Abstract
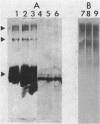
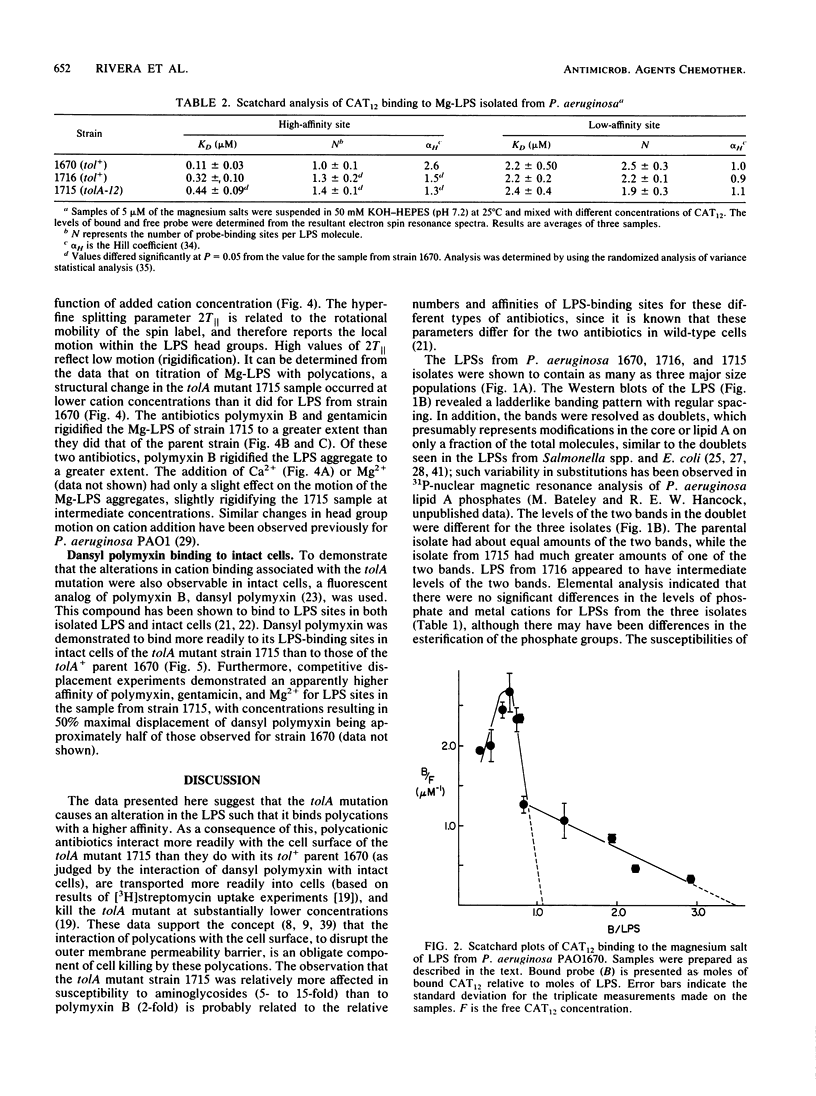
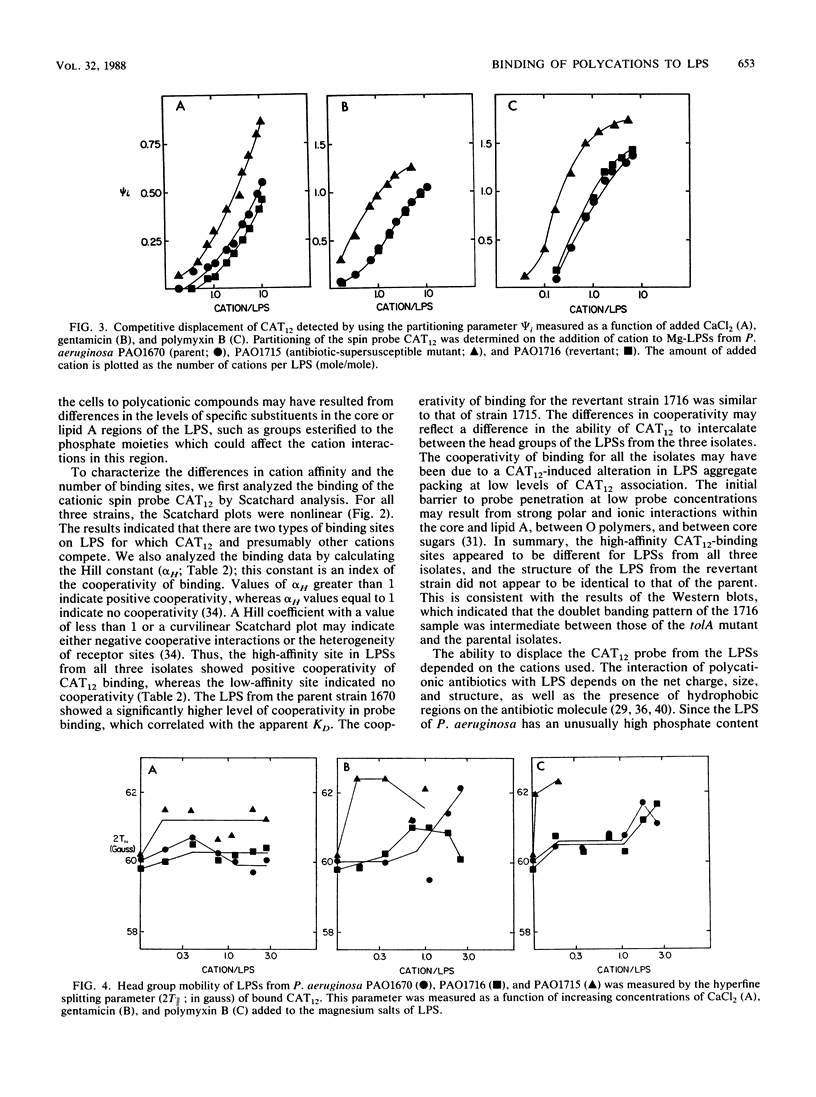
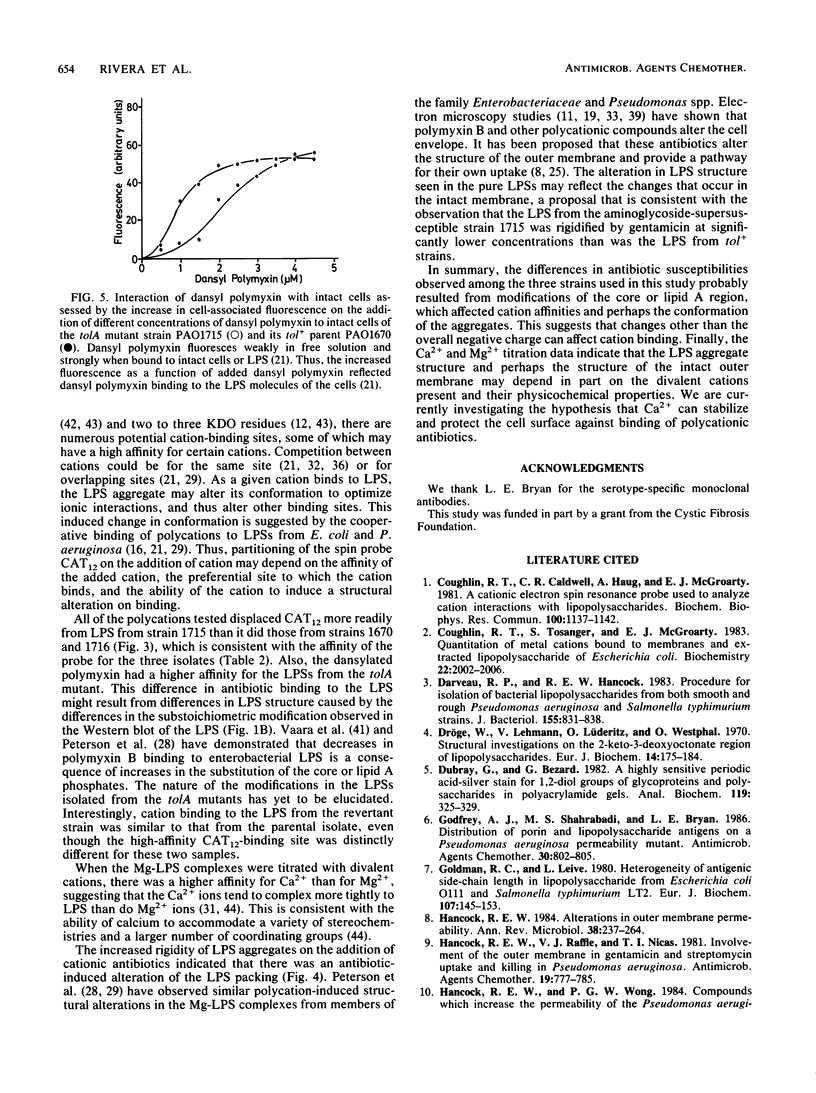
The lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of the aminoglycoside-supersusceptible Pseudomonas aeruginosa tolA mutant PAO1715 was compared with its parent strain PAO1670 and tol+ revertant PAO1716. Electrophoretic separation of purified LPSs from the three isolates showed similar LPS banding patterns. Analysis of the Western blots of these LPSs from the three isolates with O-antigen-specific monoclonal antibody indicated that the ladder pattern consisted of doublet bands, which presumably reflected a modification of core or lipid A; the level of one of the bands in the doublet was in much lower amounts in the isolate from the tolA mutant than in that from the parent or revertant. Results of competitive displacement experiments, in which the cationic spin probe 4-dodecyldimethylammonium-1-oxyl-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine bromide was displaced from its LPS-binding site by polycations, revealed that the tolA mutant had a much higher affinity for gentamicin, polymyxin, Ca2+, and Mg2+ than did the parent or revertant. The order of affinity for all samples was polymyxin B much greater than gentamicin C much greater than Ca2+ greater than Mg2+. Both gentamicin and polymyxin induced rigidification of all of the LPS samples, but for the sample from the tolA mutant, rigidification occurred at substantially lower concentrations. Dansyl polymyxin titration experiments with intact cells demonstrated that the increased affinity of the LPS from the tolA mutant for polycations was reflected in an increase in the affinity of binding to the cell. Together these data suggest that the tolA mutant is supersusceptible to aminoglycosides by virtue of an LPS change which increases the binding affinity of the LPS for polycations, including gentamicin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coughlin R. T., Caldwell C. R., Haug A., McGroarty E. J. A cationic electron spin resonance probe used to analyze cation interactions with lipopolysaccharide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun 16;100(3):1137–1142. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91942-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin R. T., Tonsager S., McGroarty E. J. Quantitation of metal cations bound to membranes and extracted lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):2002–2007. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Hancock R. E. Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):831–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.831-838.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge W., Lehmann V., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Structural investigations on the 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate region of lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):175–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Bezard G. A highly sensitive periodic acid-silver stain for 1,2-diol groups of glycoproteins and polysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 15;119(2):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90593-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey A. J., Shahrabadi M. S., Bryan L. E. Distribution of porin and lipopolysaccharide antigens on a Pseudomonas aeruginosa permeability mutant. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):802–805. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. Alterations in outer membrane permeability. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:237–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Raffle V. J., Nicas T. I. Involvement of the outer membrane in gentamicin and streptomycin uptake and killing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):777–785. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Wong P. G. Compounds which increase the permeability of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):48–52. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike M., Iida K., Matsuo T. Electron microscopic studies on mode of action of polymyxin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):448–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.448-452.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Chan L. C., Milazzo F. H. The extraction and analysis of lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO, and three rough mutants. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Mar;25(3):390–398. doi: 10.1139/m79-060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Jewell B., Kuzio J., Milazzo F., Berry D. Structure and functions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1985;36:58–73. doi: 10.1159/000410472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. The barrier function of the gram-negative envelope. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):109–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh B., Grant C., Hancock R. E. Use of the fluorescent probe 1-N-phenylnaphthylamine to study the interactions of aminoglycoside antibiotics with the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Oct;26(4):546–551. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.4.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin N. L., Beveridge T. J. Gentamicin interaction with Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell envelope. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1079–1087. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills B. J., Holloway B. W. Mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that show specific hypersensitivity to aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Sep;10(3):411–416. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. A., Bates N. C., Hancock R. E. Interaction of polycationic antibiotics with Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide and lipid A studied by using dansyl-polymyxin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):496–500. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. A., Hancock R. E. Involvement of outer membrane of Pseudomonas cepacia in aminoglycoside and polymyxin resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):923–926. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Hancock R. E. Outer membrane protein H1 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: involvement in adaptive and mutational resistance to ethylenediaminetetraacetate, polymyxin B, and gentamicin. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):872–878. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.872-878.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten S., Iyer S., Johnson W., Montgomery R. Serospecific antigens of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):893–904. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.893-904.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity in Salmonella typhimurium analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., Fesik S. W., McGroarty E. J. Decreased binding of antibiotics to lipopolysaccharides from polymyxin-resistant strains of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):230–237. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., Hancock R. E., McGroarty E. J. Binding of polycationic antibiotics and polyamines to lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1256–1261. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1256-1261.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., McGroarty E. J. High-molecular-weight components in lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella typhimurium, Salmonella minnesota, and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):738–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.738-745.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler M., Osborn M. J. Interaction of divalent cations and polymyxin B with lipopolysaccharide. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 2;18(20):4425–4430. doi: 10.1021/bi00587a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler P. R., Teuber M. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes: morphological changes in the cytoplasm and in the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jul;8(1):95–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm D. R., Rosenthal K. S., Swanson P. E. Polymyxin and related peptide antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:723–763. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M. Increased outer membrane resistance to ethylenediaminetetraacetate and cations in novel lipid A mutants. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):426–434. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.426-434.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T., Jensen M., Helander I., Nurminen M., Rietschel E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from the polymyxin-resistant pmrA mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 29;129(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Outer membrane permeability barrier disruption by polymyxin in polymyxin-susceptible and -resistant Salmonella typhimurium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):578–583. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Polycations as outer membrane-disorganizing agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Polycations sensitize enteric bacteria to antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. G. Composition and structure of lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;5 (Suppl 5):S941–S949. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_5.s941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. G., Galbrath L. Studies of lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Mar 17;52(2):331–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]