Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To evaluate the accuracy of contrast enhanced electron beam computed tomography (EBCT) after acute myocardial infarction in determining patency of the infarct related artery and detecting high grade stenoses and occlusions in the coronary vessels. DESIGN—Case study using blinded comparison with invasive coronary angiography. PATIENTS—36 patients (mean age 53 years) 4-70 days after acute myocardial infarction. INTERVENTIONS—The patients were studied by EBCT and invasive coronary angiography. For EBCT, 50 axial images of the heart (3 mm slice thickness) were acquired. They were triggered by the ECG during breath holding, after intravenous injection of contrast agent. The original images, surface reconstructions, and maximum intensity projections were evaluated for the presence of high grade stenoses and occlusions of the coronary arteries. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES—EBCT results were compared with invasive coronary angiography. RESULTS—Of a total of 144 coronary arteries (left main, left anterior descending, left circumflex, and right coronary artery in 36 patients), 29 (20%) were unevaluable by EBCT. In the remaining arteries, 33 of 36 high grade lesions were correctly detected (92% sensitivity). Specificity was also 92% (73/79). Patency of the infarct related artery was correctly detected in 15 of 16 cases (94%). Five of the 14 occluded infarct related arteries (35%) were mistaken as stenotic but patent, and six could not be assessed. CONCLUSIONS—EBCT is very accurate in detecting significant coronary artery lesions in patients after acute myocardial infarction, but differentiation between occluded and patent infarct related arteries is currently unreliable. Keywords: electron beam CT; coronary angiography; myocardial infarction; computed tomography
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (173.1 KB).
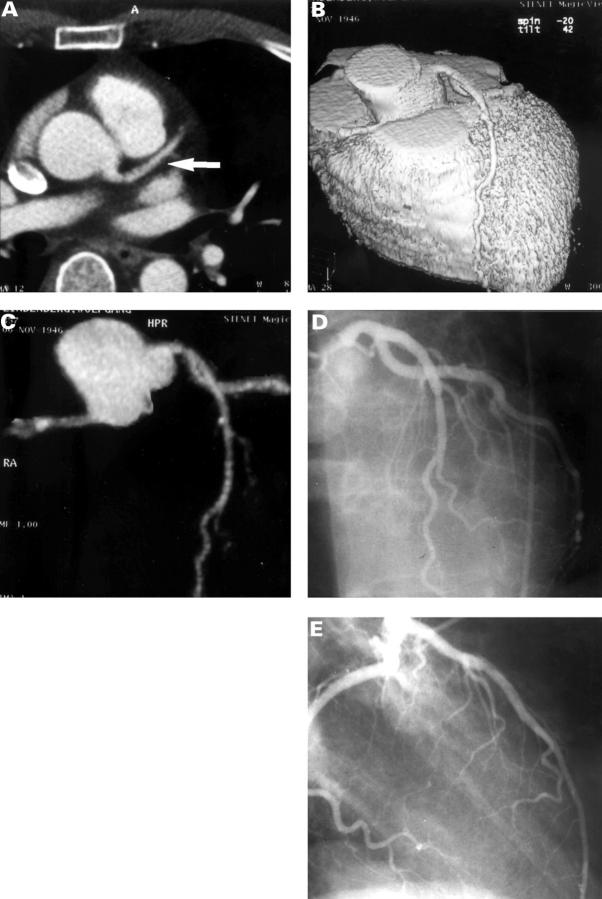
Figure 1 .
Contrast enhanced EBCT study in a 36 year old male patient after anterior myocardial infarction, without significant stenoses on invasive coronary angiography. (A) Contrast enhanced tomogram at the level of the aortic root shows the left main and left anterior descending coronary artery (arrow). (B) Three dimensional reconstruction of the heart showing left anterior descending coronary artery without significant stenosis. The surface reconstruction is thresholded to show only the contrast enhanced lumen of the coronary arteries. (C) Maximum intensity projection of the coronary arteries showing left anterior descending coronary artery without stenosis. (D, E) Invasive coronary angiography: absence of significant stenoses in the left anterior descending coronary artery after anterior myocardial infarction.
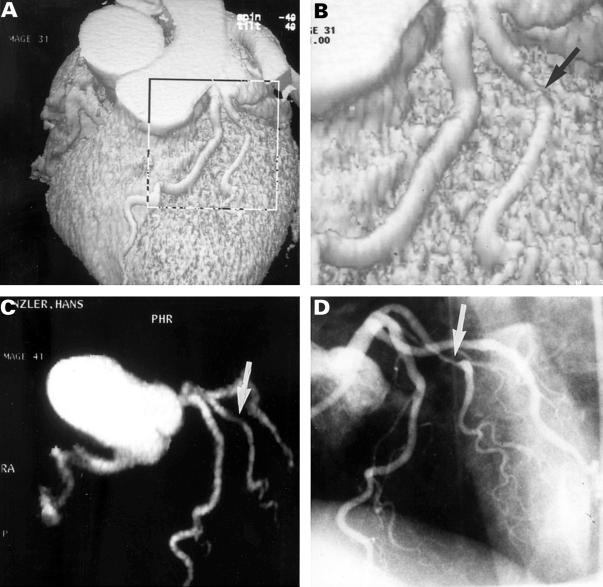
Figure 2 .
Thirty nine year old male patient after anterolateral myocardial infarction. (A, B) Surface reconstruction shows a high grade stenosis in a large diagonal branch (arrow). (C) Maximum intensity projection of the coronary arteries (arrow: stenosis of diagonal branch). (D) Invasive coronary angiography confirms high grade stenosis of the diagonal branch (arrow).
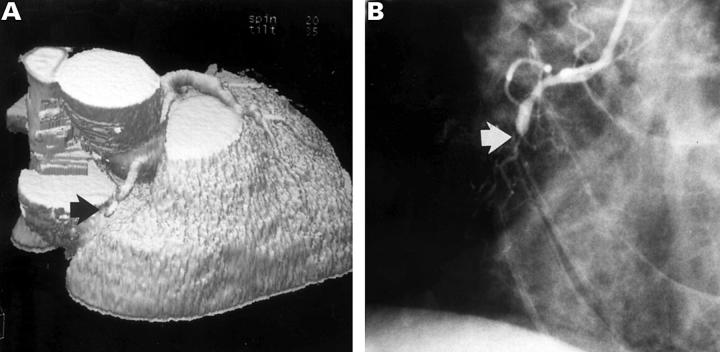
Figure 3 .
Sixty four year old male patient after posterior myocardial infarction. (A) Shaded surface display: occlusion of the right coronary artery (arrow). (B) Invasive coronary angiography confirms occlusion of the right coronary artery (arrow).
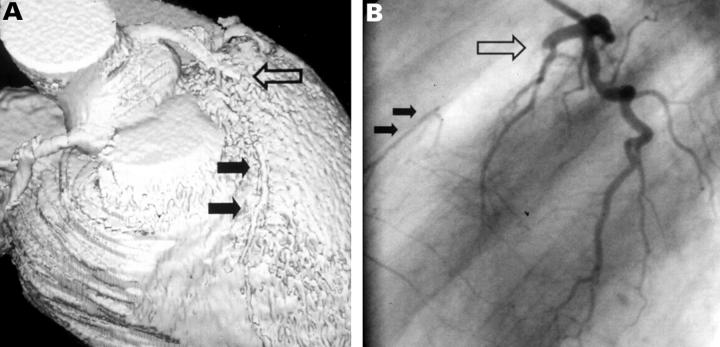
Figure 4 .
Thirty six year old male patient after anterior myocardial infarction. (A) On EBCT, a long subtotal stenosis of the left anterior descending coronary artery is diagnosed. (B) Invasive coronary angiography shows complete occlusion of the left anterior descending coronary artery (large arrow) with filling of the distal vessel segments via collaterals (small arrows).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achenbach S., Moshage W., Ropers D., Bachmann K. Comparison of vessel diameters in electron beam tomography and quantitative coronary angiography. Int J Card Imaging. 1998 Feb;14(1):1–9. doi: 10.1023/a:1005814117755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achenbach S., Moshage W., Ropers D., Nossen J., Daniel W. G. Value of electron-beam computed tomography for the noninvasive detection of high-grade coronary-artery stenoses and occlusions. N Engl J Med. 1998 Dec 31;339(27):1964–1971. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199812313392702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C., Schätzl M., Feist H., Bäuml A., Schöpf U. J., Michalski G., Lechel U., Hengge M., Brüning R., Reiser M. Abschätzung der effektiven Dosis für Routineprotokolle beim konventionellen CT, Elektronenstrahl-CT und bei der Koronarangiographie. Rofo. 1999 Jan;170(1):99–104. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1011015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossaert L., Conraads V., Pintens H. ST-segment analysis: a useful marker for reperfusion after thrombolysis with APSAC? The Belgian EMS Study Group. Eur Heart J. 1991 Mar;12(3):357–362. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budoff M. J., Oudiz R. J., Zalace C. P., Bakhsheshi H., Goldberg S. L., French W. J., Rami T. G., Brundage B. H. Intravenous three-dimensional coronary angiography using contrast enhanced electron beam computed tomography. Am J Cardiol. 1999 Mar 15;83(6):840–845. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(98)01075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb J. W., Edelman R. R. Coronary arteries: breath-hold, gadolinium-enhanced, three-dimensional MR angiography. Radiology. 1998 Mar;206(3):830–834. doi: 10.1148/radiology.206.3.9494509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler W., Achenbach S., Moshage W., Zink D., Kroeker R., Nitz W., Laub G., Bachmann K. Usefulness of respiratory gated magnetic resonance coronary angiography in assessing narrowings > or = 50% in diameter in native coronary arteries and in aortocoronary bypass conduits. Am J Cardiol. 1997 Oct 15;80(8):989–993. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(97)00590-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krucoff M. W., Green C. E., Satler L. F., Miller F. C., Pallas R. S., Kent K. M., Del Negro A. A., Pearle D. L., Fletcher R. D., Rackley C. E. Noninvasive detection of coronary artery patency using continuous ST-segment monitoring. Am J Cardiol. 1986 Apr 15;57(11):916–922. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(86)90730-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning W. J., Li W., Edelman R. R. A preliminary report comparing magnetic resonance coronary angiography with conventional angiography. N Engl J Med. 1993 Mar 25;328(12):828–832. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199303253281202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moshage W. E., Achenbach S., Seese B., Bachmann K., Kirchgeorg M. Coronary artery stenoses: three-dimensional imaging with electrocardiographically triggered, contrast agent-enhanced, electron-beam CT. Radiology. 1995 Sep;196(3):707–714. doi: 10.1148/radiology.196.3.7644633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. F., Fleisch M., Kroeker R., Chatterjee T., Meier B., Vock P. Proximal coronary artery stenosis: three-dimensional MRI with fat saturation and navigator echo. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1997 Jul-Aug;7(4):644–651. doi: 10.1002/jmri.1880070406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi T., Ito K., Imazu M., Yamakido M. Evaluation of coronary artery stenoses using electron-beam CT and multiplanar reformation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1997 Jan-Feb;21(1):121–127. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199701000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennell D. J., Bogren H. G., Keegan J., Firmin D. N., Underwood S. R. Assessment of coronary artery stenosis by magnetic resonance imaging. Heart. 1996 Feb;75(2):127–133. doi: 10.1136/hrt.75.2.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post J. C., van Rossum A. C., Hofman M. B., Valk J., Visser C. A. Three-dimensional respiratory-gated MR angiography of coronary arteries: comparison with conventional coronary angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996 Jun;166(6):1399–1404. doi: 10.2214/ajr.166.6.8633453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pump H., Moehlenkamp S., Sehnert C., Schimpf S. S., Erbel R., Seibel R. M., Groenemeyer D. H. Electron-beam CT in the noninvasive assessment of coronary stent patency. Acad Radiol. 1998 Dec;5(12):858–862. doi: 10.1016/s1076-6332(98)80247-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy G. P., Chernoff D. M., Adams J. R., Higgins C. B. Coronary artery stenoses: assessment with contrast-enhanced electron-beam CT and axial reconstructions. Radiology. 1998 Jul;208(1):167–172. doi: 10.1148/radiology.208.1.9646809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rensing B. J., Bongaerts A., van Geuns R. J., van Ooijen P., Oudkerk M., de Feyter P. J. Intravenous coronary angiography by electron beam computed tomography: a clinical evaluation. Circulation. 1998 Dec 8;98(23):2509–2512. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.98.23.2509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandstede J. J., Pabst T., Beer M., Geis N., Kenn W., Neubauer S., Hahn D. Three-dimensional MR coronary angiography using the navigator technique compared with conventional coronary angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999 Jan;172(1):135–139. doi: 10.2214/ajr.172.1.9888755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmermund A., Haude M., Baumgart D., Görge G., Grönemeyer D., Seibel R., Sehnert C., Erbel R. Non-invasive assessment of coronary Palmaz-Schatz stents by contrast enhanced electron beam computed tomography. Eur Heart J. 1996 Oct;17(10):1546–1553. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a014719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmermund A., Rensing B. J., Sheedy P. F., Bell M. R., Rumberger J. A. Intravenous electron-beam computed tomographic coronary angiography for segmental analysis of coronary artery stenoses. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998 Jun;31(7):1547–1554. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(98)00132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wielopolski P. A., van Geuns R. J., de Feyter P. J., Oudkerk M. Coronary arteries. Eur Radiol. 1998;8(6):873–885. doi: 10.1007/s003300050484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]