Abstract
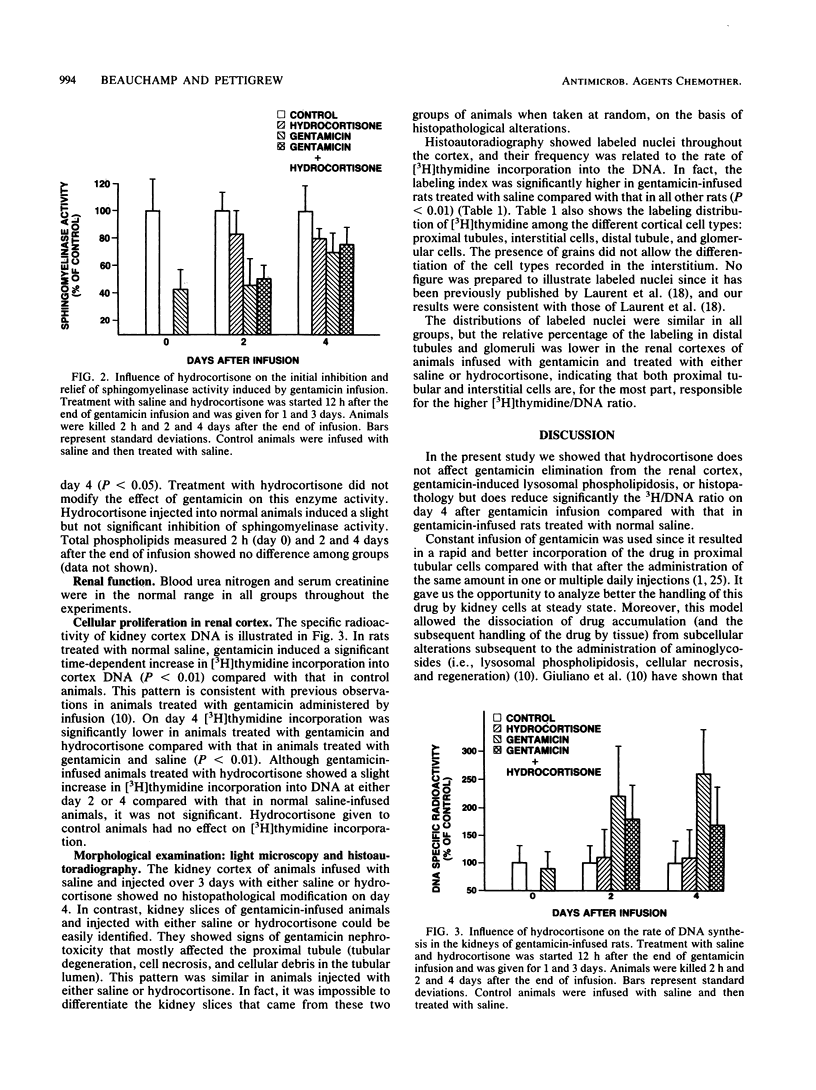
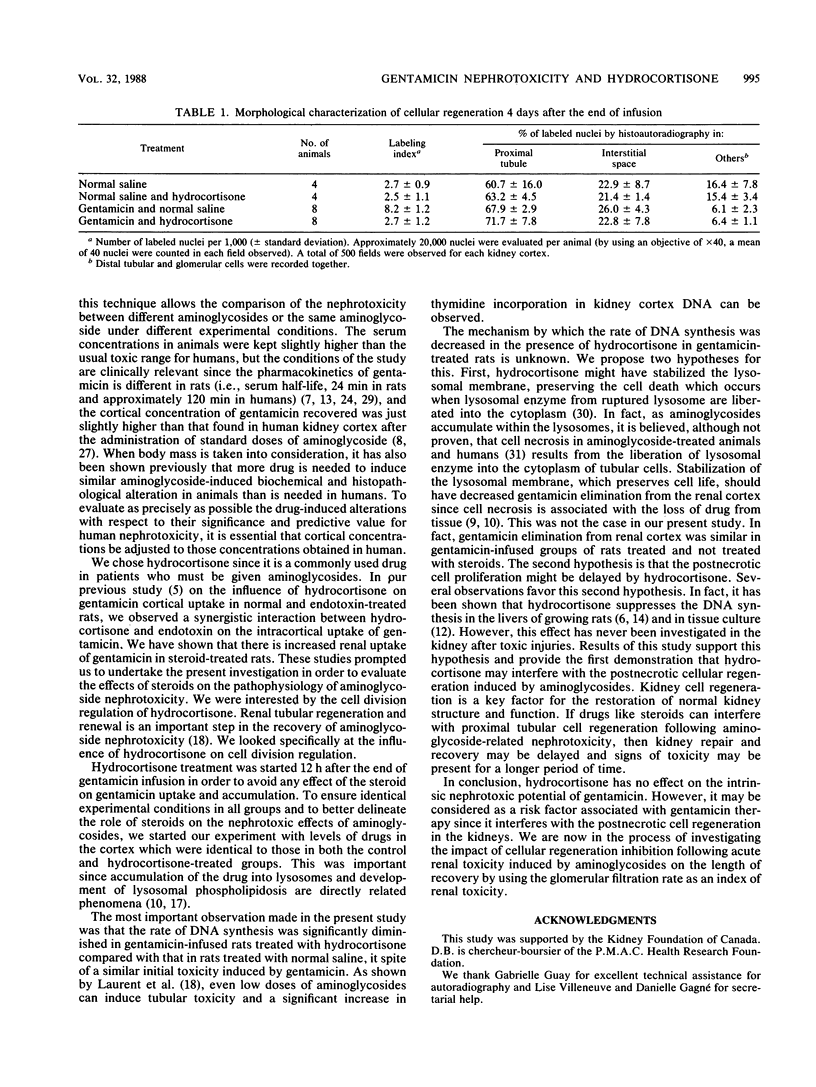
Many risk factors associated with aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity have been identified in humans and experimental animals. They include an initial high rate of creatinine clearance, high initial peak levels in serum, age, sex, duration of therapy, liver disease, and renal infection. The concomitant administration of steroids has never been investigated. We evaluated the role of hydrocortisone on gentamicin-induced nephroxicity in a model of infused rats. We showed that hydrocortisone given over 3 days after the infusion did not modify the gentamicin half-life in the renal cortex, gentamicin-induced lysosomal phospholipidosis, or histopathology but did reduce significantly the 3H/DNA ratio on day 4 after gentamicin infusion. We concluded that hydrocortisone interferes with the postnecrotic cellular regeneration process, an important step that is responsible for the recovery of normal kidney structure following toxic injuries associated with aminoglycoside therapy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronoff G. R., Pottratz S. T., Brier M. E., Walker N. E., Fineberg N. S., Glant M. D., Luft F. C. Aminoglycoside accumulation kinetics in rat renal parenchyma. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):74–78. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp D., Poirier A., Bergeron M. G. Increased nephrotoxicity of gentamicin in pyelonephritic rats. Kidney Int. 1985 Aug;28(2):106–113. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. M., Parker R. A., Elliott W. C., Gilbert D. N., Houghton D. C. Sex-related differences in the susceptibility of rats to gentamicin nephrotoxicity. J Infect Dis. 1982 Mar;145(3):370–373. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.3.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. M., Plamp C. E., Gilbert D. N., Parker R. A., Porter G. A. The influence of dosage regimen on experimental gentamicin nephrotoxicity: dissociation of peak serum levels from renal failure. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):576–580. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Bergeron Y., Beauchamp D. Influence of hydrocortisone succinate on intrarenal accumulation of gentamicin in endotoxemic rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1816–1821. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellano T. J., Schiffman R. L., Jacob M. C., Loeb J. N. Suppression of liver cell proliferation by glucocorticoid hormone: a comparison of normally growing and regenerating tissue in the immature rat. Endocrinology. 1978 Apr;102(4):1107–1112. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-4-1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J. T., Libke R. D., Regamey C., Kirby W. M. Comparative pharmacokinetics of amikacin and kanamycin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Jun;15(6):610–616. doi: 10.1002/cpt1974156610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Broe M. E., Giuliano R. A., Verpooten G. A. Choice of drug and dosage regimen. Two important risk factors for aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity. Am J Med. 1986 Jun 30;80(6B):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90488-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSSFELD H., RAGAN C. Action of hydrocortisone on cells in tissue culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 May;86(1):63–68. doi: 10.3181/00379727-86-21011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. N., Houghton D. C., Bennett W. M., Plamp C. E., Reger K., Porter G. A. Reversibility of gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats: recovery during continuous drug administration. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Jan;160(1):99–103. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giurgea-Marion L., Toubeau G., Laurent G., Heuson-Stiennon J. A., Tulkens P. M. Impairment of lysosome-pinocytic vesicle fusion in rat kidney proximal tubules after treatment with gentamicin at low doses. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;86(2):271–285. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(86)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyselynck A. M., Forrey A., Cutler R. Pharmacokinetics of gentamicin: distribution and plasma and renal clearance. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S70–S76. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson I. C., Fischel R. E., Loeb J. N. Suppression of liver DNA synthesis by cortisone. Endocrinology. 1971 Jun;88(6):1471–1476. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-6-1471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kourilsky O., Solez K., Morel-Maroger L., Whelton A., Duhoux P., Sraer J. D. The pathology of acute renal failure due to interstitial nephritis in man with comments on the role of interstitial inflammation and sex in gentamicin nephrotoxicity. Medicine (Baltimore) 1982 Jul;61(4):258–268. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198207000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G., Carlier M. B., Rollman B., Van Hoof F., Tulkens P. Mechanism of aminoglycoside-induced lysosomal phospholipidosis: in vitro and in vivo studies with gentamicin and amikacin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 1;31(23):3861–3870. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G., Maldague P., Carlier M. B., Tulkens P. M. Increased renal DNA synthesis in vivo after administration of low doses of gentamicin to rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Oct;24(4):586–593. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.4.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb J. N., Yeung L. L. Effects of cortisone on thymidine incorporation by various nonlymphoid tissues of the weanling rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jun;143(2):502–507. doi: 10.3181/00379727-143-37353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Rankin L. I., Sloan R. S., Yum M. N. Recovery from aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity with continued drug administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):284–287. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marre R., Tarara N., Louton T., Sack K. Age-dependent nephrotoxicity and the pharmacokinetics of gentamicin in rats. Eur J Pediatr. 1980;133(1):25–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00444750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMartin D. N., Engel S. G. Effect of aging on gentamicin nephrotoxicity and pharmacokinetics in rats. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;38(2):193–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D., Smith C. R., Lipsky J. J., Mellits E. D., Lietman P. S. Risk factors for nephrotoxicity in patients treated with aminoglycosides. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Mar;100(3):352–357. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-3-352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regamey C., Gordon R. C., Kirby W. M. Comparative pharmacokinetics of tobramycin and gentamicin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1973 May-Jun;14(3):396–403. doi: 10.1002/cpt1973143396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Bloxham D. D., Thompson W. L. Nephrotoxicity of gentamicin and tobramycin given once daily or continuously in dogs. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 May;4 (Suppl A):85–101. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.suppl_a.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyers C. L., Moore R. D., Lerner S. A., Smith C. R. A model for predicting nephrotoxicity in patients treated with aminoglycosides. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1062–1068. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schentag J. J., Plaut M. E., Cerra F. B. Comparative nephrotoxicity of gentamicin and tobramycin: pharmacokinetic and clinical studies in 201 patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):859–866. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J., Kuehn C. Autoradiography of gentamicin uptake by the rat proximal tubule cell. Kidney Int. 1979 Apr;15(4):335–345. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon V. K., Mösinger E. U., Malerczy V. Pharmacokinetic studies of tobramycin and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Apr;3(4):445–450. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.4.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. J., Sabin C., Gilchrest H., Williams S. Effect of anti-inflammatory drugs on lysosomes and lysosomal enzymes from rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Oct 1;25(19):2171–2177. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulkens P. M. Experimental studies on nephrotoxicity of aminoglycosides at low doses. Mechanisms and perspectives. Am J Med. 1986 Jun 30;80(6B):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90487-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. A., Kohlhepp S. J., Kohnen P. W., Houghton D. C., Gilbert D. N. Vancomycin enhancement of experimental tobramycin nephrotoxicity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):20–24. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


