Abstract
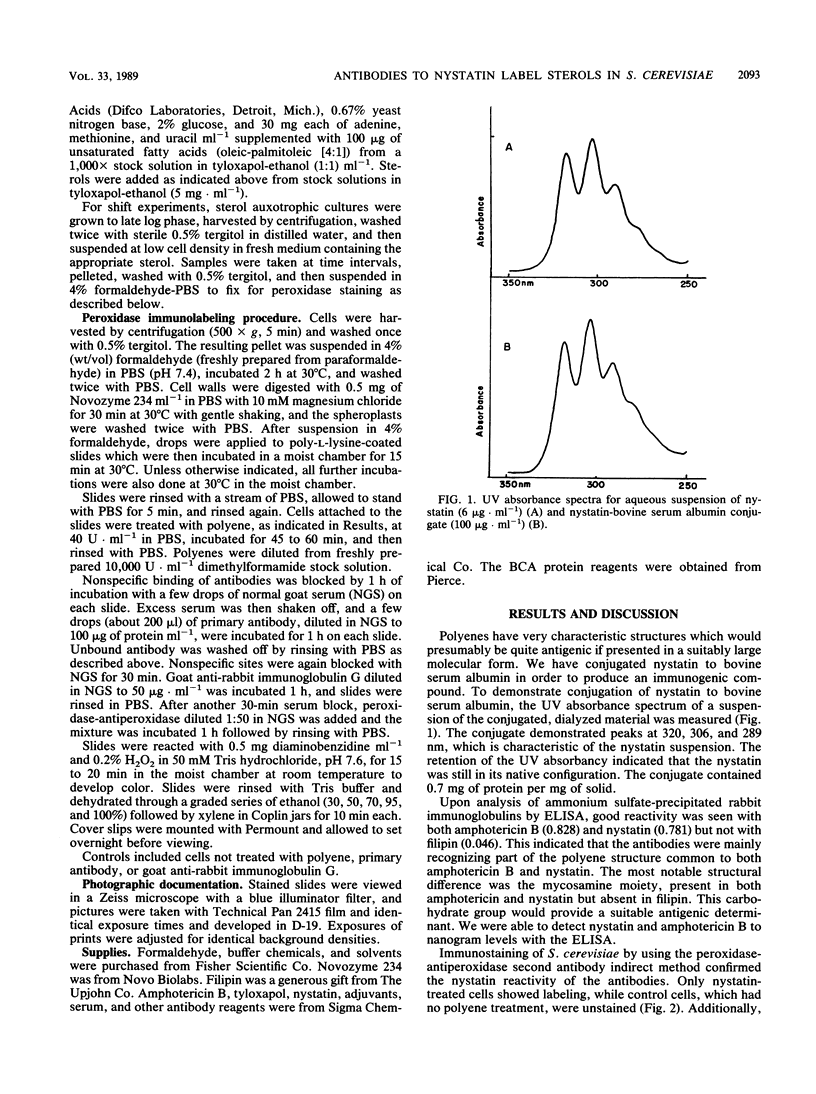
Polyclonal antibodies elicited by injection into rabbits of a nystatin-bovine serum albumin conjugate were reactive with both nystatin and amphotericin B. Upon labeling of polyene-treated Saccharomyces cerevisiae sterol auxotrophs grown on various sterols, nystatin reacted specifically with ergosterol, while amphotericin B did not react preferentially with ergosterol, cholesterol, or cholestanol. Time course labeling experiments demonstrated the rate of ergosterol transport into cholesterol-grown cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastide M., Jouvert S., Bastide J. M. A comparison of the effects of several antifungal imidazole derivatives and polyenes on Candida albicans: an ultrastructural study by scanning electron microscopy. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Oct;28(10):1119–1126. doi: 10.1139/m82-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke O., Tranum-Jensen J., van Deurs B. Filipin as a cholesterol probe. II. Filipin-cholesterol interaction in red blood cell membranes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;35(2):200–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolard J. How do the polyene macrolide antibiotics affect the cellular membrane properties? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 22;864(3-4):257–304. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(86)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clejan S., Bittman R. Rates of amphotericin B and filipin association with sterols. A study of changes in sterol structure and phospholipid composition of vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2884–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gary-Bobo C. M. Polyene--sterol interaction and selective toxicity. Biochimie. 1989 Jan;71(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(89)90129-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. R., Little K. D., Plut E., Koldin M., Kobayashi G. S. Induction of amphotericin B-specific antibodies for use in immunoassays. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):824–828. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. G. The use and abuse of filipin to localize cholesterol in membranes. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1984 Jul;8(7):519–535. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(84)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks L. W. Metabolism of sterols in yeast. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1978;6(4):301–341. doi: 10.3109/10408417809090625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez R. J., Low C., Bottema C. D., Parks L. W. Multiple functions for sterols in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 4;837(3):336–343. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez R. J., Parks L. W. Structural and physiological features of sterols necessary to satisfy bulk membrane and sparking requirements in yeast sterol auxotrophs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Sep;225(2):861–871. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90099-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartz G. M., Jr, Gentry M. K., Amende L. M., Blanchette-Mackie E. J., Alving C. R. Antibodies to cholesterol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1902–1906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzke N. M., Bittman R. Dissociation kinetics and equilibrium binding properties of polyene antibiotic complexes with phosphatidylcholine/sterol vesicles. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1668–1674. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]