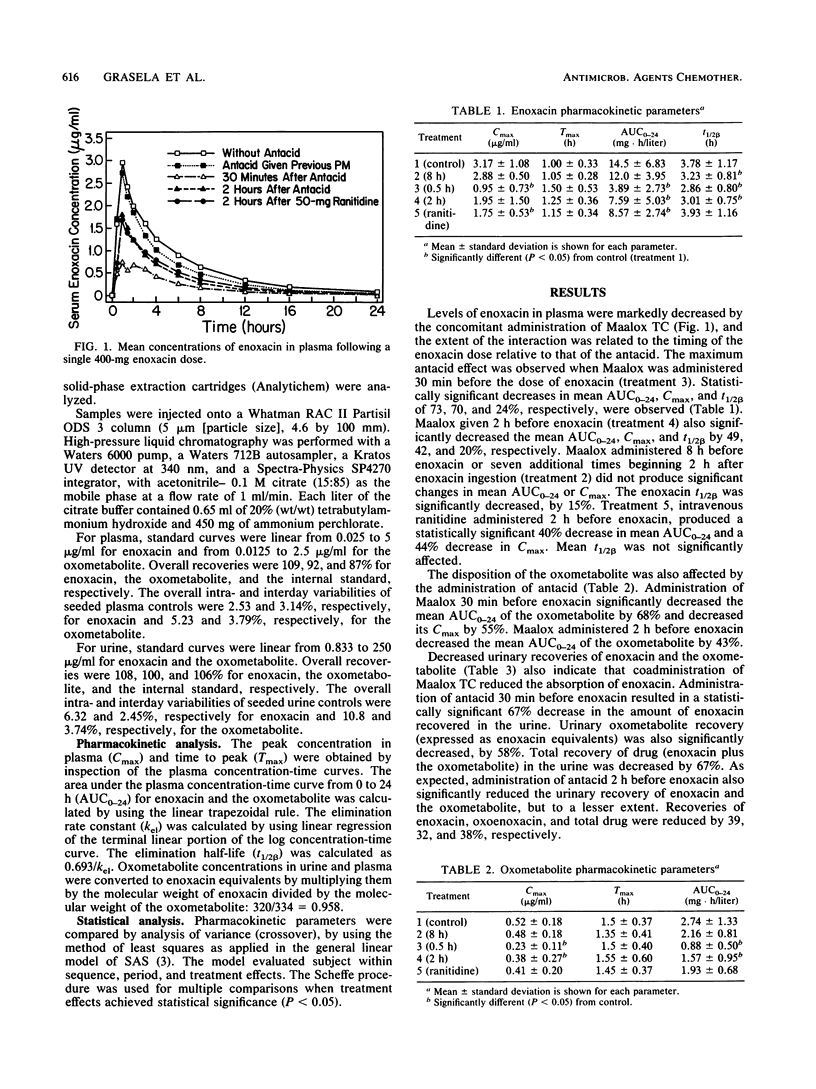
Abstract
Ten normal volunteers participated in a randomized, five-way crossover study to determine the effect of concurrent enoxacin and antacid or ranitidine administration on enoxacin absorption. The bioavailability of a single oral 400-mg enoxacin dose was significantly decreased, by 73 and 49%, when Maalox TC was administered 0.5 and 2 h before enoxacin, respectively. Enoxacin bioavailability was not significantly altered when the antacid was given 8 h before or 2 h after enoxacin administration. Ranitidine, administered intravenously 2 h before enoxacin, also significantly decreased enoxacin bioavailability, by 40%. The correlation between the proximity of antacid administration and the magnitude of the decrease in enoxacin bioavailability supports complexation as the mechanism of the antacid-enoxacin interaction. However, reduction of enoxacin bioavailability by ranitidine suggests that elevated gastric pH may also play a role in the antacid-enoxacin drug-drug interaction.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Frank W. O., Peace K. E., Watson M., Seaman J. J., Szego P. L., Braverman A., Mico B., Dickson B. The effect of single intravenous doses of cimetidine or ranitidine on gastric secretion. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1986 Dec;40(6):665–672. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1986.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golper T. A., Hartstein A. I., Morthland V. H., Christensen J. M. Effects of antacids and dialysate dwell times on multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of oral ciprofloxacin in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1787–1790. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi A. A., Bochner F., Keal J. A., Rolan P. E., Smith M. Effect of food on enoxacin absorption. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):638–639. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmers K., Sternglanz R. Ionization and divalent cation dissociation constants of nalidixic and oxolinic acids. Bioinorg Chem. 1978 Aug;9(2):145–155. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3061(00)80286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


