Abstract
Aim—To investigate whether mutations in the STK11/LKB1 gene and genes implicated in the colorectal adenoma–carcinoma sequence are involved in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (PJS) related tumorigenesis.
Methods—Thirty nine polyps and five carcinomas from 17 patients (from 13 families) with PJS were analysed for loss of heterozygosity (LOH) at 19p13.3 (STK11/LKB1 gene locus), 5q21 (APC gene locus), 18q21–22 (Smad4 and Smad2 gene locus), and 17p13 (p53 gene locus), and evaluated for immunohistochemical staining of p53. In addition, mutational analysis of K-ras codon 12, APC, and p53 and immunohistochemistry for Smad4 expression were performed on all carcinomas.
Results—LOH at 19p was seen in 15 of the 39 polyps and in all carcinomas (n = 5). Interestingly, six of the seven polyps from patients with cancer had LOH, compared with nine of the 31 polyps from the remaining patients (p = 0.01). In one polyp from a patient without a germline STK11/LKB1 mutation, no LOH at 19p or at three alternative PJS candidate loci (19q, 6p, and 6q) was found. No LOH at 5q was observed. However, mutational analysis revealed an APC mutation in four of the five carcinomas. LOH at 17p was not seen in polyps or carcinomas; immunohistochemistry showed expression of p53 in one carcinoma and focal expression in three polyps. At subsequent sequence analysis, no p53 mutation was found. One carcinoma had an activating K-ras codon 12 mutation and another carcinoma showed 18q LOH; however, no loss of Smad4 expression was seen.
Conclusions—These results provide further evidence that STK11/LKB1 acts as a tumour suppressor gene, and may be involved in the early stages of PJS tumorigenesis. Further research is needed to see whether LOH in PJS polyps could be used as a biomarker to predict cancer. Differences in molecular genetic alterations noted between the adenoma–carcinoma sequence and PJS related tumours suggest the presence of a distinct pathway of carcinogenesis.
Key Words: Peutz-Jeghers syndrome • carcinogenesis • STK11/LKB1 • hamartoma
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (166.3 KB).
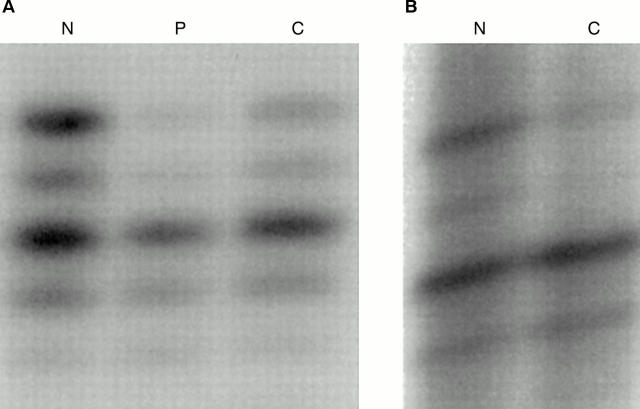
Figure 1 (A) Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) at the STK11/LKB1 locus 19p in a hamartomatous polyp (P) and a colonic carcinoma (C) from patients with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. DNA extracted from normal tissue (N) is displayed next to tumour DNA. (B) LOH at 18q in a colonic carcinoma (C) compared with normal tissue (N).

Figure 2 Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis pattern of an APC gene mutation in fragment S3 of the APC mutation cluster region (MCR) in a Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (PJS) carcinoma (lane 1). Wild-type fragment S3 from a different PJS carcinoma (lane 2). Wild-type fragment S3 from the colon carcinoma cell line CaCo2 (lane 3).
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical expression of p53 in a colon carcinoma of a patient with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avizienyte E., Loukola A., Roth S., Hemminki A., Tarkkanen M., Salovaara R., Arola J., Bützow R., Husgafvel-Pursiainen K., Kokkola A. LKB1 somatic mutations in sporadic tumors. Am J Pathol. 1999 Mar;154(3):677–681. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65314-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avizienyte E., Roth S., Loukola A., Hemminki A., Lothe R. A., Stenwig A. E., Fosså S. D., Salovaara R., Aaltonen L. A. Somatic mutations in LKB1 are rare in sporadic colorectal and testicular tumors. Cancer Res. 1998 May 15;58(10):2087–2090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas I. O., Mulder J. W., Offerhaus G. J., Vogelstein B., Hamilton S. R. An evaluation of six antibodies for immunohistochemistry of mutant p53 gene product in archival colorectal neoplasms. J Pathol. 1994 Jan;172(1):5–12. doi: 10.1002/path.1711720104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas I. O., van den Berg F. M., Mulder J. W., Clement M. J., Slebos R. J., Hamilton S. R., Offerhaus G. J. Potential false-positive results with antigen enhancement for immunohistochemistry of the p53 gene product in colorectal neoplasms. J Pathol. 1996 Mar;178(3):264–267. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199603)178:3<264::AID-PATH485>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignell G. R., Barfoot R., Seal S., Collins N., Warren W., Stratton M. R. Low frequency of somatic mutations in the LKB1/Peutz-Jeghers syndrome gene in sporadic breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1998 Apr 1;58(7):1384–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boardman L. A., Thibodeau S. N., Schaid D. J., Lindor N. M., McDonnell S. K., Burgart L. J., Ahlquist D. A., Podratz K. C., Pittelkow M., Hartmann L. C. Increased risk for cancer in patients with the Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1998 Jun 1;128(11):896–899. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-128-11-199806010-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiGiuseppe J. A., Hruban R. H., Offerhaus G. J., Clement M. J., van den Berg F. M., Cameron J. L., van Mansfeld A. D. Detection of K-ras mutations in mucinous pancreatic duct hyperplasia from a patient with a family history of pancreatic carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1994 May;144(5):889–895. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entius M. M., Westerman A. M., Giardiello F. M., van Velthuysen M. L., Polak M. M., Slebos R. J., Wilson J. H., Hamilton S. R., Offerhaus G. J. Peutz-Jeghers polyps, dysplasia, and K-ras codon 12 mutations. Gut. 1997 Sep;41(3):320–322. doi: 10.1136/gut.41.3.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futreal P. A., Barrett J. C., Wiseman R. W. An Alu polymorphism intragenic to the TP53 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6977–6977. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giardiello F. M., Offerhaus J. G. Phenotype and cancer risk of various polyposis syndromes. Eur J Cancer. 1995 Jul-Aug;31A(7-8):1085–1087. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(95)00139-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giardiello F. M., Welsh S. B., Hamilton S. R., Offerhaus G. J., Gittelsohn A. M., Booker S. V., Krush A. J., Yardley J. H., Luk G. D. Increased risk of cancer in the Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jun 11;316(24):1511–1514. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198706113162404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber S. B., Entius M. M., Petersen G. M., Laken S. J., Longo P. A., Boyer R., Levin A. M., Mujumdar U. J., Trent J. M., Kinzler K. W. Pathogenesis of adenocarcinoma in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Cancer Res. 1998 Dec 1;58(23):5267–5270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminki A., Markie D., Tomlinson I., Avizienyte E., Roth S., Loukola A., Bignell G., Warren W., Aminoff M., Höglund P. A serine/threonine kinase gene defective in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Nature. 1998 Jan 8;391(6663):184–187. doi: 10.1038/34432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminki A. The molecular basis and clinical aspects of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999 May;55(5):735–750. doi: 10.1007/s000180050329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminki A., Tomlinson I., Markie D., Järvinen H., Sistonen P., Björkqvist A. M., Knuutila S., Salovaara R., Bodmer W., Shibata D. Localization of a susceptibility locus for Peutz-Jeghers syndrome to 19p using comparative genomic hybridization and targeted linkage analysis. Nat Genet. 1997 Jan;15(1):87–90. doi: 10.1038/ng0197-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruban R. H., van Mansfeld A. D., Offerhaus G. J., van Weering D. H., Allison D. C., Goodman S. N., Kensler T. W., Bose K. K., Cameron J. L., Bos J. L. K-ras oncogene activation in adenocarcinoma of the human pancreas. A study of 82 carcinomas using a combination of mutant-enriched polymerase chain reaction analysis and allele-specific oligonucleotide hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):545–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEGHERS H., McKUSICK V. A., KATZ K. H. Generalized intestinal polyposis and melanin spots of the oral mucosa, lips and digits; a syndrome of diagnostic significance. N Engl J Med. 1949 Dec 29;241(26):1031–1036. doi: 10.1056/NEJM194912292412601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D. E., Reimann H., Nezu J., Friedel W., Loff S., Jeschke R., Müller O., Back W., Zimmer M. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is caused by mutations in a novel serine threonine kinase. Nat Genet. 1998 Jan;18(1):38–43. doi: 10.1038/ng0198-38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Lessons from hereditary colorectal cancer. Cell. 1996 Oct 18;87(2):159–170. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81333-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markie D., Huson S., Maher E., Davies A., Tomlinson I., Bodmer W. F. A pericentric inversion of chromosome six in a patient with Peutz-Jeghers' syndrome and the use of FISH to localise the breakpoints on a genetic map. Hum Genet. 1996 Aug;98(2):125–128. doi: 10.1007/s004390050173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehenni H., Blouin J. L., Radhakrishna U., Bhardwaj S. S., Bhardwaj K., Dixit V. B., Richards K. F., Bermejo-Fenoll A., Leal A. S., Raval R. C. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: confirmation of linkage to chromosome 19p13.3 and identification of a potential second locus, on 19q13.4. Am J Hum Genet. 1997 Dec;61(6):1327–1334. doi: 10.1086/301644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehenni H., Gehrig C., Nezu J., Oku A., Shimane M., Rossier C., Guex N., Blouin J. L., Scott H. S., Antonarakis S. E. Loss of LKB1 kinase activity in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, and evidence for allelic and locus heterogeneity. Am J Hum Genet. 1998 Dec;63(6):1641–1650. doi: 10.1086/302159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi Y., Nagase H., Ando H., Horii A., Ichii S., Nakatsuru S., Aoki T., Miki Y., Mori T., Nakamura Y. Somatic mutations of the APC gene in colorectal tumors: mutation cluster region in the APC gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):229–233. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.4.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olschwang S., Markie D., Seal S., Neale K., Phillips R., Cottrell S., Ellis I., Hodgson S., Zauber P., Spigelman A. Peutz-Jeghers disease: most, but not all, families are compatible with linkage to 19p13.3. J Med Genet. 1998 Jan;35(1):42–44. doi: 10.1136/jmg.35.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park W. S., Moon Y. W., Yang Y. M., Kim Y. S., Kim Y. D., Fuller B. G., Vortmeyer A. O., Fogt F., Lubensky I. A., Zhuang Z. Mutations of the STK11 gene in sporadic gastric carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 1998 Sep;13(3):601–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perzin K. H., Bridge M. F. Adenomatous and carcinomatous changes in hamartomatous polyps of the small intestine (Peutz-Jeghers syndrome): report of a case and review of the literature. Cancer. 1982 Mar 1;49(5):971–983. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19820301)49:5<971::aid-cncr2820490522>3.0.co;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncin J., Mulkens J., Arends J. W., de Goeij A. Optimizing the APC gene mutation analysis in archival colorectal tumor tissue. Diagn Mol Pathol. 1999 Mar;8(1):11–19. doi: 10.1097/00019606-199903000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell S. M., Petersen G. M., Krush A. J., Booker S., Jen J., Giardiello F. M., Hamilton S. R., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. Molecular diagnosis of familial adenomatous polyposis. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 30;329(27):1982–1987. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312303292702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resta N., Simone C., Mareni C., Montera M., Gentile M., Susca F., Gristina R., Pozzi S., Bertario L., Bufo P. STK11 mutations in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and sporadic colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1998 Nov 1;58(21):4799–4801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spigelman A. D., Murday V., Phillips R. K. Cancer and the Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Gut. 1989 Nov;30(11):1588–1590. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.11.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su G. H., Hruban R. H., Bansal R. K., Bova G. S., Tang D. J., Shekher M. C., Westerman A. M., Entius M. M., Goggins M., Yeo C. J. Germline and somatic mutations of the STK11/LKB1 Peutz-Jeghers gene in pancreatic and biliary cancers. Am J Pathol. 1999 Jun;154(6):1835–1840. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65440-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiainen M., Ylikorkala A., Mäkelä T. P. Growth suppression by Lkb1 is mediated by a G(1) cell cycle arrest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Aug 3;96(16):9248–9251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.16.9248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. J., Taylor F., Churchman M., Norbury G., Tomlinson I. Genetic pathways of colorectal carcinogenesis rarely involve the PTEN and LKB1 genes outside the inherited hamartoma syndromes. Am J Pathol. 1998 Aug;153(2):363–366. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65579-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerman A. M., Entius M. M., Boor P. P., Koole R., de Baar E., Offerhaus G. J., Lubinski J., Lindhout D., Halley D. J., de Rooij F. W. Novel mutations in the LKB1/STK11 gene in Dutch Peutz-Jeghers families. Hum Mutat. 1999;13(6):476–481. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1999)13:6<476::AID-HUMU7>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerman A. M., Entius M. M., de Baar E., Boor P. P., Koole R., van Velthuysen M. L., Offerhaus G. J., Lindhout D., de Rooij F. W., Wilson J. H. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: 78-year follow-up of the original family. Lancet. 1999 Apr 10;353(9160):1211–1215. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(98)08018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilentz R. E., Su G. H., Dai J. L., Sparks A. B., Argani P., Sohn T. A., Yeo C. J., Kern S. E., Hruban R. H. Immunohistochemical labeling for dpc4 mirrors genetic status in pancreatic adenocarcinomas : a new marker of DPC4 inactivation. Am J Pathol. 2000 Jan;156(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64703-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]