Abstract
Background—Routine coagulation tests do not necessarily reflect haemostasis in vivo in cirrhotic patients, particularly those who have bleeding varices. Thrombelastography (TEG) can provide a global assessment of haemostatic function from initial clot formation to clot dissolution. Aim—To evaluate TEG changes in cirrhotic patients with variceal bleeding and their association with early rebleeding. Patients/Methods—Twenty cirrhotic patients with active variceal bleeding had serial TEG and routine coagulation tests daily for seven days. The TEG variables before the day of rebleeding (n = 6) were compared with those of patients without rebleeding (n =14). Results—Baseline characteristics of the rebleeding and non-rebleeding groups were comparable apart from a higher incidence of uncontrolled infection on the day of rebleeding in the rebleeding group (p = 0.007). The patients in the rebleeding group were more hypocoagulable before the day of rebleeding as shown by longer r (42 v 24 mm, p<0.001) and k (48 v 13 mm, p<0.001) and smaller a (12 v 38°, p<0.001) compared with the mean of daily results of the non-rebleeding group. Routine coagulation tests, however, showed no significant differences between the two groups. Conclusion—The results of serial TEG measurements suggest that hypocoagulability may be associated with early rebleeding in cirrhotic patients.
Keywords: thrombelastography; variceal bleeding; early rebleeding; cirrhosis
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (126.4 KB).
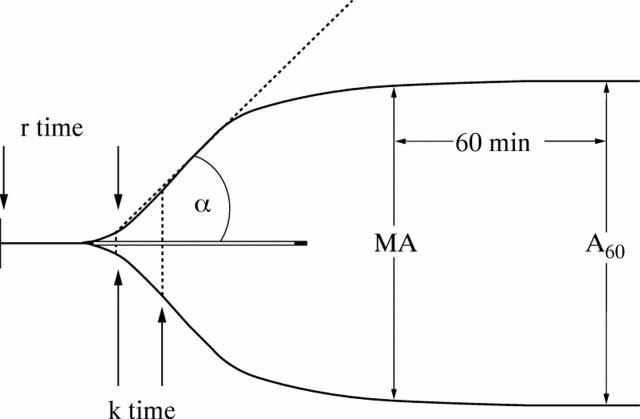
Figure 1 .
Thrombelastographic (TEG) variables: reaction time (r; normal range 19-28 mm) is related to the rate of initial fibrin formation. k (range 8-13 mm) is clot formation time. Maximum amplitude (MA; range 48-60 mm) represents the strength of the clot. Alpha angle (α; range 29-43°) represents the rate of clot formation. A60 is a measure of clot retraction or lysis.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beal A. L., Cerra F. B. Multiple organ failure syndrome in the 1990s. Systemic inflammatory response and organ dysfunction. JAMA. 1994 Jan 19;271(3):226–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ari Z., Panagou M., Patch D., Bates S., Osman E., Pasi J., Burroughs A. Hypercoagulability in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis evaluated by thrombelastography. J Hepatol. 1997 Mar;26(3):554–559. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80420-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard B., Cadranel J. F., Valla D., Escolano S., Jarlier V., Opolon P. Prognostic significance of bacterial infection in bleeding cirrhotic patients: a prospective study. Gastroenterology. 1995 Jun;108(6):1828–1834. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burroughs A. K., D'Heygere F., McIntyre N. Pitfalls in studies of prophylactic therapy for variceal bleeding in cirrhotics. Hepatology. 1986 Nov-Dec;6(6):1407–1413. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clason A. E., Macleod D. A., Elton R. A. Clinical factors in the prediction of further haemorrhage or mortality in acute upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage. Br J Surg. 1986 Dec;73(12):985–987. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800731213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. G., Miro A. M., Kramer D. J., Rodman N., Wearden S. Quantification of thrombelastographic changes after blood component transfusion in patients with liver disease in the intensive care unit. Anesth Analg. 1995 Aug;81(2):272–278. doi: 10.1097/00000539-199508000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. L., Chandler W. L. Thromboelastography for the prediction of bleeding after transplant renal biopsy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1995 Oct;6(4):1250–1255. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V641250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essell J. H., Martin T. J., Salinas J., Thompson J. M., Smith V. C. Comparison of thromboelastography to bleeding time and standard coagulation tests in patients after cardiopulmonary bypass. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 1993 Aug;7(4):410–415. doi: 10.1016/1053-0770(93)90161-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewe K. Bleeding after liver biopsy does not correlate with indices of peripheral coagulation. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 May;26(5):388–393. doi: 10.1007/BF01313579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatta A., Merkel C., Amodio P., Bellon S., Bellumat A., Bolognesi M., Borsato L., Buttò M., Casson F. F., Cavallarin G. Development and validation of a prognostic index predicting death after upper gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with liver cirrhosis: a multicenter study. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994 Sep;89(9):1528–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassman A. B. Platelet abnormalities in hepatobiliary diseases. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1990 Mar-Apr;20(2):119–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. Y., Smith J. L. The course of patients after variceal hemorrhage. Gastroenterology. 1981 Apr;80(4):800–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heresbach D., Bretagne J. F., Raoul J. L., Chaperon J., Piette C., Siproudhis L., Gastard J., Gosselin M. Pronostic et facteurs pronostiques de l'hémorragie par rupture de varice chez le cirrhotique à l'ère de la sclérose endoscopique. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1991;15(11):838–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewett J. A., Roth R. A. Hepatic and extrahepatic pathobiology of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Pharmacol Rev. 1993 Dec;45(4):382–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. A., Tuddenham E. G. Haemostatic problems in liver disease. Gut. 1986 Mar;27(3):339–349. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.3.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallett S. V., Cox D. J. Thrombelastography. Br J Anaesth. 1992 Sep;69(3):307–313. doi: 10.1093/bja/69.3.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicol P. L., Liu G., Harley I. D., McCall P. R., Przybylowski G. M., Bowkett J., Angus P. W., Hardy K. J., Jones R. M. Blood loss and transfusion requirements in liver transplantation: experience with the first 75 cases. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1994 Dec;22(6):666–671. doi: 10.1177/0310057X9402200604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicol P. L., Liu G., Harley I. D., McCall P. R., Przybylowski G. M., Bowkett J., Angus P. W., Hardy K. J., Jones R. M. Patterns of coagulopathy during liver transplantation: experience with the first 75 cases using thrombelastography. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1994 Dec;22(6):659–665. doi: 10.1177/0310057X9402200603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardy B. J., Spencer R. C., Dudley H. A. Hepatic reticuloendothelial protection against bacteremia in experimental hemorrhagic shock. Surgery. 1977 Feb;81(2):193–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pivalizza E. G., Abramson D. C. Thromboelastography as a guide to platelet transfusion. Anesthesiology. 1995 Apr;82(4):1086–1086. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199504000-00039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planas R., Quer J. C., Boix J., Canet J., Armengol M., Cabre E., Pintanel T., Humbert P., Oller B., Broggi M. A. A prospective randomized trial comparing somatostatin and sclerotherapy in the treatment of acute variceal bleeding. Hepatology. 1994 Aug;20(2):370–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevak D., Divertie G., Carton E., Bowie E. J., Rettke S., Taswell H., Wiesner R., Krom R. Blood product transfusion therapy after liver transplantation: comparison of the thromboelastogram and conventional coagulation studies. Transplant Proc. 1993 Apr;25(2):1838–1838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimola A., Soto R., Bory F., Arroyo V., Piera C., Rodes J. Reticuloendothelial system phagocytic activity in cirrhosis and its relation to bacterial infections and prognosis. Hepatology. 1984 Jan-Feb;4(1):53–58. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzel L., Wolbergs E., Merki H. Prophylactic endoscopic sclerotherapy of oesophageal varices. A prospective controlled study. Lancet. 1985 Apr 6;1(8432):773–775. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91444-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman L., Cohen E., Vagher J. P., Woodward E., Caprini J. A. Comparison of thrombelastography with common coagulation tests. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Dec 23;46(4):752–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Dombal F. T., Clarke J. R., Clamp S. E., Malizia G., Kotwal M. R., Morgan A. G. Prognostic factors in upper G.I. bleeding. Endoscopy. 1986 May;18 (Suppl 2):6–10. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1018418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]