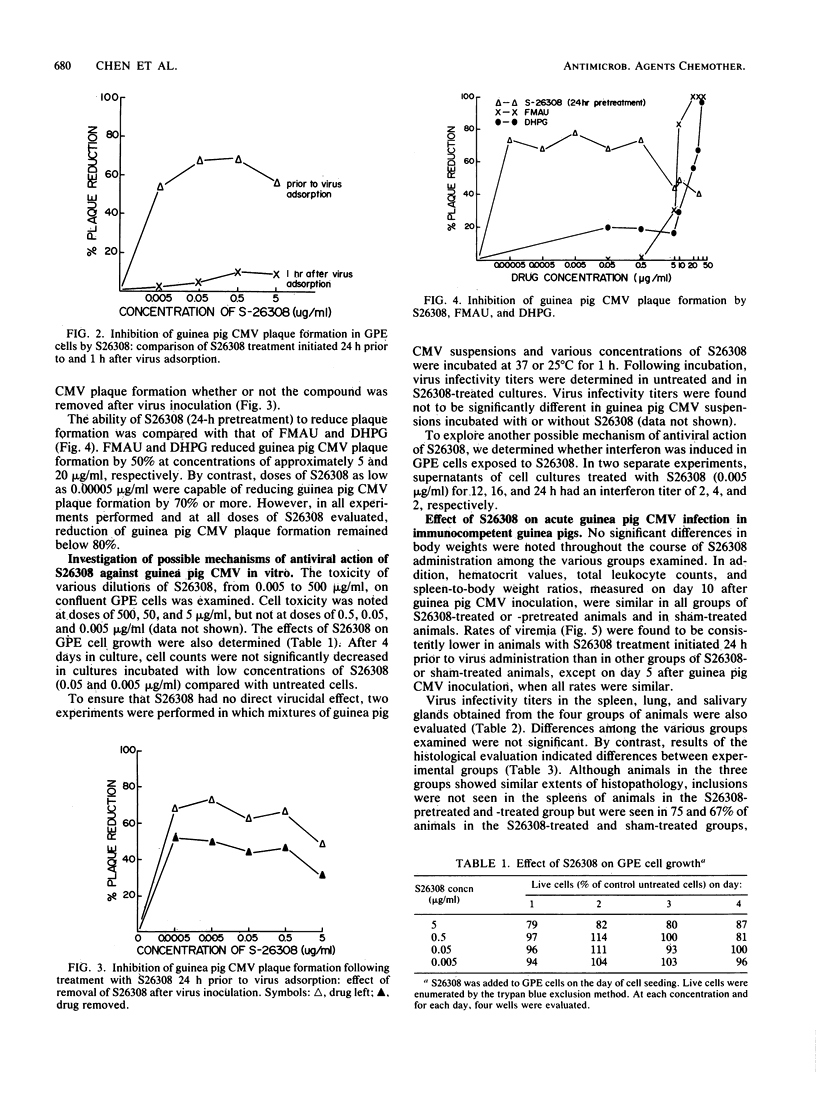
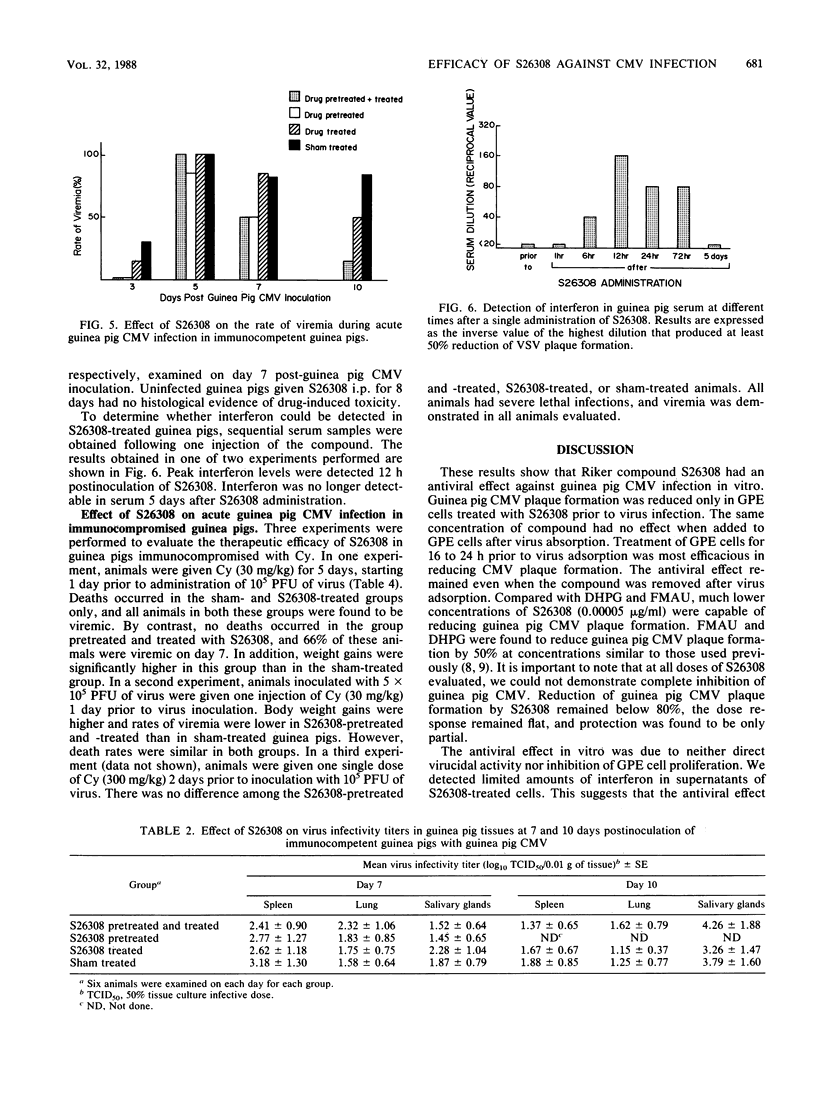
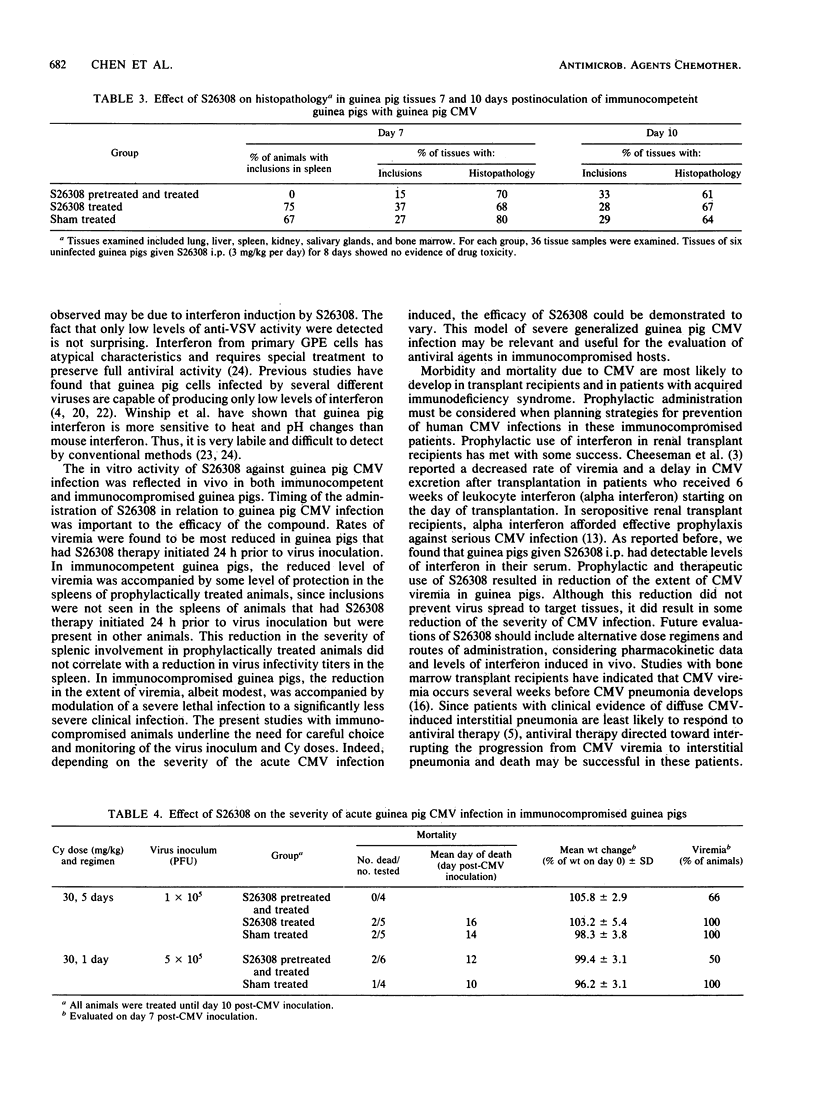
Abstract
Prophylactic use of antiviral agents against cytomegalovirus (CMV) is particularly indicated for the immunocompromised host because morbidity and mortality due to CMV occur most frequently following immunosuppression. We have evaluated the new Riker compound S26308 for its therapeutic and prophylactic antiviral activity against CMV in guinea pigs. The efficacy of the compound was assessed in vitro in guinea pig embryo cells and in vivo in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised guinea pigs. Guinea pig CMV plaque formation was reduced only in cells treated with S26308 prior to virus infection. The antiviral activity remained even when the compound was removed after virus absorption and was due to neither virus destruction nor inhibition of cell growth. The frequency of viremia was reduced in guinea pigs for which S26308 therapy was initiated 24 h prior to virus inoculation compared with sham-treated animals. This reduction in the frequency of viremia did not prevent virus spread to target tissues but did result in a reduction of the severity of CMV-induced disease in immunocompromised guinea pigs. Low levels of interferon were detected in supernatants of S26308-treated cells, and interferon was detected in the serum of guinea pigs given S26308. These results indicate that S26308 can induce interferon and reduce CMV infectivity in vivo and in vitro when used prophylactically. This antiviral activity, although modest, was accompanied by beneficial effects on CMV-induced morbidity and mortality. Prophylactic use of S26308 in combination with other therapeutic agents may be a useful strategy against CMV infections.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bia F. J., Griffith B. P., Fong C. K., Hsiung G. D. Cytomegaloviral infections in the guinea pig: experimental models for human disease. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):177–195. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron K. K., Fyfe J. A., Stanat S. C., Leslie L. K., Sorrell J. B., Lambe C. U., Coen D. M. A human cytomegalovirus mutant resistant to the nucleoside analog 9-([2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]methyl)guanine (BW B759U) induces reduced levels of BW B759U triphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8769–8773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman S. H., Rubin R. H., Stewart J. A., Tolkoff-Rubin N. E., Cosimi A. B., Cantell K., Gilbert J., Winkle S., Herrin J. T., Black P. H. Controlled clinical trial of prophylactic human-leukocyte interferon in renal transplantation. Effects on cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex virus infections. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jun 14;300(24):1345–1349. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197906143002401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofinis G. J. Heterospecific antiviral activity of human interferon on guinea pig endothelial cells. Dev Biol Stand. 1980;46:193–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amico D. J., Talamo J. H., Felsenstein D., Hirsch M. S., Albert D. M., Schooley R. T. Ophthalmoscopic and histologic findings in cytomegalovirus retinitis treated with BW-B759U. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986 Dec;104(12):1788–1793. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1986.01050240062041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Davies M. E., DeWitt C., Perry H. C., Liou R., Germershausen J., Karkas J. D., Ashton W. T., Johnston D. B., Tolman R. L. 9-([2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]methyl)guanine: a selective inhibitor of herpes group virus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4139–4143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong C. K., Cohen S. D., McCormick S., Hsiung G. D. Antiviral effect of 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine against cytomegalovirus infection in a guinea pig model. Antiviral Res. 1987 Jan;7(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(87)90035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff E., Griffith B. P., Booss J. Delayed amplification of cytomegalovirus infection in the placenta and maternal tissues during late gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987 May;156(5):1265–1270. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(87)90159-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith B. P., Lavallee J. T., Jennings T. A., Hsiung G. D. Transmission of maternal cytomegalovirus-specific immunity in the guinea pig. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 May;35(2):169–181. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90063-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith B. P., Lucia H. L., Bia F. J., Hsiung G. D. Cytomegalovirus-induced mononucleosis in guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):857–863. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.857-863.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T., Cosimi A. B., Russell P. S., Delmonico F. L., Tolkoff-Rubin N. E., Herrin J. T., Cantell K., Farrell M. L., Rota T. R. Effects of interferon-alpha on cytomegalovirus reactivation syndromes in renal-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jun 23;308(25):1489–1493. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306233082501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland G. N., Sakamoto M. J., Hardy D., Sidikaro Y., Kreiger A. E., Frenkel L. M. Treatment of cytomegalovirus retinopathy in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Use of the experimental drug 9-[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxymethyl]guanine. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986 Dec;104(12):1794–1800. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1986.01050240068042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucia H. L., Griffith B. P., Hsiung G. D. Effect of acyclovir and phosphonoformate on cytomegalovirus infection in guinea pigs. Intervirology. 1984;21(3):141–149. doi: 10.1159/000149512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Lane H. C., Palestine A., Smith P. D., Manischewitz J., Stevens G., Fujikawa L., Macher A. M., Nussenblatt R., Baird B. Effect of 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl) guanine on serious cytomegalovirus disease in eight immunosuppressed homosexual men. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Jan;104(1):41–44. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-104-1-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell J. J., Jacobson M. A., Mills J. Development of cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis in a patient with AIDS during ganciclovir therapy of CMV colitis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jun 18;316(25):1607–1608. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198706183162516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotkin S. A., Drew W. L., Felsenstein D., Hirsch M. S. Sensitivity of clinical isolates of human cytomegalovirus to 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):833–834. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosecan L. R., Stahl-Bayliss C. M., Kalman C. M., Laskin O. L. Antiviral therapy for cytomegalovirus retinitis in AIDS with dihydroxy propoxymethyl guanine. Am J Ophthalmol. 1986 Apr 15;101(4):405–418. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(86)90638-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenfeld G. INduction and production of guinea pig interferon. Methods Enzymol. 1981;78(Pt A):162–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)78112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. A., Rua J. A., Spector D. H., McMillan R. Detection of human cytomegalovirus in clinical specimens by DNA-DNA hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):121–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warfel A. H., Stewart W. E., 2nd Production and initial characterization of guinea pig interferon. J Interferon Res. 1980 Fall;1(1):19–22. doi: 10.1089/jir.1980.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship T. R., Fong C. K., Hsiung G. D. Distinctive characteristics of crude interferon from virus-infected guinea-pig embryo fibroblasts. J Gen Virol. 1984 Apr;65(Pt 4):843–847. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-4-843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship T. R., Fong C. K., Hsiung G. D. Improved conditions for the production and detection of interferon from guinea pig embryo cells. J Interferon Res. 1983;3(1):71–74. doi: 10.1089/jir.1983.3.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


