Abstract
Background and aims—The pathophysiology of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) diarrhoea remains uncertain. EPEC adhere to enterocytes and transduce signals which produce a characteristic "attaching and effacing" (A/E) lesion in the brush border membrane. The present in vitro study was designed to determine whether signal transduction by EPEC also influences electrolyte transport. Methods—Caco-2 cell monolayers were rapidly infected with wild type EPEC strain E2348/69, or the signal transduction-defective mutant 14.2.1(1), and mounted in Ussing chambers. Results—Strain E2348/69 stimulated a rapid but transient increase in short circuit current (Isc) which coincided with A/E lesion formation; this Isc response was absent on infection with strain 14.2.1(1). While the initial rise in Isc induced by E2348/69 was partially (~35%) dependent on chloride, the remainder possibly represents an influx of sodium and amino acid(s) across the apical membrane. Conclusions—The study directly shows that, after initial adhesion, EPEC induce major alterations in host cell electrolyte transport. The observed Isc responses indicate a rapid modulation of electrolyte transport in Caco-2 cells by EPEC, including stimulation of chloride secretion, for which signal transduction to host cells is a prerequisite.
Keywords: enteropathogenic Escherichia coli; Caco-2 cells; Ussing chambers; electrolyte transport; signal transduction
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (193.2 KB).
Figure 1 .
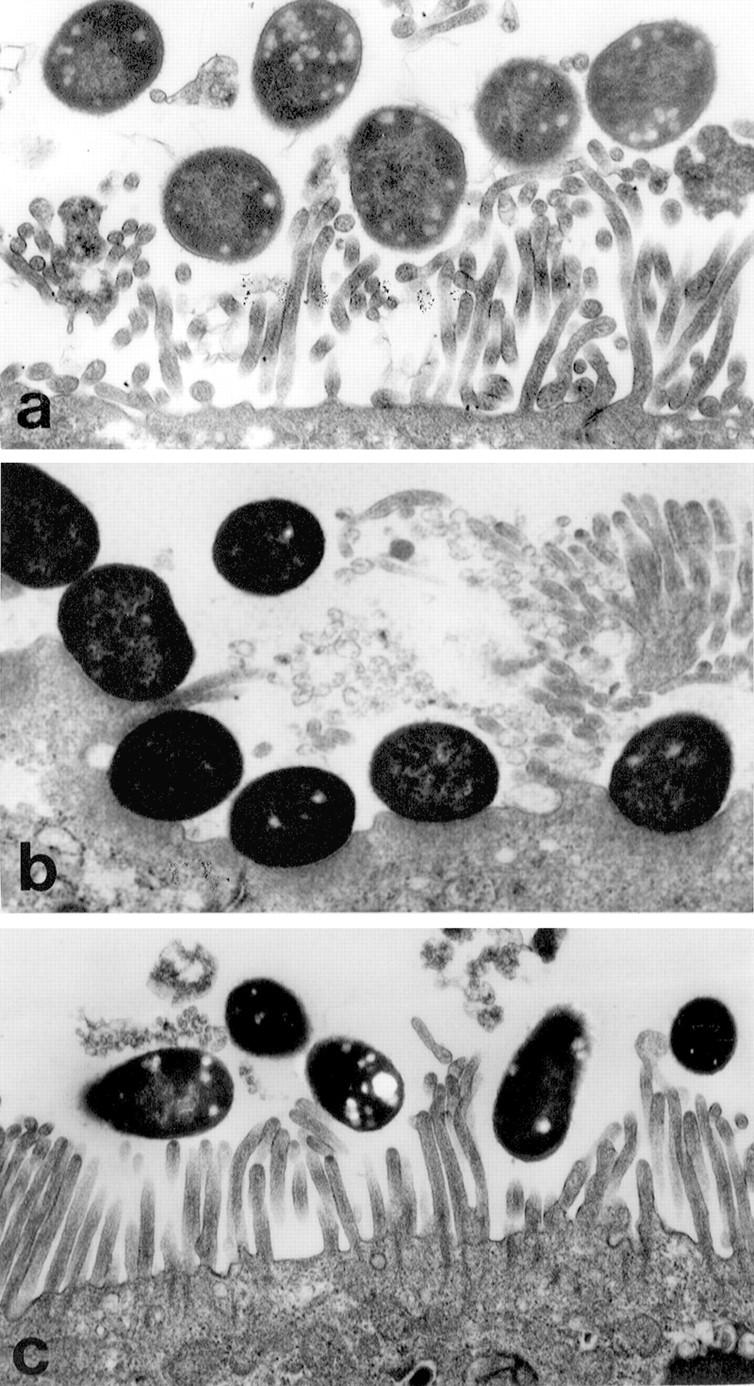
Transmission electron micrographs of EPEC adhesion to Caco-2 monolayers. On initial infection, both wild type strain E2348/69 (a) and cfm strain 14.2.1(1) adhered to intact brush border microvilli. After 15 minutes, E23438/69 were intimately attached to the apical membrane devoid of microvilli (b); however, even after 60 minutes, 14.2.1(1) did not intimately adhere to host cells (c). Original magnification: × 17 500.
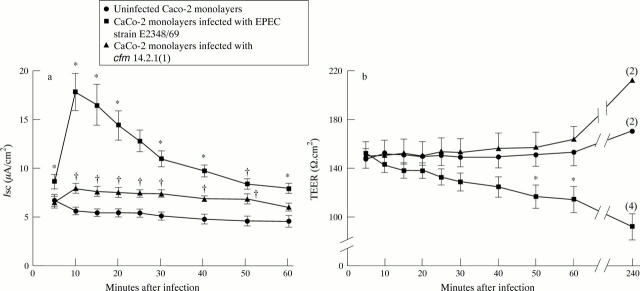
Figure 2 .
(a) Short circuit current (Isc; µA/cm2) and (b) transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER; Ω.cm2) in uninfected Caco-2 monolayers, and those infected with EPEC strain E2348/69 or cfm 14.2.1(1). Each point represents the mean (SEM) from nine monolayers, unless otherwise indicated in parentheses. *p<0.05 v uninfected or 14.2.1(1) infected monolayers; †p<0.05 v uninfected monolayers only.
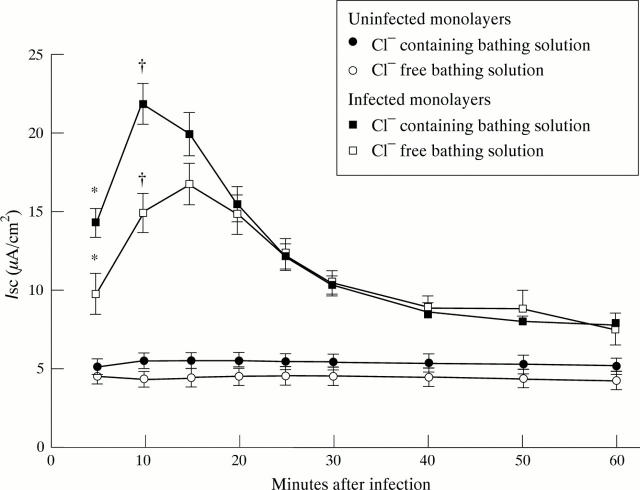
Figure 3 .
Cl dependence of short circuit current (Isc; µA/cm2) in uninfected Caco-2 monolayers and those infected with EPEC strain E2348/69. The Isc of uninfected monolayers did not differ significantly between Cl -inclusive and Cl -free bathing solutions; each point represents the mean (SEM) of seven monolayers. The rapid increase in Isc induced by E2348/69 in Cl -inclusive bathing solution was significantly reduced in Cl -free solution; each point represents mean Isc (SEM) from nine monolayers. *p<0.05 v uninfected or 14.2.1(1) infected monolayers; †p<0.05 v uninfected monolayers.
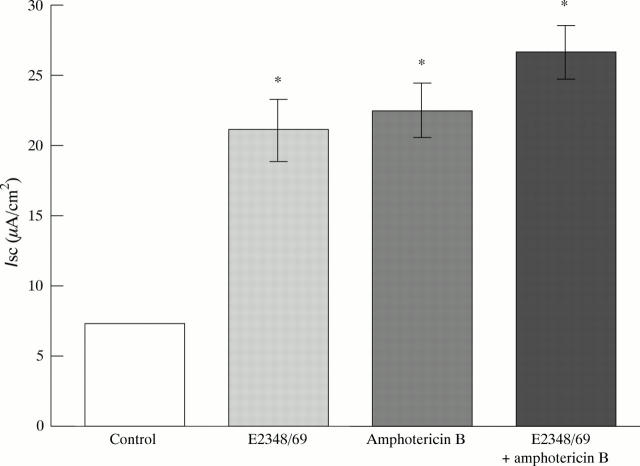
Figure 4 .
Effect of amphotericin B (10 µg/ml apical application) on short circuit current (Isc; µA/cm2) in uninfected Caco-2 monolayers and those infected with EPEC strain E2348/69. Values presented were determined 15 minutes after initial infection. Although E2348/69 infection or amphotericin B treatment induced increases in Isc, these effects were not cumulative. Each bar represents the mean (SEM) from three monolayers. *p<0.05 v control (uninfected and untreated) monolayers.
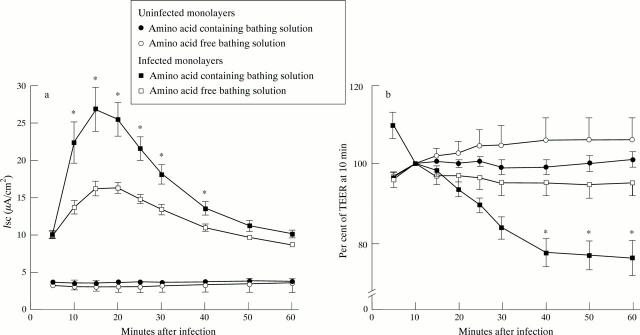
Figure 5 .
Amino acid dependence of (a) short circuit current (Isc; µA/cm2) and (b) change in transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER; expressed as % of TEER at 10 minutes) in uninfected Caco-2 monolayers and those infected with EPEC strain E2348/69. The Isc of uninfected monolayers did not differ significantly between amino acid-inclusive and amino acid-free bathing solutions; each point represents the mean (SEM) from eight monolayers. The rapid and sustained increase in Isc induced by E2348/69 in amino acid-inclusive bathing solution was significantly reduced in amino acid-free solution; each point represents the mean (SEM) from five monolayers. Loss of TEER associated with E2348/69 infection did not occur under amino acid-free conditions. *p<0.05 v infected monolayers in amino acid-free bathing solution.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blais A., Bissonnette P., Berteloot A. Common characteristics for Na+-dependent sugar transport in Caco-2 cells and human fetal colon. J Membr Biol. 1987;99(2):113–125. doi: 10.1007/BF01871231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canil C., Rosenshine I., Ruschkowski S., Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B., Finlay B. B. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli decreases the transepithelial electrical resistance of polarized epithelial monolayers. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2755–2762. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2755-2762.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang E. B., Bookstein C., Vaandrager A., DeJonge H. R., Buse J., Musch M. W. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator mRNA expression relative to ion-nutrient transport in spontaneously differentiating human intestinal CaCo-2 epithelial cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1991 Oct;118(4):377–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Calderwood S. B., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Kaper J. B. Construction and analysis of TnphoA mutants of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli unable to invade HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1565–1571. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1565-1571.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):3953–3961. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.3953-3961.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Tacket C. O., James S. P., Losonsky G., Nataro J. P., Wasserman S. S., Kaper J. B., Levine M. M. Role of the eaeA gene in experimental enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection. J Clin Invest. 1993 Sep;92(3):1412–1417. doi: 10.1172/JCI116717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Orskov F., Orskov I., Knutton S., Scheutz F., Brown J. E., Lexomboon U. Attaching and effacing enteropathogenic Escherichia coli as a cause of infantile diarrhea in Bangkok. J Infect Dis. 1991 Sep;164(3):550–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.3.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasset E., Pinto M., Dussaulx E., Zweibaum A., Desjeux J. F. Epithelial properties of human colonic carcinoma cell line Caco-2: electrical parameters. Am J Physiol. 1984 Sep;247(3 Pt 1):C260–C267. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.247.3.C260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo I. J., Borchardt R. T. Transport of a large neutral amino acid (phenylalanine) in a human intestinal epithelial cell line: Caco-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 21;1028(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90261-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis K. G., Girón J. A., Jerse A. E., McDaniel T. K., Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli contains a putative type III secretion system necessary for the export of proteins involved in attaching and effacing lesion formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7996–8000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Kaper J. B. The eae gene of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli encodes a 94-kilodalton membrane protein, the expression of which is influenced by the EAF plasmid. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4302–4309. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4302-4309.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny B., Finlay B. B. Protein secretion by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is essential for transducing signals to epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7991–7995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldwin T., Williams P. H., McNeish A. S. Actin accumulation at sites of bacterial adhesion to tissue culture cells: basis of a new diagnostic test for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1290-1298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law D., Wilkie K. M., Freeman R. Examination of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strains for an adenylcyclase stimulating factor. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Jun;23(4):335–338. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-4-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long-Krug S. A., Weikel C. S., Tiemens K. T., Hewlett E. L., Levine M. M., Guerrant R. L. Does enteropathogenic Escherichia coli produce heat-labile enterotoxin, heat-stable enterotoxins a or b, or cholera toxin A subunits? Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):612–614. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.612-614.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Pappenheimer J. R. Structural basis for physiological regulation of paracellular pathways in intestinal epithelia. J Membr Biol. 1987;100(2):149–164. doi: 10.1007/BF02209147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel T. K., Jarvis K. G., Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. A genetic locus of enterocyte effacement conserved among diverse enterobacterial pathogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1664–1668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohrmann I., Mohrmann M., Biber J., Murer H. Sodium-dependent transport of Pi by an established intestinal epithelial cell line (CaCo-2). Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 1):G323–G330. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.250.3.G323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath S. K., Desjeux J. F. Human intestinal cell lines as in vitro tools for electrolyte transport studies with relevance to secretory diarrhoea. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1990 Dec;8(4):133–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer J. R. Physiological regulation of transepithelial impedance in the intestinal mucosa of rats and hamsters. J Membr Biol. 1987;100(2):137–148. doi: 10.1007/BF02209146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Levine M. M., Rowe B., Gabriel E. M. Failure to detect conventional enterotoxins in classical enteropathogenic (serotyped) Escherichia coli strains of proven pathogenicity. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):798–801. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.798-801.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M. Traditional enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of infantile diarrhea. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):28–53. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenshine I., Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B., Finlay B. B. Signal transduction between enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) and epithelial cells: EPEC induces tyrosine phosphorylation of host cell proteins to initiate cytoskeletal rearrangement and bacterial uptake. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3551–3560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenshine I., Ruschkowski S., Finlay B. B. Expression of attaching/effacing activity by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli depends on growth phase, temperature, and protein synthesis upon contact with epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1996 Mar;64(3):966–973. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.3.966-973.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R., McAdams A. J., Giannella R., Partin J. C. A clinicopathologic study of enterocyte-adherent Escherichia coli: a cause of protracted diarrhea in infants. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):441–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset M., Laburthe M., Pinto M., Chevalier G., Rouyer-Fessard C., Dussaulx E., Trugnan G., Boige N., Brun J. L., Zweibaum A. Enterocytic differentiation and glucose utilization in the human colon tumor cell line Caco-2: modulation by forskolin. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jun;123(3):377–385. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041230313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein M. A., Mathers D. A., Yan H., Baimbridge K. G., Finlay B. B. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli markedly decreases the resting membrane potential of Caco-2 and HeLa human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1996 Nov;64(11):4820–4825. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.11.4820-4825.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai Y. H., Gage T. P., McQueen C., Formal S. B., Boedeker E. C. Electrolyte transport in rabbit cecum. I. Effect of RDEC-1 infection. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 1):G721–G726. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.4.G721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. Infectious infantile enteritis, yesterday and today. Proc R Soc Med. 1970 Dec;63(12):1297–1301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulshen M. H., Rollo J. L. Pathogenesis of escherichia coli gastroenteritis in man--another mechanism. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 10;302(2):99–101. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001103020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIth meeting of the European Intestinal Transport Group. Pamplona, Spain, September 27-29, 1984. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1984 Nov;8(11):861–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuopio-Varkila J., Schoolnik G. K. Localized adherence by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is an inducible phenotype associated with the expression of new outer membrane proteins. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1167–1177. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]