Abstract
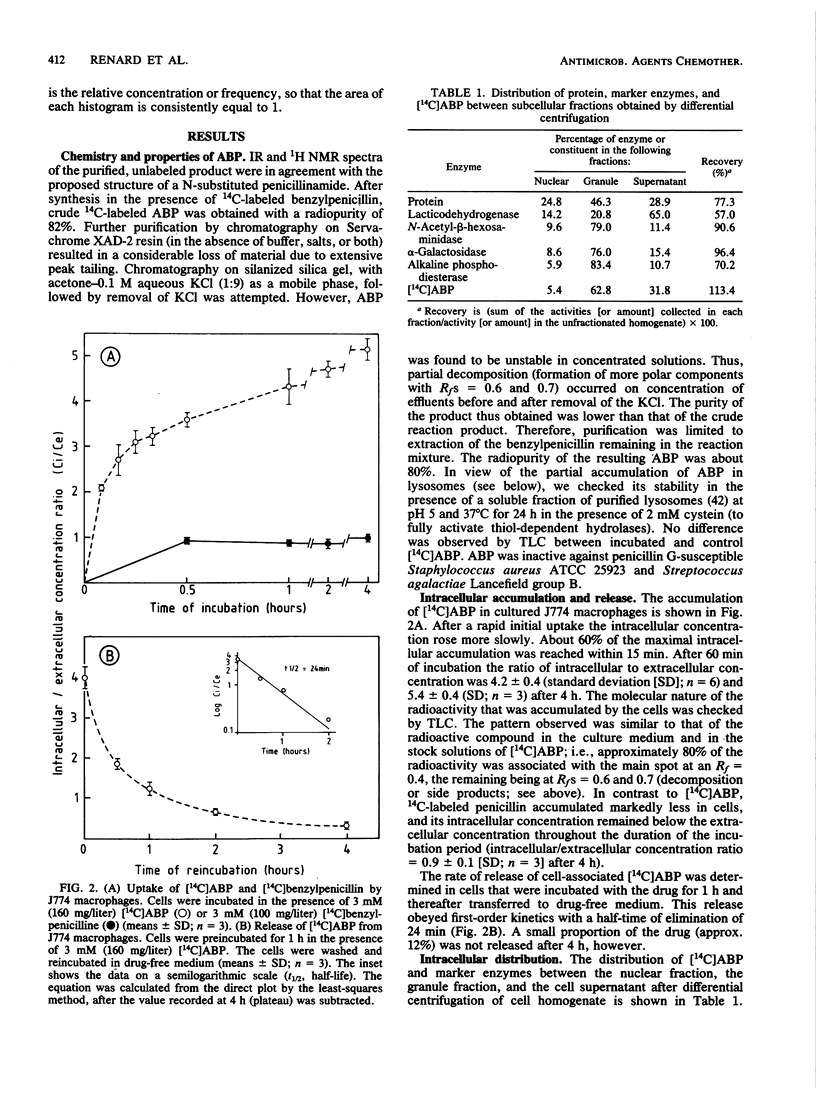
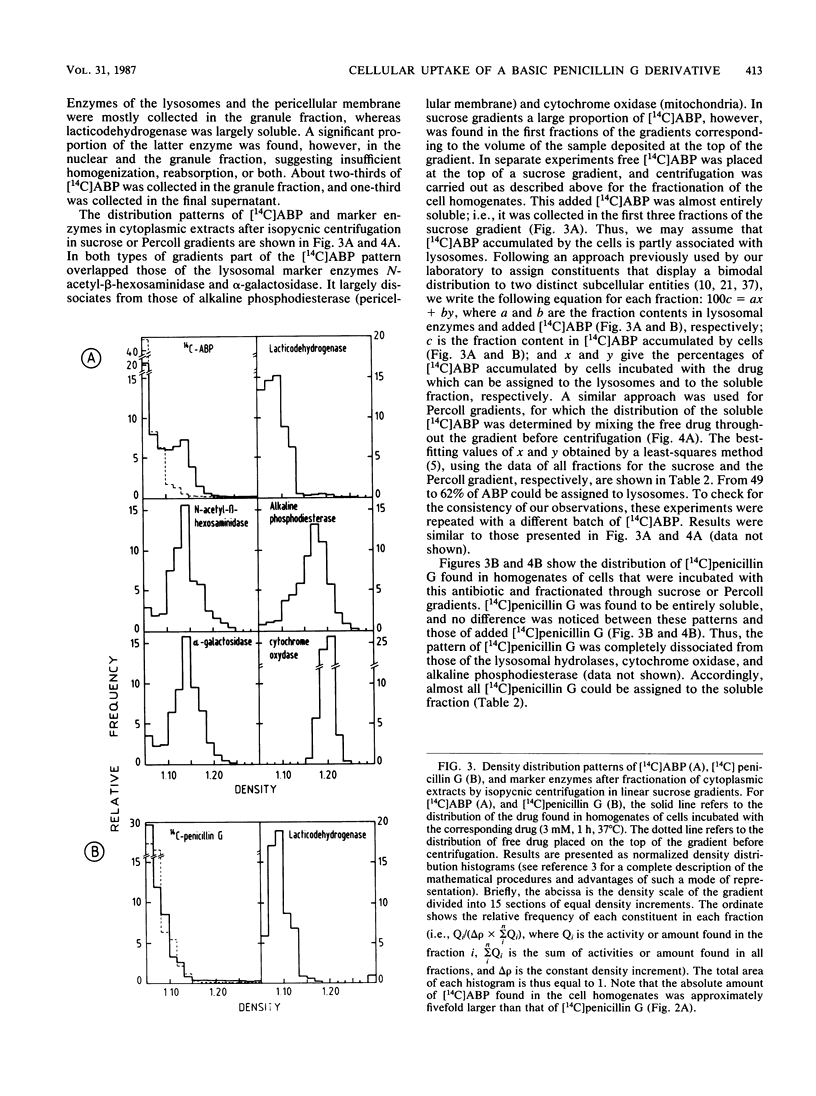
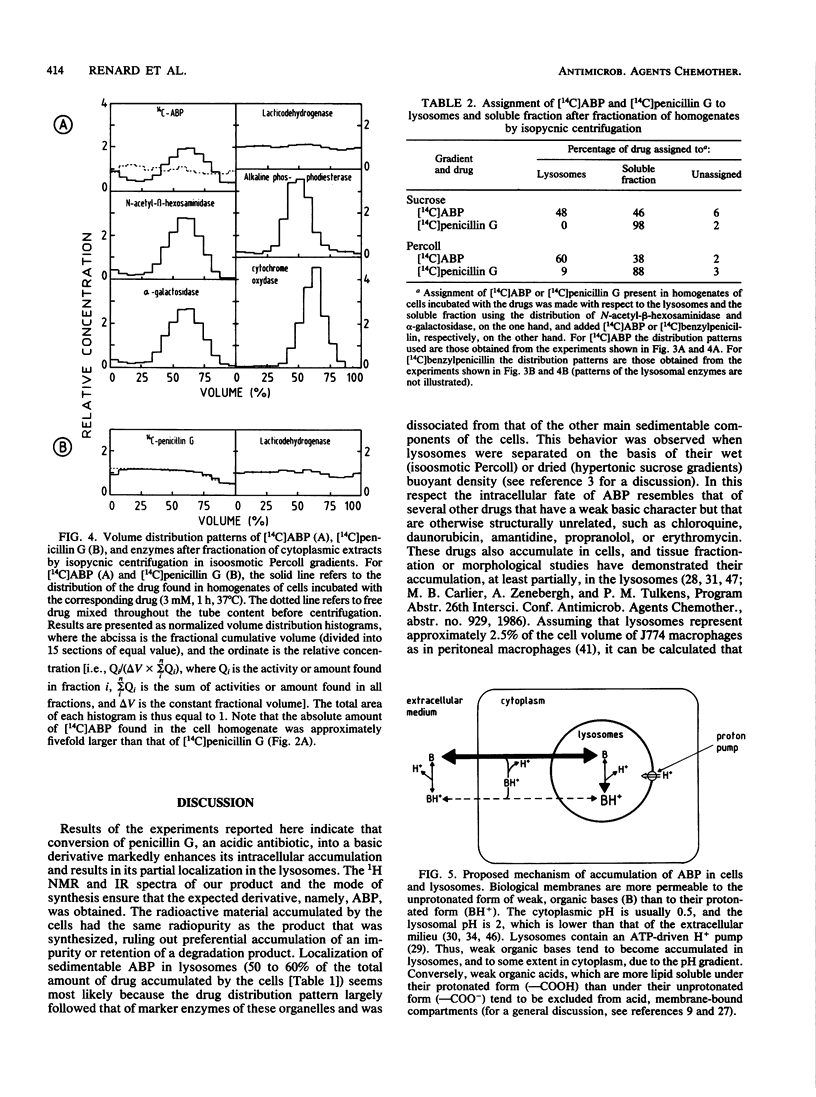
beta-Lactam antibiotics do not accumulate in phagocytes, probably because of their acidic character. We therefore synthesized a basic derivative of penicillin G, namely, 14C-labeled N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)benzylpenicillinamide (ABP), and studied its uptake and subcellular localization in J774 macrophages compared with that of 14C-labeled penicillin G. Whereas the intracellular concentration (Ci) of penicillin G remained lower than its extracellular concentration (Ce), ABP reached a Ci/Ce ratio of 4 to 5. Moreover, approximately 50% of intracellular ABP was found associated with lysosomes after isopycnic centrifugation of cell homogenates in isoosmotic Percoll or hyperosmotic sucrose gradients. The behavior of ABP was thus partly consistent with the model of de Duve et al. (C. de Duve, T. de Barsy, B. Poole, A. Trovet, P. Tulkens, and A. Van Hoof, Biochem. Pharmacol. 23:2495-2531, 1974), in which they described the intralysosomal accumulation of weak organic bases in lysosomes. Although ABP is microbiologically inactive, our results show that beta-lactam antibiotics can be driven into cells by appropriate modification. Further efforts therefore may be warranted in the design of active compounds or prodrugs that may prove useful in the chemotherapy of intracellular infections.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. W., Good R. A. Effect of antibiotics on the bactericidal activity of human leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jun;71(6):971–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaufay H., Jacques P., Baudhuin P., Sellinger O. Z., Berthet J., De Duve C. Tissue fractionation studies. 18. Resolution of mitochondrial fractions from rat liver into three distinct populations of cytoplasmic particles by means of density equilibration in various gradients. Biochem J. 1964 Jul;92(1):184–205. doi: 10.1042/bj0920184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Percival A. Penetration of antimicrobials into tissue culture cells and leucocytes. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):251–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. G., Beaufay H., Nyssens-Jadin M. Analytical fractionation of mouse peritoneal macrophages: physical and biochemical properties of subcellular organelles from resident (unstimulated) and cultivated cells. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Aug;24(2):115–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., PRESSMAN B. C., GIANETTO R., WATTIAUX R., APPELMANS F. Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):604–617. doi: 10.1042/bj0600604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darte C., Beaufay H. Analytical subcellular fractionation of cultivated mouse resident peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Apr 1;157(4):1208–1228. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.4.1208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulis B. H., Wilson I. B. The uptake of amines by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 6;643(2):398–406. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. The binding of penicillin in relation to its cytotoxic action. III. The binding of penicillin by mammalian cells in tissue culture (HeLa and L strains). J Exp Med. 1954 Jul 1;100(1):117–124. doi: 10.1084/jem.100.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Bellahsène A. Antibiotic accumulation in human polymorphonuclear leucocytes and lymphocytes. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1985;44:16–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., Boozer R. M., King-Thompson N. L. Antibiotic uptake by alveolar macrophages of smokers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):42–45. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Quie P. G., Windhorst D. B., Pollara B., Good R. A. Protection of phagocytized bacteria from the killing action of antibiotics. Nature. 1966 Jun 11;210(5041):1131–1132. doi: 10.1038/2101131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of microorganisms. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):104–123. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs R. F., Wilson C. B., Laxton J. G., Haas J. E., Smith A. L. Cellular uptake and intracellular activity of antibiotics against Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):152–159. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Styrt B. Clindamycin uptake by human neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1981 Nov;144(5):472–479. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.5.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krisans S. K., Mortensen R. M., Lazarow P. B. Acyl-CoA synthetase in rat liver peroxisomes. Computer-assisted analysis of cell fractionation experiments. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9599–9607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange A., Assmann G. Penetration von Penicillin G und Ampicillin in Mäusefibroblasten (Earle's strain L). Auswirkungen von Temperatur und Serumgehalt des Nährmediums. Z Med Mikrobiol Immunol. 1966;153(1):60–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILNE M. D., SCRIBNER B. H., CRAWFORD M. A. Non-ionic diffusion and the excretion of weak acids and bases. Am J Med. 1958 May;24(5):709–729. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90376-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L. Interaction of intraleukocytic bacteria and antibiotics. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1673–1679. doi: 10.1172/JCI107348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. R., Johnson P., Miller M. F. Uptake, accumulation, and egress of erythromycin by tissue culture cells of human origin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):314–319. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. F., Martin J. R., Johnson P., Ulrich J. T., Rdzok E. J., Billing P. Erythromycin uptake and accumulation by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and efficacy of erythromycin in killing ingested Legionella pneumophila. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):714–718. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel G., Peterson C., Trouet A., Tulkens P. Uptake and subcellular localization of daunorubicin and adriamycin in cultured fibroblasts. Eur J Cancer. 1978 Apr;14(4):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(78)90206-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Moriyama Y., Takano T. Identification and characterization of a proton pump on lysosomes by fluorescein-isothiocyanate-dextran fluorescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2758–2762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Poole B. Cytoplasmic vacuolation of mouse peritoneal macrophages and the uptake into lysosomes of weakly basic substances. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):656–664. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Poole B. Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3327–3331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokesch R. C., Hand W. L. Antibiotic entry into human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Mar;21(3):373–380. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Prichard J., Cohn M. Reticulum cell sarcoma: an effector cell in antibody-dependent cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):898–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reijngoud D. J., Tager J. M. The permeability properties of the lysosomal membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 14;472(3-4):419–449. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(77)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renard C., Michel A., Tulkens P. M. Hydrolysis of Pro-Ala dipeptides by lysosomal hydrolases. Models for the study of lysosomotropic amino acid prodrugs of penicillins. J Med Chem. 1986 Jul;29(7):1291–1293. doi: 10.1021/jm00157a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELLINGER O. Z., BEAUFAY H., JACQUES P., DOYEN A., DE DUVE C. Tissue fractionation studies. 15. Intracellular distribution and properties of beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase and beta-galactosidase in rat liver. Biochem J. 1960 Mar;74:450–456. doi: 10.1042/bj0740450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez M. S., Ford C. W., Yancey R. J., Jr Evaluation of antibacterial agents in a high-volume bovine polymorphonuclear neutrophil Staphylococcus aureus intracellular killing assay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):634–638. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider Y. J., Tulkens P., de Duve C., Trouet A. Fate of plasma membrane during endocytosis. I. Uptake and processing of anti-plasma membrane and control immunoglobulins by cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):449–465. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:669–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solberg C. O., Hellum K. B. Protection of phagocytosed bacteria against antimicrobial agents. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):246–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Brodie S. E., Cohn Z. A. Membrane flow during pinocytosis. A stereologic analysis. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):665–687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trouet A. Isolation of modified liver lysosomes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:323–329. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulkens P., Beaufay H., Trouet A. Analytical fractionation of homogenates from cultured rat embryo fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):383–401. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulkens P., Trouet A. The uptake and intracellular accumulation of aminoglycoside antibiotics in lysosomes of cultured rat fibroblasts. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978 Feb 15;27(4):415–424. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell W. J., Bates R. G. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1969 Apr;49(2):285–329. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1969.49.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wibo M., Poole B. Protein degradation in cultured cells. II. The uptake of chloroquine by rat fibroblasts and the inhibition of cellular protein degradation and cathepsin B1. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):430–440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Duve C., de Barsy T., Poole B., Trouet A., Tulkens P., Van Hoof F. Commentary. Lysosomotropic agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Sep 15;23(18):2495–2531. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


