Abstract
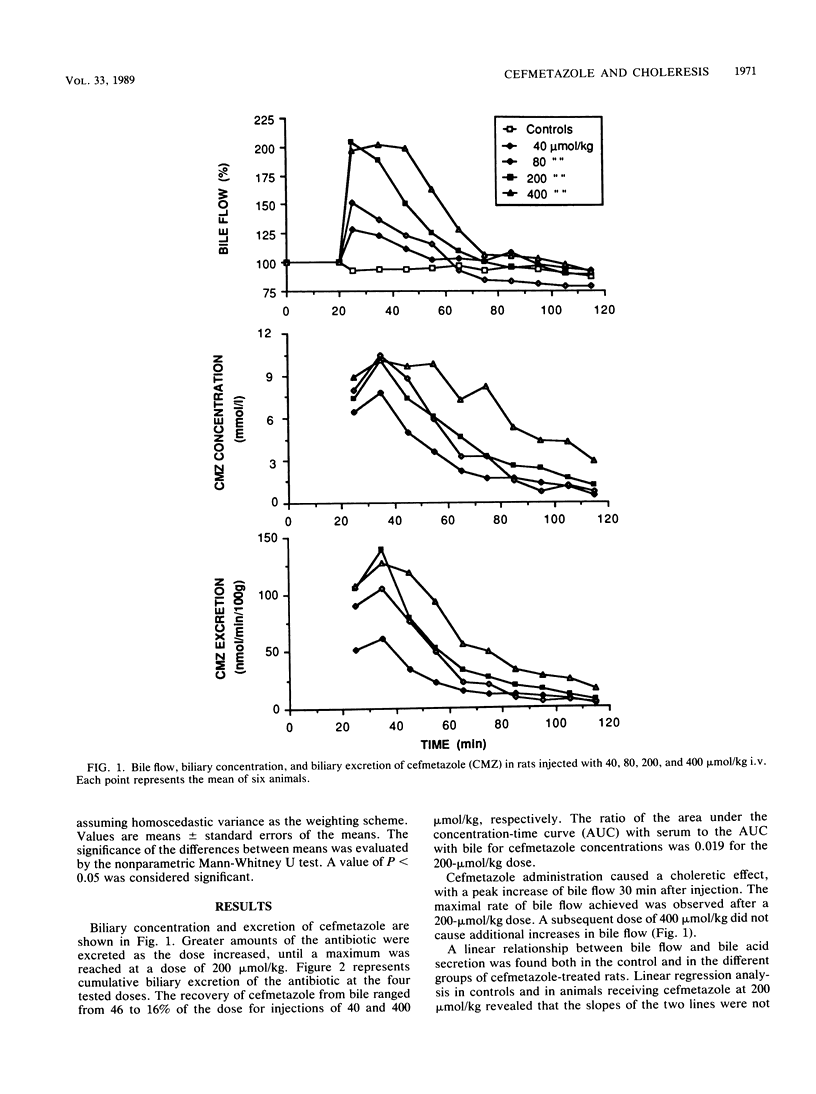
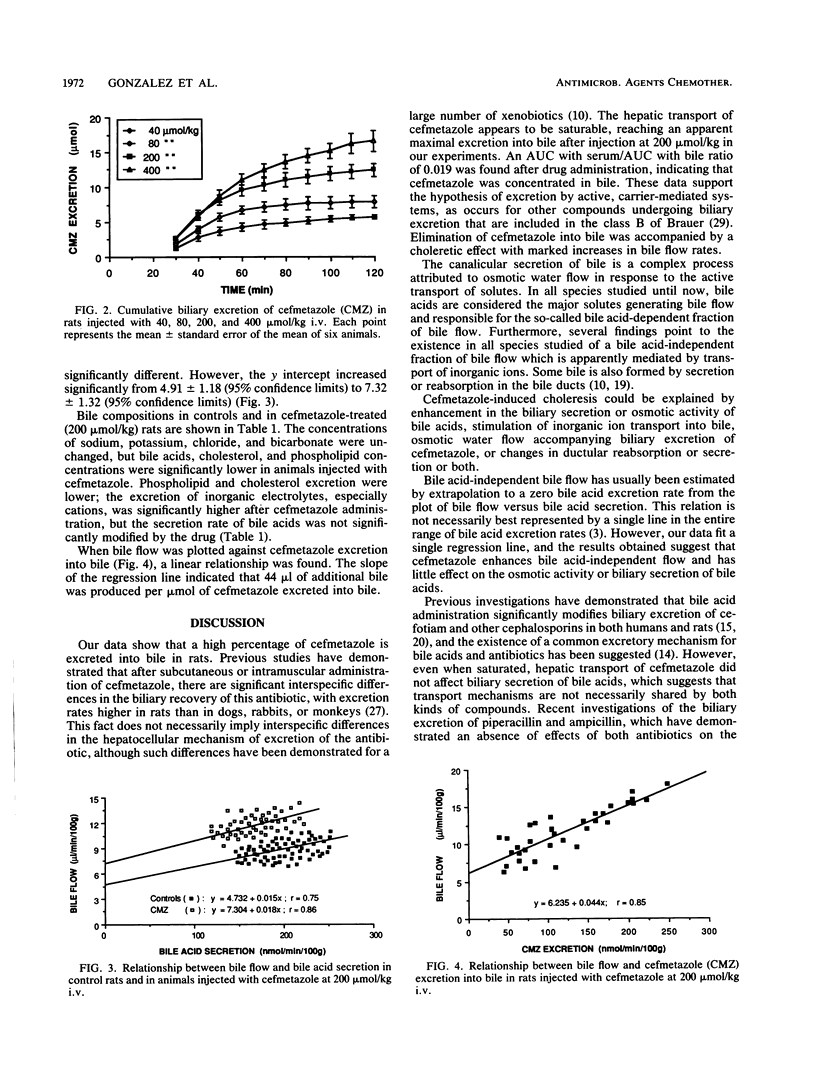
The effect of cefmetazole, a broad-spectrum cephalosporin, on bile flow and composition in rats was studied. Intravenous injection of cefmetazole at doses ranging from 40 to 400 mumol/kg of body weight led to an increase in its biliary concentration and excretion rate, with a maximum at 30 min after injection. Excretion of cefmetazole into bile was associated with a marked choleresis. The magnitude of the increase in bile flow was dose dependent, with a maximal increase at a dose of 200 mumol/kg. Cefmetazole administration did not affect the secretion of bile acids or their osmotic activities, whereas the bile acid-independent bile flow increased by 49% at a dose of 200 mumol/kg. Cefmetazole administration at a dose of 200 mumol/kg significantly increased the biliary outputs of sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate (+36, +56, +28, and +31%, respectively) compared with outputs of controls. A linear relationship was observed between bile flow and cefmetazole excretion, 44 microliters of bile being produced per mumol of cefmetazole excreted into bile. Our results demonstrate that cefmetazole induces choleresis by stimulating bile acid-independent bile flow. This effect appears to be partly due to the osmotic properties of cefmetazole transported into bile.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apstein M. D. Inhibition of biliary phospholipid and cholesterol secretion by bilirubin in the Sprague-Dawley and Gunn rat. Gastroenterology. 1984 Sep;87(3):634–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apstein M. D., Russo A. R. Ampicillin inhibits biliary cholesterol secretion. Dig Dis Sci. 1985 Mar;30(3):253–256. doi: 10.1007/BF01347893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balabaud C., Kron K. A., Gumucio J. J. The assessment of the bile salt-nondependent fraction of canalicular bile water in the rat. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Feb;89(2):393–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnhart J. L., Combes B. Choleresis associated with metabolism and biliary excretion of diethyl maleate in the rat and dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Sep;206(3):614–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. D., Doran J., Fayadh M., Murphy G., Dowling R. H. Effect of ioglycamide (Biligram) on bile flow and biliary lipid secretion in man. Gut. 1978 Apr;19(4):300–307. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.4.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton C. H., Nicholls J. S., Heaton K. W. Estimation of cholesterol in bile: assessment of an enzymatic method. Clin Chim Acta. 1980 Aug 4;105(2):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(80)90464-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun P., Brown K. B., Strunk R., Krusch D. A., Scheld W. M., Hanks J. B. Experimental studies of biliary excretion of piperacillin. Ann Surg. 1987 Apr;205(4):420–427. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198704000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenderovitch J., Raizman A., Infante R. Mechanism of ethacrynic acid-induced choleresis in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1975 Nov;229(5):1180–1187. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.5.1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. M., Gollan J. L. Hepatocyte cotransport of taurocholate and bilirubin glucuronides: role of microtubules. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jul;255(1 Pt 1):G121–G131. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.255.1.G121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forker E. L. Mechanisms of hepatic bile formation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1977;39:323–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.39.030177.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurantz D., Laker M. F., Hofmann A. F. Enzymatic measurement of choline-containing phospholipids in bile. J Lipid Res. 1981 Feb;22(2):373–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi K., Hayakawa T., Katagiri K., Tsukada K., Ito K., Hoshino M., Miyaji M., Takeuchi T., Yamamoto T. Effect of ursodeoxycholate on the biliary excretion of cefotiam and sulbenicillin in patients with percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):726–729. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesa V. A., Fevery J., De Groote J. The maximal biliary excretory rate (Tm) of ioglycamide in the rat. Effect of taurocholate. J Hepatol. 1985;1(3):243–252. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(85)80052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyano T., Arai T., Shimomura H., Ogawa T., Sasaki K., Deguchi E., Suruga K., Nittono H. [The correlation between the biliary excretion of cefmetazole and the bile acid metabolism in postoperative patients with biliary atresia]. Jpn J Antibiot. 1984 Feb;37(2):243–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyano T., Suruga K., Arai T., Nittono H., Kato H. Antibiotic excretion into the bile after hepatic-portojejunostomy in biliary atresia. J Pediatr Surg. 1983 Feb;18(1):42–46. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(83)80271-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley R. H., Boyer J. L. Mechanisms of electrolyte transport in the liver and their functional significance. Semin Liver Dis. 1985 May;5(2):122–135. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1063917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paumgartner G., Horak W., Probst P., Grabner G. Effect of phenobarbital on bile flow and bile salt excretion in the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol. 1971;270(1):98–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00997305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricci G. L., Michiels R., Fevery J., De Groote J. Enhancement by secretin of the apparently maximal hepatic transport of bilirubin in the rat. Hepatology. 1984 Jul-Aug;4(4):651–657. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Barbero J., Mariño E. L., Dominguez-Gil A. Pharmacokinetics of cefmetazole administered intramuscularly and intravenously to healthy adults. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):544–547. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafter E. A., Preshaw R. M. Effects of sulfobromophthalein excretion on biliary lipid secretion in humans and dogs. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jan;240(1):G85–G89. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.240.1.G85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada J., Hayashi Y., Nakamura K. Cefmetazole: clinical evaluation of efficacy and safety in Japan. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1985;11(3):181–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo H., Kawai K., Ikeda T., Igarashi I., Sugawara S. Absorption, distribution, excretion and metabolism of cefmetazole in cynomolgus monkeys. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Jun;35(6):742–754. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALALAY P. Enzymic analysis of steroid hormones. Methods Biochem Anal. 1960;8:119–143. doi: 10.1002/9780470110249.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. B., Klaassen C. D. Choleretic effect of valproic acid in the rat. Hepatology. 1981 Jul-Aug;1(4):341–347. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler H. O., King K. K. Biliary excretion of lecithin and cholesterol in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1337–1350. doi: 10.1172/JCI106930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yura J., Shinagawa N., Ishikawa S., Hayasaka H., Shiramatsu K., Ishibiki K., Aikawa N., Suzuki H., Takahashi T., Sakai K. [Antibiotic susceptibility of bacteria isolated from surgical infections (first report)]. Jpn J Antibiot. 1986 Oct;39(10):2557–2578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


