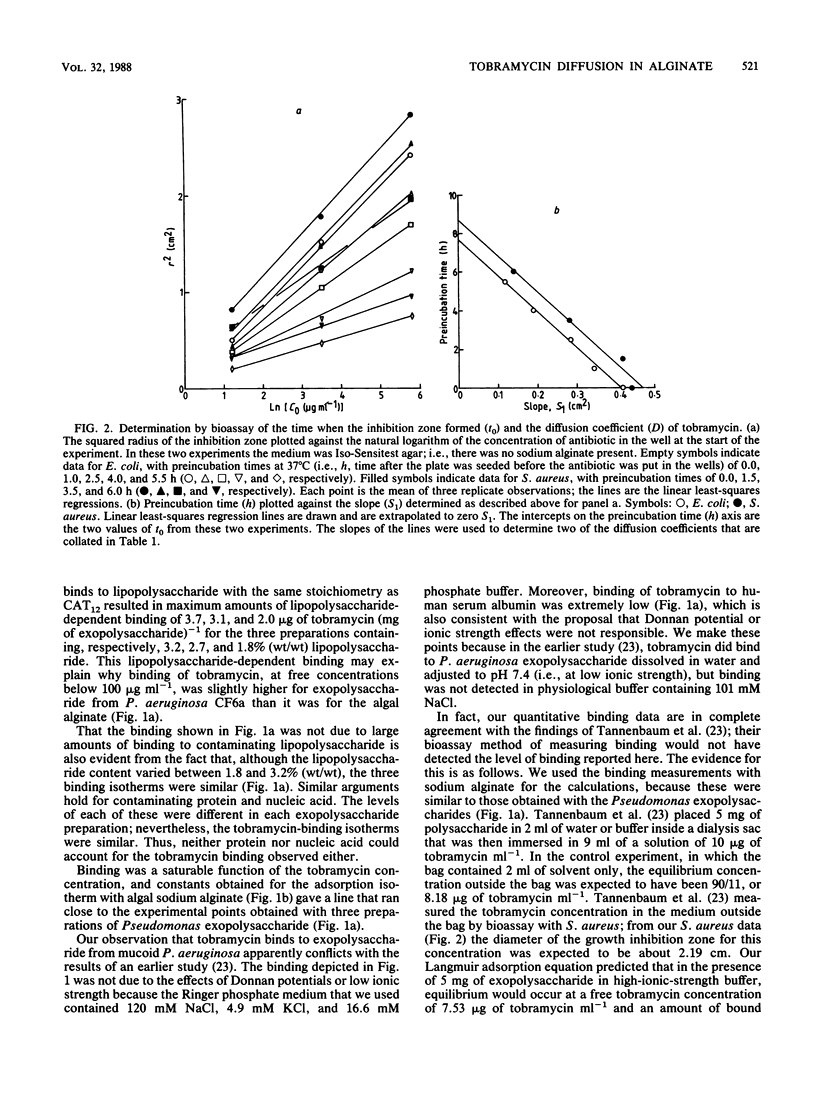
[3H]tobramycin bound to sodium alginate and to exopolysaccharide prepared from two mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Binding to sodium alginate was similar to binding to exopolysaccharide, both in the dependence on tobramycin concentration and in the maximum binding observed at saturation. Incorporation of sodium alginate into agar plates reduced the zone sizes of growth inhibition caused by tobramycin. The reductions in zone sizes were quantitatively accounted for by the binding of tobramycin to sodium alginate during diffusion of the antibiotic away from the well in which it had been placed at the start of the experiment. However, the binding of tobramycin to the exopolysaccharide of P. aeruginosa, and the resulting inhibition of diffusion of the antibiotic, did not significantly increase the penetration time of a spherical microcolony with a radius of 125 micron, such as might be found in the respiratory tract of a patient with cystic fibrosis (from a 90% penetration time of 12 s in the absence of exopolysaccharide to one of 35 s with an exopolysaccharide concentration of 1.0% [wt/vol]).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Costerton J. W., Cheng K. J., Geesey G. G., Ladd T. I., Nickel J. C., Dasgupta M., Marrie T. J. Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:435–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drugeon H. B., Juvin M. E., Caillon J., Courtieu A. L. Assessment of formulas for calculating critical concentration by the agar diffusion method. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jun;31(6):870–875. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.6.870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. R., Linker A. Production and characterization of the slime polysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):915–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.915-924.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert P., Brown M. R., Costerton J. W. Inocula for antimicrobial sensitivity testing: a critical review. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Aug;20(2):147–154. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J., Chan R., Lam K., Costerton J. W. Production of mucoid microcolonies by Pseudomonas aeruginosa within infected lungs in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):546–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.546-556.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linker A., Jones R. S. A new polysaccharide resembling alginic acid isolated from pseudomonads. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3845–3851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir M. E., van Heeswyck R. S., Wallace B. J. Effect of growth rate on streptomycin accumulation by Escherichia coli and Bacillus megaterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Aug;130(8):2015–2022. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-8-2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. W., Young S. N. Respiration-dependent uptake of dihydrostreptomycin by Escherichia coli. Its irreversible nature and lack of evidence for a uniport process. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 1;228(2):505–512. doi: 10.1042/bj2280505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel J. C., Ruseska I., Wright J. B., Costerton J. W. Tobramycin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells growing as a biofilm on urinary catheter material. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):619–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., Hancock R. E., McGroarty E. J. Binding of polycationic antibiotics and polyamines to lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1256–1261. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1256-1261.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack M. P., Nichols W. W. Antibiotic penetration through bacterial capsules and exopolysaccharides. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Nov;10(5):368–372. doi: 10.1093/jac/10.5.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack M. P., Nichols W. W. The penetration of antibiotics through sodium alginate and through the exopolysaccharide of a mucoid strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Lancet. 1981 Sep 5;2(8245):502–503. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90885-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum C. S., Hastie A. T., Higgins M. L., Kueppers F., Weinbaum G. Inability of purified Pseudomonas aeruginosa exopolysaccharide to bind selected antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jun;25(6):673–675. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.6.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Cozens R., Tosch W., Zak O., Tomasz A. The rate of killing of Escherichia coli by beta-lactam antibiotics is strictly proportional to the rate of bacterial growth. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 May;132(5):1297–1304. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-5-1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH A., HURWITZ J. The formation of 2-keto-3-deoxyheptonic acid in extracts of Escherichia coli B. I. Identification. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


