Abstract
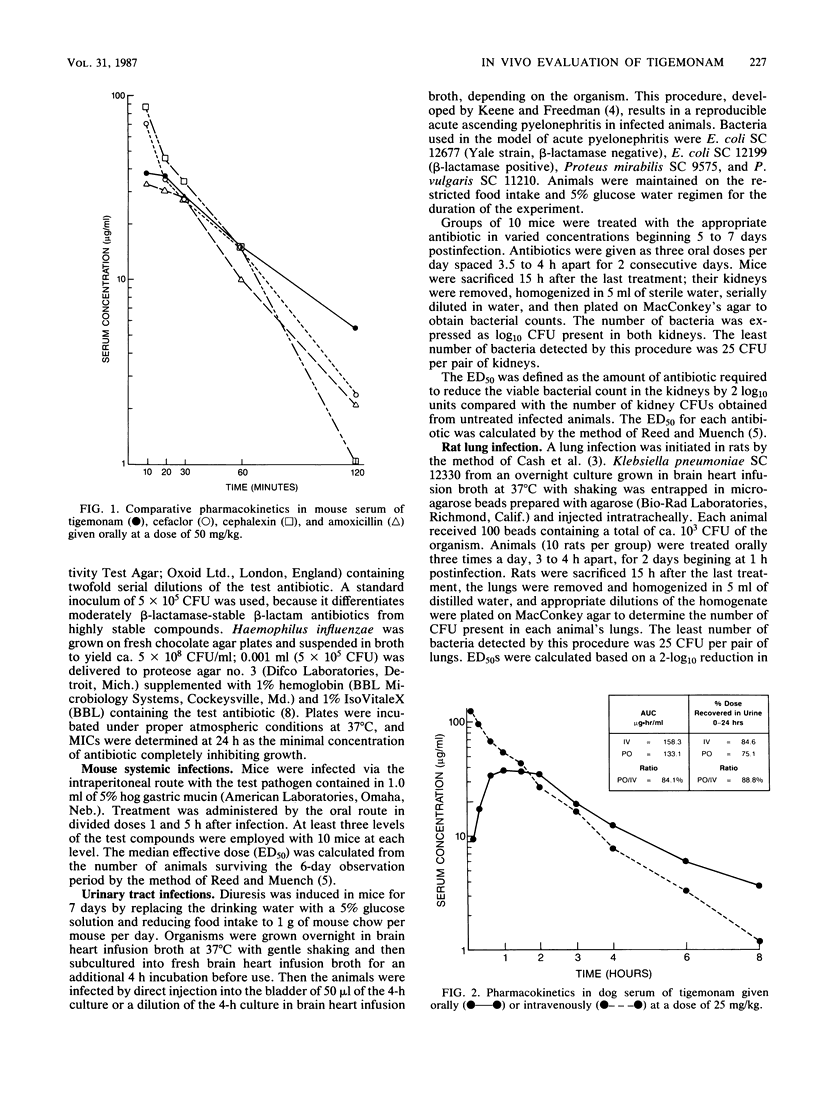
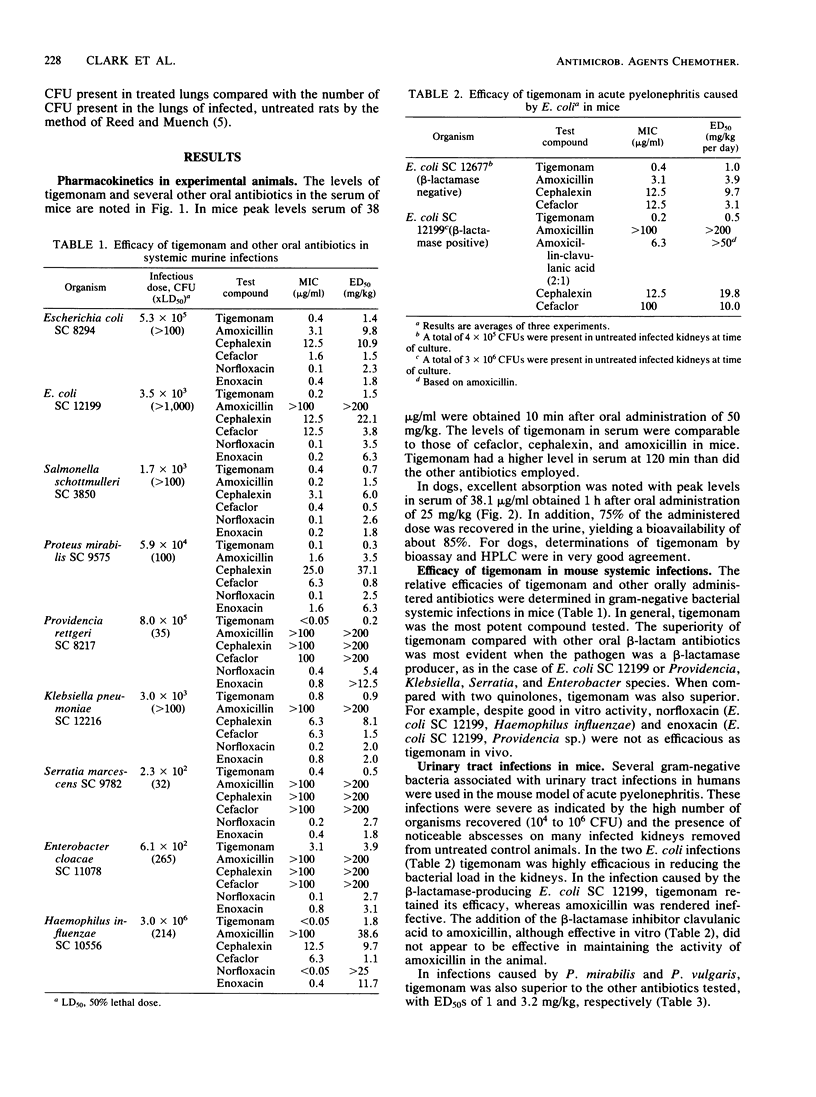
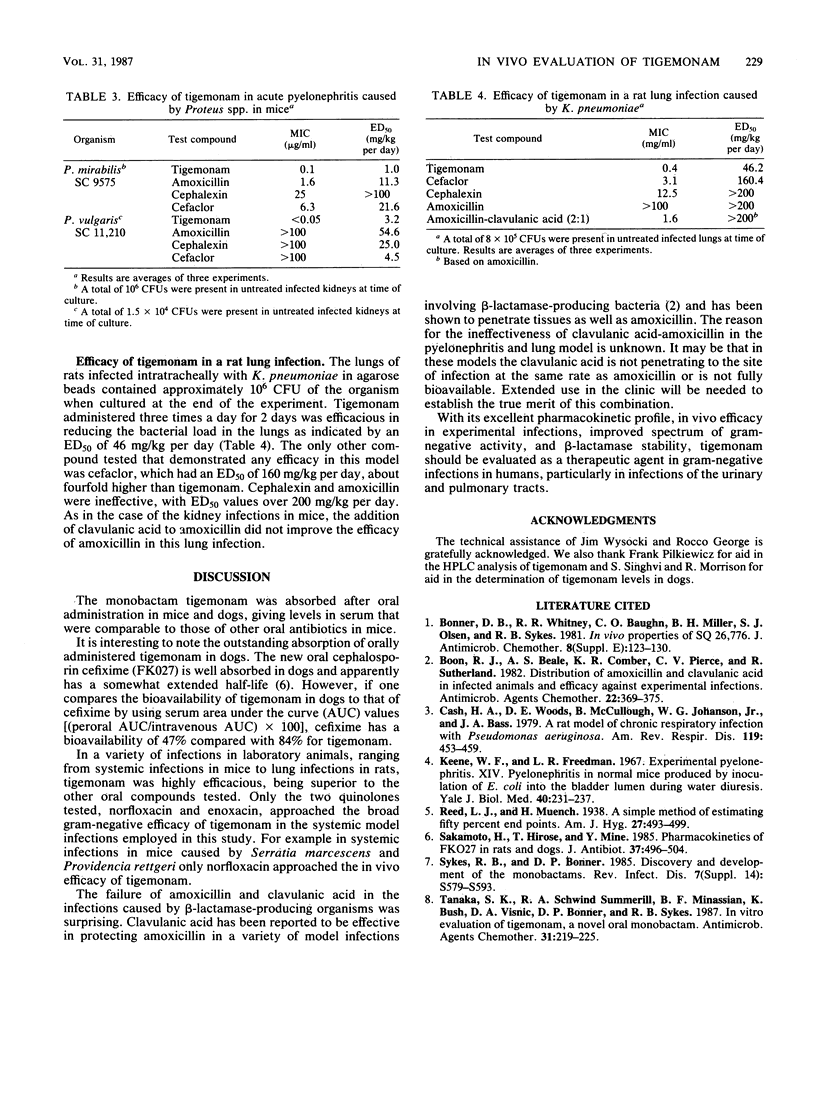
Tigemonam, a new monobactam with excellent activity against gram-negative bacteria, was evaluated for in vivo efficacy and absorption after oral administration to laboratory animals. Tigemonam is absorbed when administered orally to mice and dogs. In a variety of gram-negative systemic infections in mice, orally administered tigemonam was efficacious in all infections studied. Comparison drugs such as amoxicillin, cephalexin, and cefaclor were less efficacious, especially in infections caused by beta-lactamase-producing organisms. In localized infections, tigemonam also demonstrated excellent in vivo activity. In acute pyelonephritis in mice caused by Escherichia coli or Proteus sp., tigemonam was very effective. In a rat lung model with Klebsiella pneumoniae, tigemonam was active with a median effective dose of 46 mg/kg compared with 160 mg/kg for cefaclor and over 200 mg/kg for amoxicillin. Tigemonam was well absorbed in laboratory animals and with its excellent gram-negative spectrum of activity should prove of value in oral antibiotic therapy in humans.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner D. P., Whitney R. R., Baughn C. O., Miller B. H., Olsen S. J., Sykes R. B. In-vivo properties of SQ 26,776. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):123–130. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon R. J., Beale A. S., Comber K. R., Pierce C. V., Sutherland R. Distribution of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid in infected animals and efficacy against experimental infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):369–375. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash H. A., Woods D. E., McCullough B., Johanson W. G., Jr, Bass J. A. A rat model of chronic respiratory infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Mar;119(3):453–459. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.3.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane W. F., Freedman L. R. Experimental pyelonephritis. XIV. Pyelonephritis in normal mice produced by inoculation of E. coli into the bladder lumen during water diuresis. Yale J Biol Med. 1967 Dec;40(3):231–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto H., Hirose T., Mine Y. Pharmacokinetics of FK027 in rats and dogs. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1985 Apr;38(4):496–504. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.38.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Bonner D. P. Discovery and development of the monobactams. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Nov-Dec;7 (Suppl 4):S579–S593. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.supplement_4.s579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S. K., Summerill R. A., Minassian B. F., Bush K., Visnic D. A., Bonner D. P., Sykes R. B. In vitro evaluation of tigemonam, a novel oral monobactam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):219–225. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


