Abstract
Background—Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is a clinically well defined hereditary disease caused by germline mutations within the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene. Although several techniques are applied in the mutation analysis of FAP kindreds about 20-50% of cases remain unclear, with no APC mutation identified (APC negative). Aims—To delineate phenotypic differences between APC positive and APC negative patients with respect to colonic and extracolonic disease in order to determine whether additional mechanisms are involved in the pathogenesis of FAP. Methods—The entire coding region of the APC gene was analysed using single stranded conformation polymorphism and protein truncation tests in 50 Swiss FAP families with a total of 161affected individuals. Differences in phenotypic manifestation were statistically evaluated by Student's t test, Fisher's exact test, and χ2 test. Results—Thirty six families (72%) were APC positive. Statistically significant differences between APC positive and APC negative groups were found for the mean age at diagnosis of colonic polyposis (35.2 versus 45.3 years, respectively) and for the occurrence of stomach polyps (14 patients, all APC positive). Additionally, APC negative patients displayed lower polyp numbers at diagnosis and less extracolonic manifestations. Conclusions—FAP kindreds without detected APC gene mutations present with a notably milder disease phenotype compared with APC positive families, suggesting that different genetic factors might be involved.
Keywords: familial adenomatous polyposis; adenomatous polyposis coli gene; mutation; colorectal cancer; extracolonic manifestations
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (128.3 KB).
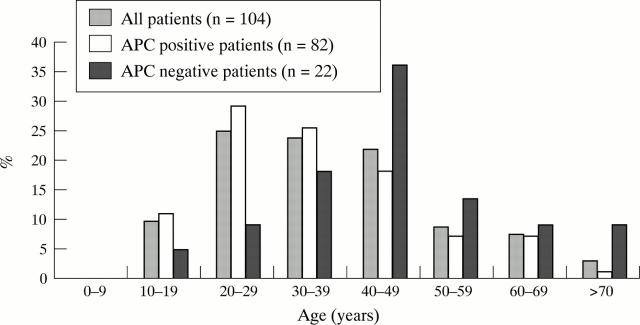
Figure 1 .
Age at diagnosis of colonic polyposis in FAP patients.
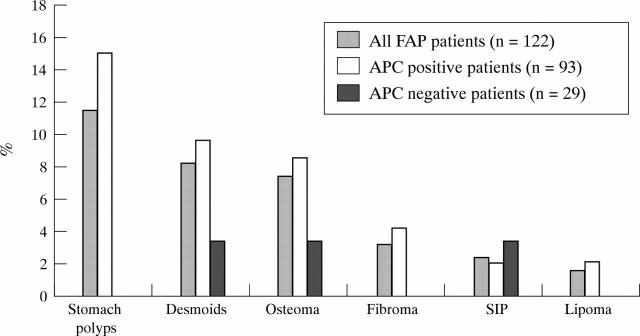
Figure 2 .
Percentage of extracolonic manifestations in 27 FAP patients. SIP, small intestinal polyps.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archimandritis A., Spiliadis C., Tzivras M., Vamvakousis B., Davaris P., Manika Z., Scandalis N. Gastric epithelial polyps: a retrospective endoscopic study of 12974 symptomatic patients. Ital J Gastroenterol. 1996 Sep;28(7):387–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. G., Davies D. R., Guy S. P., Frayling I. M., Evans D. G. APC mutations in familial adenomatous polyposis families in the Northwest of England. Hum Mutat. 1997;10(5):376–380. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1997)10:5<376::AID-HUMU7>3.0.CO;2-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba S., Ando H., Nakamura Y. Identification of germ line mutation of APC gene in possible carriers of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). Anticancer Res. 1994 Sep-Oct;14(5B):2189–2192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F., Bailey C. J., Bodmer J., Bussey H. J., Ellis A., Gorman P., Lucibello F. C., Murday V. A., Rider S. H., Scambler P. Localization of the gene for familial adenomatous polyposis on chromosome 5. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):614–616. doi: 10.1038/328614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bufill J. A. Colorectal cancer genetics. Closing the gap between genotype and phenotype. Cancer. 1995 Dec 15;76(12):2389–2392. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19951215)76:12<2389::aid-cncr2820761202>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow S., Alm T., Fausa O., Hultcrantz R., Järvinen H., Vasen H. Duodenal adenomatosis in familial adenomatous polyposis. DAF Project Group. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1995;10(1):43–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00337586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow S. The Danish Polyposis Register. Description of the methods of detection and evaluation of completeness. Dis Colon Rectum. 1984 Jun;27(6):351–355. doi: 10.1007/BF02552996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell W. J., Spence R. A., Parks T. G. Familial adenomatous polyposis. Br J Surg. 1994 Dec;81(12):1722–1733. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800811207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspari R., Olschwang S., Friedl W., Mandl M., Boisson C., Böker T., Augustin A., Kadmon M., Möslein G., Thomas G. Familial adenomatous polyposis: desmoid tumours and lack of ophthalmic lesions (CHRPE) associated with APC mutations beyond codon 1444. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Mar;4(3):337–340. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.3.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R., Armstrong J. G., Thakker N., Horner K., Guy S. P., Clancy T., Sloan P., Blair V., Dodd C., Warnes T. W. Severe Gardner syndrome in families with mutations restricted to a specific region of the APC gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Nov;57(5):1151–1158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Pietri S., Sassatelli R., Roncucci L., Bertoni G., Landi P., Sabadini G., Tansini P., Cavallini G., Cantoni E., Mareni C. Clinical and biologic features of adenomatosis coli in Northern Italy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1995 Aug;30(8):771–779. doi: 10.3109/00365529509096326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debinski H. S., Love S., Spigelman A. D., Phillips R. K. Colorectal polyp counts and cancer risk in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gastroenterology. 1996 Apr;110(4):1028–1030. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8612989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debinski H. S., Spigelman A. D., Hatfield A., Williams C. B., Phillips R. K. Upper intestinal surveillance in familial adenomatous polyposis. Eur J Cancer. 1995 Jul-Aug;31A(7-8):1149–1153. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(95)00171-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich W. F., Lander E. S., Smith J. S., Moser A. R., Gould K. A., Luongo C., Borenstein N., Dove W. Genetic identification of Mom-1, a major modifier locus affecting Min-induced intestinal neoplasia in the mouse. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):631–639. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90484-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbie Z., Spycher M., Hürliman R., Ammann R., Ammann T., Roth J., Müller A., Müller H., Scott R. J. Mutational analysis of the first 14 exons of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene. Eur J Cancer. 1994;30A(11):1709–1713. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(94)00294-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbie Z., Spycher M., Mary J. L., Häner M., Guldenschuh I., Hürliman R., Amman R., Roth J., Müller H., Scott R. J. Correlation between the development of extracolonic manifestations in FAP patients and mutations beyond codon 1403 in the APC gene. J Med Genet. 1996 Apr;33(4):274–280. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.4.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahtan V., Nochomovitz L. E., Robinson A. M., Garcia V. F., Smith L. E. Gastroduodenal polyps in familial polyposis coli. Am Surg. 1989 May;55(5):278–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gayther S. A., Wells D., SenGupta S. B., Chapman P., Neale K., Tsioupra K., Delhanty J. D. Regionally clustered APC mutations are associated with a severe phenotype and occur at a high frequency in new mutation cases of adenomatous polyposis coli. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):53–56. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giardiello F. M., Brensinger J. D., Luce M. C., Petersen G. M., Cayouette M. C., Krush A. J., Bacon J. A., Booker S. V., Bufill J. A., Hamilton S. R. Phenotypic expression of disease in families that have mutations in the 5' region of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Ann Intern Med. 1997 Apr 1;126(7):514–519. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-126-7-199704010-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giardiello F. M., Petersen G. M., Piantadosi S., Gruber S. B., Traboulsi E. I., Offerhaus G. J., Muro K., Krush A. J., Booker S. V., Luce M. C. APC gene mutations and extraintestinal phenotype of familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut. 1997 Apr;40(4):521–525. doi: 10.1136/gut.40.4.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groden J., Gelbert L., Thliveris A., Nelson L., Robertson M., Joslyn G., Samowitz W., Spirio L., Carlson M., Burt R. Mutational analysis of patients with adenomatous polyposis: identical inactivating mutations in unrelated individuals. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Feb;52(2):263–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groden J., Thliveris A., Samowitz W., Carlson M., Gelbert L., Albertsen H., Joslyn G., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):589–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurbuz A. K., Giardiello F. M., Petersen G. M., Krush A. J., Offerhaus G. J., Booker S. V., Kerr M. C., Hamilton S. R. Desmoid tumours in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut. 1994 Mar;35(3):377–381. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.3.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwama T., Mishima Y. Mortality in young first-degree relatives of patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Cancer. 1994 Apr 15;73(8):2065–2068. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940415)73:8<2065::aid-cncr2820730809>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joslyn G., Carlson M., Thliveris A., Albertsen H., Gelbert L., Samowitz W., Groden J., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification of deletion mutations and three new genes at the familial polyposis locus. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):601–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Nilbert M. C., Su L. K., Vogelstein B., Bryan T. M., Levy D. B., Smith K. J., Preisinger A. C., Hedge P., McKechnie D. Identification of FAP locus genes from chromosome 5q21. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):661–665. doi: 10.1126/science.1651562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leggett B. A., Young J. P., Biden K., Buttenshaw R. L., Knight N., Cowen A. E. Severe upper gastrointestinal polyposis associated with sparse colonic polyposis in a familial adenomatous polyposis family with an APC mutation at codon 1520. Gut. 1997 Oct;41(4):518–521. doi: 10.1136/gut.41.4.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Dobbs M., Scambler P., O'Connell P., Nakamura Y., Stauffer D., Woodward S., Burt R., Hughes J., Gardner E. The gene for familial polyposis coli maps to the long arm of chromosome 5. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1411–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.3479843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch H. T., Smyrk T. C., Lanspa S. J., Jenkins J. X., Lynch P. M., Cavalieri J., Lynch J. F. Upper gastrointestinal manifestations in families with hereditary flat adenoma syndrome. Cancer. 1993 May 1;71(9):2709–2714. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930501)71:9<2709::aid-cncr2820710904>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee M., Chepenik K. P., Liddell R. A., Nelson K. K., Siracusa L. D., Buchberg A. M. The secretory phospholipase A2 gene is a candidate for the Mom1 locus, a major modifier of ApcMin-induced intestinal neoplasia. Cell. 1995 Jun 16;81(6):957–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandl M., Paffenholz R., Friedl W., Caspari R., Sengteller M., Propping P. Frequency of common and novel inactivating APC mutations in 202 families with familial adenomatous polyposis. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):181–184. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi Y., Ando H., Nagase H., Nishisho I., Horii A., Miki Y., Mori T., Utsunomiya J., Baba S., Petersen G. Germ-line mutations of the APC gene in 53 familial adenomatous polyposis patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4452–4456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. G., Macdonald F., Haydon J., Cullen R., Barker G., Hultén M., Neoptolemos J. P., Keighley M. R., McKeown C. Screening practice for familial adenomatous polyposis: the potential for regional registers. Br J Surg. 1993 Feb;80(2):255–258. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800800249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase H., Nakamura Y. Mutations of the APC (adenomatous polyposis coli) gene. Hum Mutat. 1993;2(6):425–434. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380020602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odze R. D. Epithelial proliferation and differentiation in flat duodenal mucosa of patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Mod Pathol. 1995 Aug;8(6):648–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell S. M., Petersen G. M., Krush A. J., Booker S., Jen J., Giardiello F. M., Hamilton S. R., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. Molecular diagnosis of familial adenomatous polyposis. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 30;329(27):1982–1987. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312303292702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Bigas M. A., Mahoney M. C., Karakousis C. P., Petrelli N. J. Desmoid tumors in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Cancer. 1994 Aug 15;74(4):1270–1274. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940815)74:4<1270::aid-cncr2820740415>3.0.co;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. J., Froggatt N. J., Trembath R. C., Evans D. G., Hodgson S. V., Maher E. R. Familial infiltrative fibromatosis (desmoid tumours) (MIM135290) caused by a recurrent 3' APC gene mutation. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Dec;5(12):1921–1924. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.12.1921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. J., van der Luijt R., Spycher M., Mary J. L., Müller A., Hoppeler T., Haner M., Müller H., Martinoli S., Brazzola P. L. Novel germline APC gene mutation in a large familial adenomatous polyposis kindred displaying variable phenotypes. Gut. 1995 May;36(5):731–736. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.5.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirio L., Olschwang S., Groden J., Robertson M., Samowitz W., Joslyn G., Gelbert L., Thliveris A., Carlson M., Otterud B. Alleles of the APC gene: an attenuated form of familial polyposis. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):951–957. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90538-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stella A., Resta N., Gentile M., Susca F., Mareni C., Montera M. P., Guanti G. Exclusion of the APC gene as the cause of a variant form of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Nov;53(5):1031–1037. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolte M., Sticht T., Eidt S., Ebert D., Finkenzeller G. Frequency, location, and age and sex distribution of various types of gastric polyp. Endoscopy. 1994 Oct;26(8):659–665. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1009061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tops C. M., van der Klift H. M., van der Luijt R. B., Griffioen G., Taal B. G., Vasen H. F., Khan P. M. Non-allelic heterogeneity of familial adenomatous polyposis. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Sep 15;47(4):563–567. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320470425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varesco L., Gismondi V., James R., De Benedetti L., Heouaine A., Biticchi R., Masetti E., Bertario L., Sala P., Grammatico P. APC gene mutations in Italian familial polyposis coli patients. Cancer Detect Prev. 1993;17(2):279–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walpole I. R., Kool D. A., Edkins T., Creegan R., Levitt S., Francis S. T., Goldblatt J. Genetic counselling and gene mutation analysis in familial adenomatous polyposis in Western Australia. Med J Aust. 1995 May 1;162(9):464–467. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1995.tb140006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Luijt R. B., Khan P. M., Vasen H. F., Tops C. M., van Leeuwen-Cornelisse I. S., Wijnen J. T., van der Klift H. M., Plug R. J., Griffioen G., Fodde R. Molecular analysis of the APC gene in 105 Dutch kindreds with familial adenomatous polyposis: 67 germline mutations identified by DGGE, PTT, and southern analysis. Hum Mutat. 1997;9(1):7–16. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1997)9:1<7::AID-HUMU2>3.0.CO;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]