Abstract
BACKGROUND—Substantial evidence implicates the neuropeptide substance P (SP) in mucosal immunoinflammatory responses. Autoradiographic studies have suggested a disturbance in SP receptor expression in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). AIMS—Because of technical limitations such as poor cellular resolution with autoradiography, we used molecular methods to specifically localise the cellular expression of the neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) in IBD colon, and to quantitate NK-1R mRNA expression levels therein. METHODS—In situ hybridisation and immunohistochemistry were used to localise NK-1R mRNA and protein, respectively, in normal, ulcerative colitis (UC), and Crohn's disease (CD) colonic resections. NK-1R mRNA expression levels of normal, UC, and CD mucosal biopsies were quantitated by competitive reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. RESULTS—NK-1R expression was localised to lamina propria mononuclear cells, epithelium, submucosal vasculature, smooth muscle, and myenteric plexus of normal and IBD colon. No ectopic NK-1R expression was observed in IBD. However, we found increased numbers of NK-1R expressing lymphoid cells in IBD tissue, aberrant negative epithelial expression of NK-1R in UC, and increased expression of NK-1R in CD myenteric plexus. Quantitation of NK-1R mRNA expression in IBD colonic mucosal biopsies revealed marked upregulation of NK-1R mRNA levels compared with non-inflamed mucosal expression levels (p<0.01). CONCLUSIONS—This report demonstrates the strategic localisation and upregulation of NK-1R expression in IBD colon, and thereby suggests the involvement of substance P in the pathophysiological symptoms of IBD. Keywords: substance P; neurokinin-1 receptor; inflammatory bowel disease
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (481.7 KB).
Figure 1 .
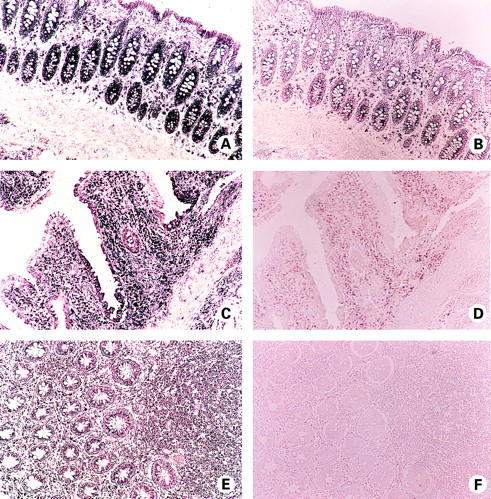
Localisation of neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) mRNA expression in non-inflamed colon (A, B), in active ulcerative colitis (UC) colon (C, D), and in active Crohn's disease (CD) colon (E, F) by in situ hybridisation. (A) NK-1R mRNA (purple) is detected in lamina propria mononuclear cells (LPMC), and in surface and crypt epithelium of normal colon. (C) NK-1R mRNA expression (purple) by LPMC and epithelial cells of UC colon. Note the "patchy" positivity of surface epithelium. (E) Expression of NK-1R mRNA (purple) by LPMC and crypt epithelium of CD colon. Note the dense inflammatory infiltrate of NK-1R mRNA expressing cells. (B, D, F) Control hybridisation of consecutive sections of normal (B), UC (D), and CD (F) colon, with a 10-fold excess of unlabelled riboprobe. Signal intensity is dramatically reduced, confirming the specificity of hybridisation.
Figure 2 .
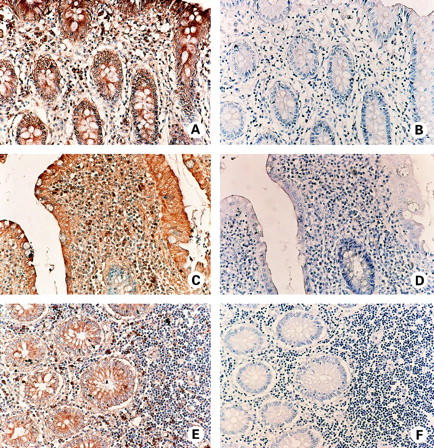
Immunohistochemical localisation of neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) protein expression in non-inflamed colon (A, B), in active ulcerative colitis (UC) colon (C, D), and in active Crohn's disease (CD) colon (E, F). Sections are consecutive to those processed for in situ hybridisation in fig 1 and are shown at higher magnification. (A) NK-1R immunoperoxidase staining (brown) is detected in lamina propria mononuclear cells (LPMC), and in surface (top right of figure) and crypt epithelium of normal colon. (C) NK-1R expression (brown) is present in LPMC and in surface epithelium of UC colon. Note the crypt epithelium is negative for NK-1R expression (blue). (E) Expression of NK-1R protein (brown) by LPMC and crypt epithelial cells of CD colon. (B, D, F) Control staining of consecutive sections of normal (B), UC (D), and CD (F) colon. Specificity of antibody binding was confirmed, as preincubation of the primary antibody with the NK-1R immunising peptide inhibited staining. All sections were counterstained with haematoxylin (blue).
Figure 3 .
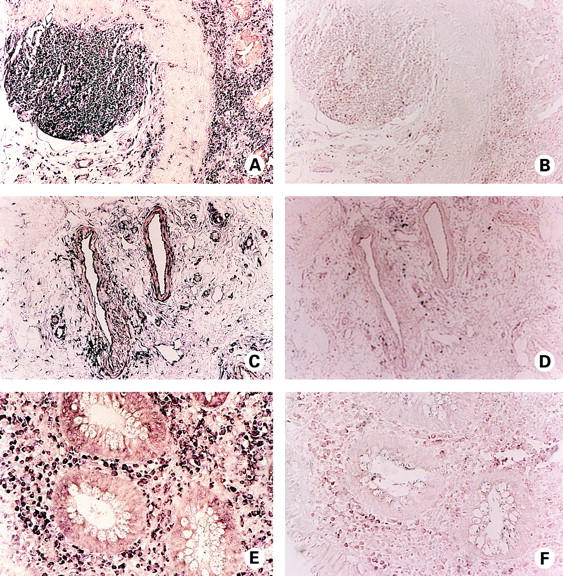
Localisation of neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) mRNA expression in active ulcerative colitis (UC) colon by in situ hybridisation. (A) NK-1R mRNA expression (purple) is detected in lamina propria mononuclear cells (LPMC) and in a lymphoid follicle of UC colon. Crypt epithelial cells negative for NK-1R mRNA are present. (C) Expression of NK-1R mRNA by submucosal arterioles and venules of UC colon. mRNA expression (purple) is evident in the endothelium and muscularis of blood vessels. (E) High magnification view of crypt epithelial cells negative for NK-1R mRNA expression, surrounded by NK-1R positive (purple) LPMC in UC colon. (B, D, F) Control hybridisation of consecutive sections of UC colon, with a 10-fold excess of unlabelled riboprobe. Signal intensity is dramatically reduced, confirming specificity of hybridisation.
Figure 4 .
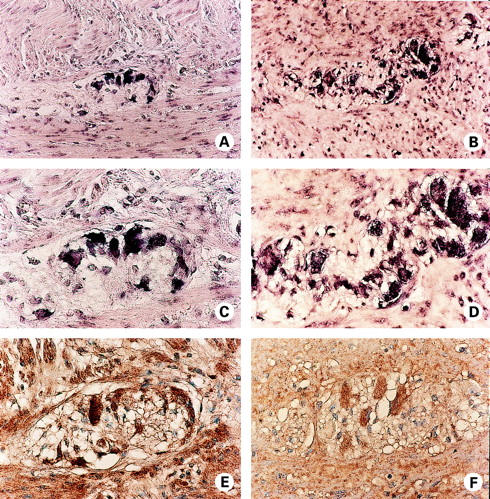
Localisation of neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) expression in non-inflamed (A, C, and E), and inflamed Crohn's disease (CD) (B, D, F) myenteric plexus by in situ hybridisation (A-D), and immunohistochemistry (E, F). (A) NK-1R mRNA (purple) is detected in enteric neurones of the myenteric plexus of normal colon. (C) Higher magnification view of (A). (E) NK-1R protein (brown) staining is evident in the myenteric plexus of normal colon. Section was counterstained with haematoxylin (blue). (B) Expression of NK-1R mRNA by enteric neurones of the myenteric plexus of CD colon. Note the NK-1R positive cells of lymphoid morphology. (D) Higher magnification view of (B). (F) Immunohistochemical detection of NK-1R protein expression (brown) in the myenteric plexus of CD colon. Section was counterstained with haematoxylin (blue).
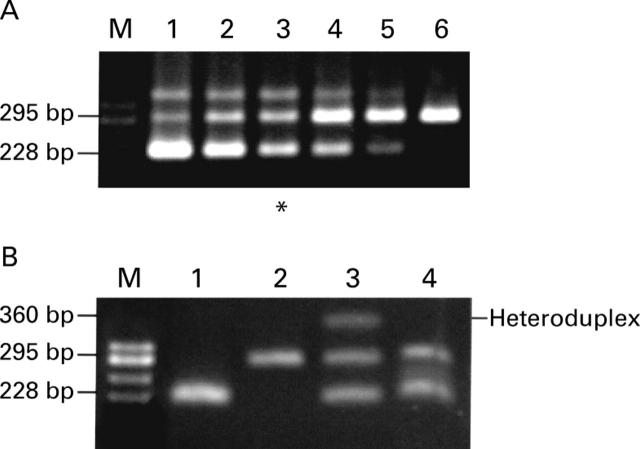
Figure 5 .
Quantitation of neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) mRNA expression in a mucosal biopsy from active ulcerative colitis (UC) colon. (A) Gel shows a representative NK-1R mRNA quantitation using qcRT-PCR. Competitive standards were spiked into the aliquoted biopsy RNA sample at concentrations ranging from 2.6×104 molecules to 2.6×102 molecules (lanes 1-6; 2.5-fold dilution series). Equivalence (*) is seen at 4.1×103 NK-1R mRNA molecules, in which target (295 bp) and competitive standard (228 bp) PCR products are of equal band intensity (lane 3). When adjusted for the amount of total RNA in the assay, this represents a level of expression of 4.1×104 NK-1R mRNA transcripts/µg RNA in this particular UC biopsy sample. HaeIII digested ϕX174 DNA size markers (M) were used. (B) Confirmation of heteroduplex formation. A third band of slower electrophoretic mobility (~360 bp) than the target (295 bp) or competitor (228 bp) PCR products was observed when the concentration of both was relatively high (lane 3). This was absent when competitor or target were amplified separately (lanes 1 and 2, respectively). To confirm that the 360 bp band consisted of a heteroduplex between one strand each of target and competitor PCR products, the PCR products from lane 3 were subjected to digestion with the single stranded DNA specific nuclease, S1 (lane 4). This treatment eliminated the 360 bp band, confirming the presence of a single stranded "loop out" amenable to S1 digestion, which is characteristic of the predicted heteroduplex.
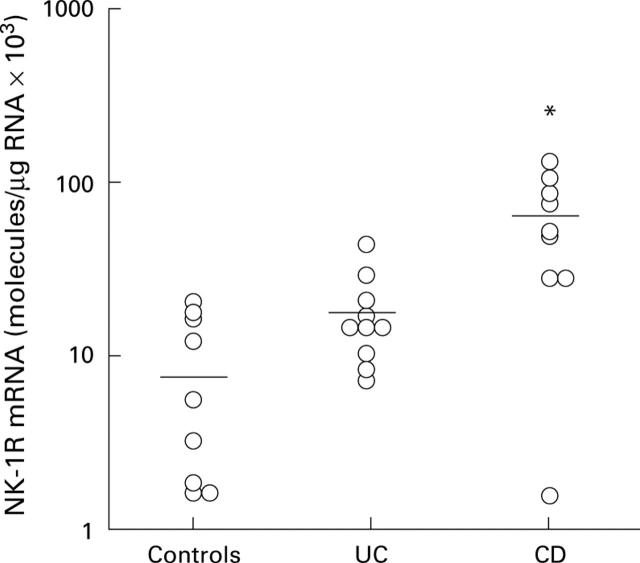
Figure 6 .
Neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) mRNA levels in mucosal biopsies from normal colon (n=9), active ulcerative colitis (UC) colon (n=10), and active Crohn's disease (CD) colon (n=10). The bar indicates mean NK-1R mRNA expression in each group. *p<0.01.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agro A., Stanisz A. M. Inhibition of murine intestinal inflammation by anti-substance P antibody. Reg Immunol. 1993 Mar-Apr;5(2):120–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit Z., Goldman R., Stabinsky Y., Gottlieb P., Fridkin M., Teichberg V. I., Blumberg S. Enhancement of phagocytosis - a newly found activity of substance P residing in its N-terminal tetrapeptide sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jun 30;94(4):1445–1451. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90581-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein C. N., Robert M. E., Eysselein V. E. Rectal substance P concentrations are increased in ulcerative colitis but not in Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993 Jun;88(6):908–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bost K. L., Breeding S. A., Pascual D. W. Modulation of the mRNAs encoding substance P and its receptor in rat macrophages by LPS. Reg Immunol. 1992 Mar-Apr;4(2):105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bost K. L., Pascual D. W. Substance P: a late-acting B lymphocyte differentiation cofactor. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):C537–C545. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.3.C537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagliuolo I., Keates A. C., Wang C. C., Pasha A., Valenick L., Kelly C. P., Nikulasson S. T., LaMont J. T., Pothoulakis C. Clostridium difficile toxin A stimulates macrophage-inflammatory protein-2 production in rat intestinal epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1998 Jun 15;160(12):6039–6045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagliuolo I., LaMont J. T., Letourneau R., Kelly C., O'Keane J. C., Jaffer A., Theoharides T. C., Pothoulakis C. Neuronal involvement in the intestinal effects of Clostridium difficile toxin A and Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin in rat ileum. Gastroenterology. 1994 Sep;107(3):657–665. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagliuolo I., Riegler M., Pasha A., Nikulasson S., Lu B., Gerard C., Gerard N. P., Pothoulakis C. Neurokinin-1 (NK-1) receptor is required in Clostridium difficile- induced enteritis. J Clin Invest. 1998 Apr 15;101(8):1547–1550. doi: 10.1172/JCI2039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS D. R., DOCKERTY M. B., MAYO C. W. The myenteric plexus in regional enteritis: a study of the number of ganglion cells in the ileum in 24 cases. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1955 Aug;101(2):208–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desreumaux P., Brandt E., Gambiez L., Emilie D., Geboes K., Klein O., Ectors N., Cortot A., Capron M., Colombel J. F. Distinct cytokine patterns in early and chronic ileal lesions of Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1997 Jul;113(1):118–126. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(97)70116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Connell A. B., Dickersin G. R. Crohn's disease: a scanning electron microscopic study. Hum Pathol. 1979 Mar;10(2):165–177. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(79)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuss I. J., Neurath M., Boirivant M., Klein J. S., de la Motte C., Strong S. A., Fiocchi C., Strober W. Disparate CD4+ lamina propria (LP) lymphokine secretion profiles in inflammatory bowel disease. Crohn's disease LP cells manifest increased secretion of IFN-gamma, whereas ulcerative colitis LP cells manifest increased secretion of IL-5. J Immunol. 1996 Aug 1;157(3):1261–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland A. M., Grady E. F., Payan D. G., Vigna S. R., Bunnett N. W. Agonist-induced internalization of the substance P (NK1) receptor expressed in epithelial cells. Biochem J. 1994 Oct 1;303(Pt 1):177–186. doi: 10.1042/bj3030177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin E., Karmeli F., Selinger Z., Rachmilewitz D. Colonic substance P levels are increased in ulcerative colitis and decreased in chronic severe constipation. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 May;34(5):754–757. doi: 10.1007/BF01540348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goode T., O'Connell J., Sternini C., Anton P., Wong H., O'Sullivan G. C., Collins J. K., Shanahan F. Substance P (neurokinin-1) receptor is a marker of human mucosal but not peripheral mononuclear cells: molecular quantitation and localization. J Immunol. 1998 Sep 1;161(5):2232–2240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greeno E. W., Mantyh P., Vercellotti G. M., Moldow C. F. Functional neurokinin 1 receptors for substance P are expressed by human vascular endothelium. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1269–1276. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines K. A., Kolasinski S. L., Cronstein B. N., Reibman J., Gold L. I., Weissmann G. Chemoattraction of neutrophils by substance P and transforming growth factor-beta 1 is inadequately explained by current models of lipid remodeling. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1491–1499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho W. Z., Kaufman D., Uvaydova M., Douglas S. D. Substance P augments interleukin-10 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha release by human cord blood monocytes and macrophages. J Neuroimmunol. 1996 Dec;71(1-2):73–80. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(96)00132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. T., Coy D. H. Progress in the development of potent bombesin receptor antagonists. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Jan;12(1):13–19. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90483-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joslin G., Krause J. E., Hershey A. D., Adams S. P., Fallon R. J., Perlmutter D. H. Amyloid-beta peptide, substance P, and bombesin bind to the serpin-enzyme complex receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21897–21902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataeva G., Agro A., Stanisz A. M. Substance-P-mediated intestinal inflammation: inhibitory effects of CP 96,345 and SMS 201-995. Neuroimmunomodulation. 1994 Nov-Dec;1(6):350–356. doi: 10.1159/000097187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keränen U., Kiviluoto T., Järvinen H., Bäck N., Kivilaakso E., Soinila S. Changes in substance P-immunoreactive innervation of human colon associated with ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1995 Oct;40(10):2250–2258. doi: 10.1007/BF02209015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Masuda T., Hiwatashi N., Toyota T., Nagura H. Changes in neuropeptide-containing nerves in human colonic mucosa with inflammatory bowel disease. Pathol Int. 1994 Aug;44(8):624–634. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1994.tb01723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch T. R., Carney J. A., Go V. L. Distribution and quantitation of gut neuropeptides in normal intestine and inflammatory bowel diseases. Dig Dis Sci. 1987 Apr;32(4):369–376. doi: 10.1007/BF01296290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause J. E., DiMaggio D. A., McCarson K. E. Alterations in neurokinin 1 receptor gene expression in models of pain and inflammation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1995 Jul;73(7):854–859. doi: 10.1139/y95-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Effect of neuropeptides on production of inflammatory cytokines by human monocytes. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1218–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.2457950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A. Capsaicin-sensitive nerves in the gastrointestinal tract. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1990 Jan-Feb;303:157–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh C. R., Gates T. S., Zimmerman R. P., Welton M. L., Passaro E. P., Jr, Vigna S. R., Maggio J. E., Kruger L., Mantyh P. W. Receptor binding sites for substance P, but not substance K or neuromedin K, are expressed in high concentrations by arterioles, venules, and lymph nodules in surgical specimens obtained from patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3235–3239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh C. R., Pappas T. N., Lapp J. A., Washington M. K., Neville L. M., Ghilardi J. R., Rogers S. D., Mantyh P. W., Vigna S. R. Substance P activation of enteric neurons in response to intraluminal Clostridium difficile toxin A in the rat ileum. Gastroenterology. 1996 Nov;111(5):1272–1280. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v111.pm8898641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh C. R., Vigna S. R., Bollinger R. R., Mantyh P. W., Maggio J. E., Pappas T. N. Differential expression of substance P receptors in patients with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1995 Sep;109(3):850–860. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90394-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh P. W., Allen C. J., Ghilardi J. R., Rogers S. D., Mantyh C. R., Liu H., Basbaum A. I., Vigna S. R., Maggio J. E. Rapid endocytosis of a G protein-coupled receptor: substance P evoked internalization of its receptor in the rat striatum in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2622–2626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Substance P binds to the formylpeptide chemotaxis receptor on the rabbit neutrophil. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 30;99(4):1065–1072. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90727-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazumdar S., Das K. M. Immunocytochemical localization of vasoactive intestinal peptide and substance P in the colon from normal subjects and patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992 Feb;87(2):176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. C., Lami J. L., Spruck C. H. Substance P increases lymphocyte traffic and lymph flow through peripheral lymph nodes of sheep. Immunology. 1989 May;67(1):109–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niessner M., Volk B. A. Altered Th1/Th2 cytokine profiles in the intestinal mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease as assessed by quantitative reversed transcribed polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 Sep;101(3):428–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb03130.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell J., Goode T., Shanahan F. Quantitative measurement of mRNA expression by competitive RT-PCR. Methods Mol Biol. 1998;92:183–193. doi: 10.1385/0-89603-497-6:183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payan D. G., Brewster D. R., Goetzl E. J. Specific stimulation of human T lymphocytes by substance P. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1613–1615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payan D. G. Neuropeptides and inflammation: the role of substance P. Annu Rev Med. 1989;40:341–352. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.40.020189.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow B. Substance P. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Jun;35(2):85–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatak M., Jr, Luk K. C., Williams B., Lifson J. D. Quantitative competitive polymerase chain reaction for accurate quantitation of HIV DNA and RNA species. Biotechniques. 1993 Jan;14(1):70–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pothoulakis C., Castagliuolo I., LaMont J. T., Jaffer A., O'Keane J. C., Snider R. M., Leeman S. E. CP-96,345, a substance P antagonist, inhibits rat intestinal responses to Clostridium difficile toxin A but not cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):947–951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer M. K., Nohr D., Krause J. E., Weihe E. Inflammation-induced upregulation of NK1 receptor mRNA in dorsal horn neurones. Neuroreport. 1993 Aug;4(8):1007–1010. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199308000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan F., Denburg J. A., Fox J., Bienenstock J., Befus D. Mast cell heterogeneity: effects of neuroenteric peptides on histamine release. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1331–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan F. Enteric neuropathophysiology and inflammatory bowel disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 1998 Jun;10(3):185–187. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2982.1998.00104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith V. C., Sagot M. A., Couraud J. Y., Buchan A. M. Localization of the neurokinin 1 (NK-1) receptor in the human antrum and duodenum. Neurosci Lett. 1998 Aug 28;253(1):49–52. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(98)00618-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisz A. M., Befus D., Bienenstock J. Differential effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide, substance P, and somatostatin on immunoglobulin synthesis and proliferations by lymphocytes from Peyer's patches, mesenteric lymph nodes, and spleen. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):152–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain M. G., Agro A., Blennerhassett P., Stanisz A., Collins S. M. Increased levels of substance P in the myenteric plexus of Trichinella-infected rats. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jun;102(6):1913–1919. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90313-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Kubota Y., Muto T. Substance P containing nerve fibers in rectal mucosa of ulcerative colitis. Dis Colon Rectum. 1997 Jun;40(6):718–725. doi: 10.1007/BF02140903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Morise K., Kusugami K., Furusawa A., Konagaya T., Nishio Y., Kaneko H., Uchida K., Nagai H., Mitsuma T. Abnormal neuropeptide concentration in rectal mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol. 1996 Aug;31(4):525–532. doi: 10.1007/BF02355052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]