Abstract
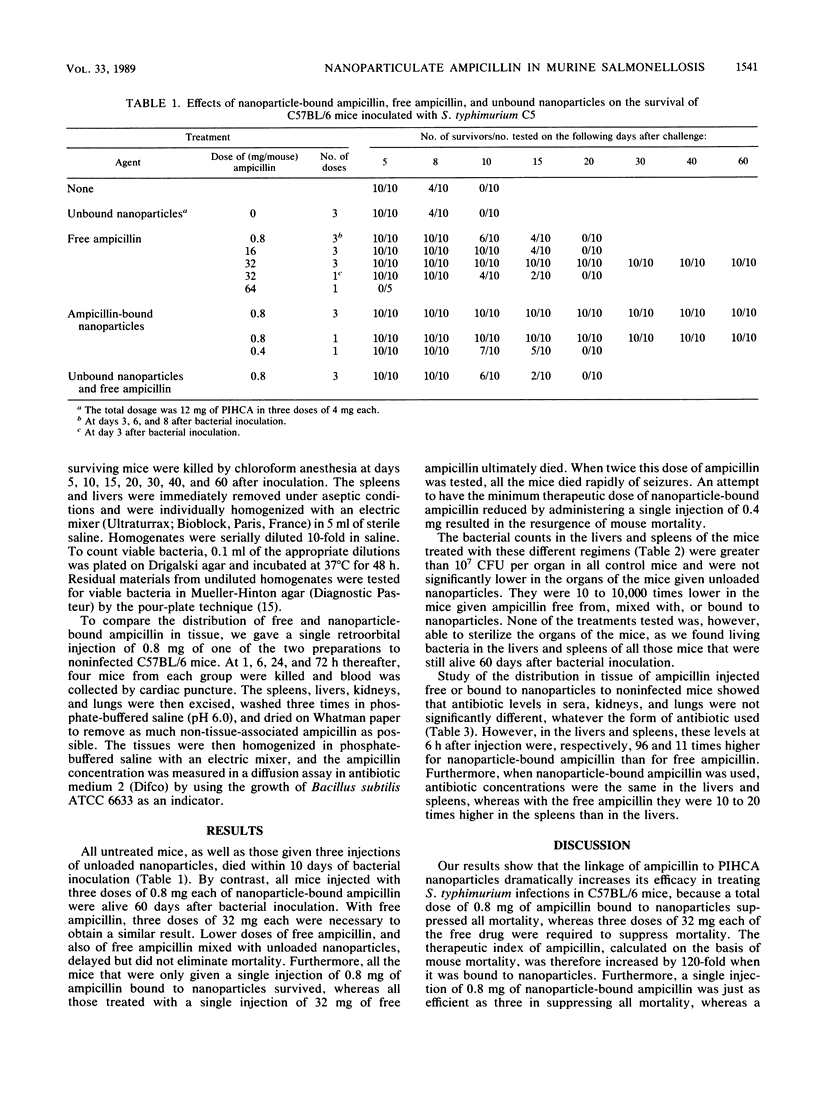
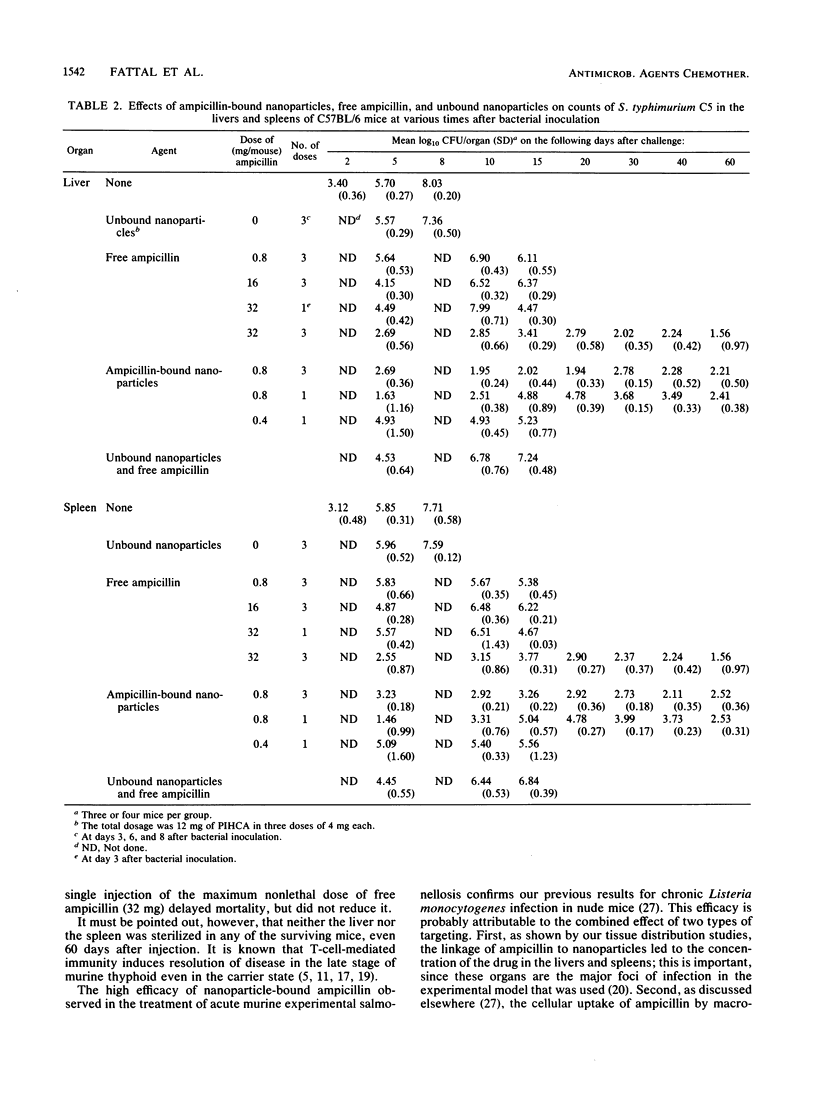
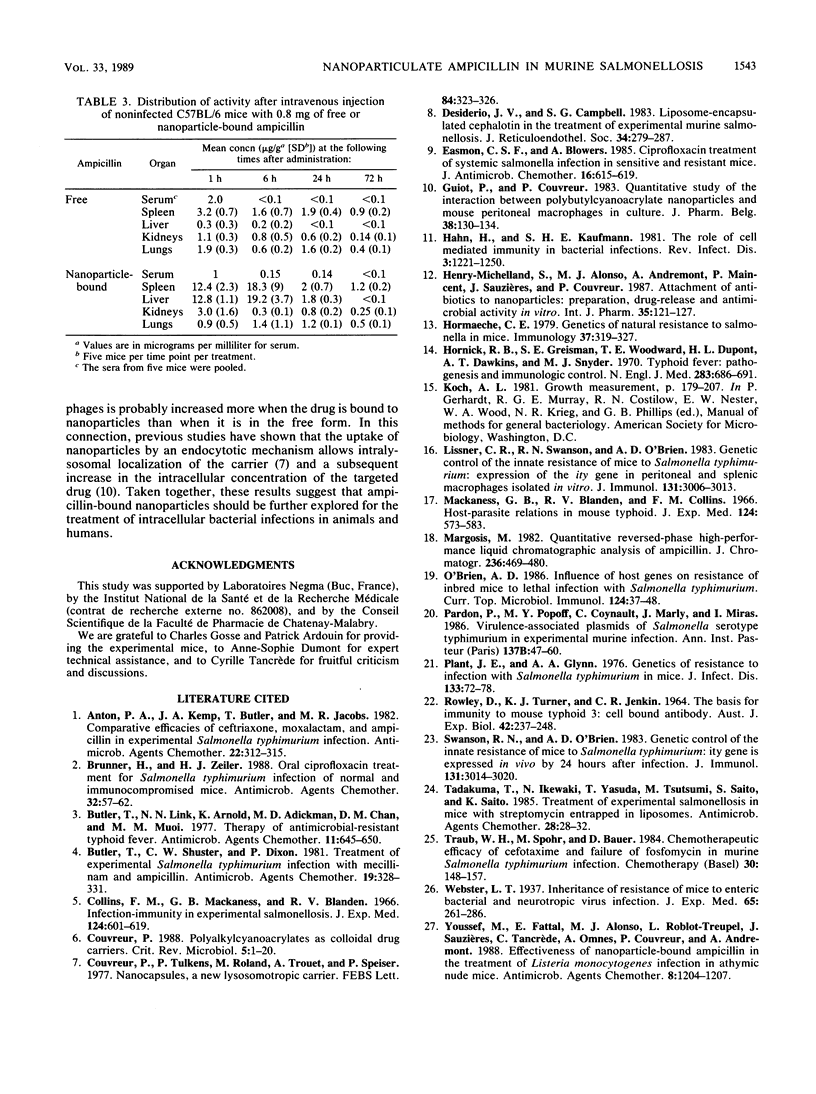
We tested the effectiveness of ampicillin bound to nanoparticles of polyisohexylcyanoacrylate (PIHCA) in treating C57BL/6 mice experimentally infected with Salmonella typhimurium C5. The diameter of the nanoparticles was 187 +/- 13 nm, and the ampicillin/PIHCA ratio was 0.2/1. The proportion of ampicillin bound was 90 +/- 3%. All control mice and all those treated with nonloaded nanoparticles died within 10 days of infection. By contrast, all mice treated with a single injection of 0.8 mg of nanoparticle-bound ampicillin survived. With free ampicillin, a similar curative effect required three doses of 32 mg each. Lower doses delayed but did not reduce mortality. The sharp increase in the therapeutic index of ampicillin after linkage to PIHCA nanoparticles was explained by studies of the distribution of ampicillin, which showed that when bound to nanoparticles, the ampicillin was concentrated mainly in the liver and spleen, the primary foci of infection in the experimental model that we used. These findings warrant further development of intracellular targeting of antibiotics on biodegradable polymeric carriers such as PIHCA.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anton P. A., Kemp J. A., Butler T., Jacobs M. R. Comparative efficacies of ceftriaxone, moxalactam, and ampicillin in experimental Salmonella typhimurium infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):312–315. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H., Zeiler H. J. Oral ciprofloxacin treatment for Salmonella typhimurium infection of normal and immunocompromised mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):57–62. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Linh N. N., Arnold K., Adickman M. D., Chau D. M., Muoi M. M. Therapy of antimicrobial-resistant typhoid fever. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):645–650. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Shuster C. W., Dixon P. Treatment of experimental Salmonella typhimurium infection with mecillinam and ampicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):328–331. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V. Infection-immunity in experimental salmonellosis. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):601–619. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couvreur P. Polyalkylcyanoacrylates as colloidal drug carriers. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 1988;5(1):1–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couvreur P., Tulkens P., Roland M., Trouet A., Speiser P. Nanocapsules: a new type of lysosomotropic carrier. FEBS Lett. 1977 Dec 15;84(2):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80717-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desiderio J. V., Campbell S. G. Liposome-encapsulated cephalothin in the treatment of experimental murine salmonellosis. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 Oct;34(4):279–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Blowers A. Ciprofloxacin treatment of systemic salmonella infection in sensitive and resistance mice. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Nov;16(5):615–619. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.5.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiot P., Couvreur P. Quantitative study of the interaction between polybutylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles and mouse peritoneal macrophages in culture. J Pharm Belg. 1983 May-Jun;38(3):130–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Kaufmann S. H. The role of cell-mediated immunity in bacterial infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1221–1250. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hormaeche C. E. Genetics of natural resistance to salmonellae in mice. Immunology. 1979 Jun;37(2):319–327. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornick R. B., Greisman S. E., Woodward T. E., DuPont H. L., Dawkins A. T., Snyder M. J. Typhoid fever: pathogenesis and immunologic control. N Engl J Med. 1970 Sep 24;283(13):686–691. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197009242831306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lissner C. R., Swanson R. N., O'Brien A. D. Genetic control of the innate resistance of mice to Salmonella typhimurium: expression of the Ity gene in peritoneal and splenic macrophages isolated in vitro. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3006–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V., Collins F. M. Host-parasite relations in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):573–583. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D. Influence of host genes on resistance of inbred mice to lethal infection with Salmonella typhimurium. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;124:37–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardon P., Popoff M. Y., Coynault C., Marly J., Miras I. Virulence-associated plasmids of Salmonella serotype Typhimurium in experimental murine infection. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Jul-Aug;137B(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Genetics of resistance to infection with Salmonella typhimurium in mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):72–78. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D., TURNER K. J., JENKIN C. R. THE BASIS FOR IMMUNITY TO MOUSE TYPHOID. 3. CELL-BOUND ANTIBODY. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Apr;42:237–248. doi: 10.1038/icb.1964.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R. N., O'Brien A. D. Genetic control of the innate resistance of mice to Salmonella typhimurium: Ity gene is expressed in vivo by 24 hours after infection. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3014–3020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadakuma T., Ikewaki N., Yasuda T., Tsutsumi M., Saito S., Saito K. Treatment of experimental salmonellosis in mice with streptomycin entrapped in liposomes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):28–32. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Spohr M., Bauer D. Chemotherapeutic efficacy of cefotaxime and failure of fosfomycin in murine Salmonella typhimurium infection. Chemotherapy. 1984;30(3):148–157. doi: 10.1159/000238261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssef M., Fattal E., Alonso M. J., Roblot-Treupel L., Sauzières J., Tancrède C., Omnès A., Couvreur P., Andremont A. Effectiveness of nanoparticle-bound ampicillin in the treatment of Listeria monocytogenes infection in athymic nude mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1204–1207. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


