Abstract
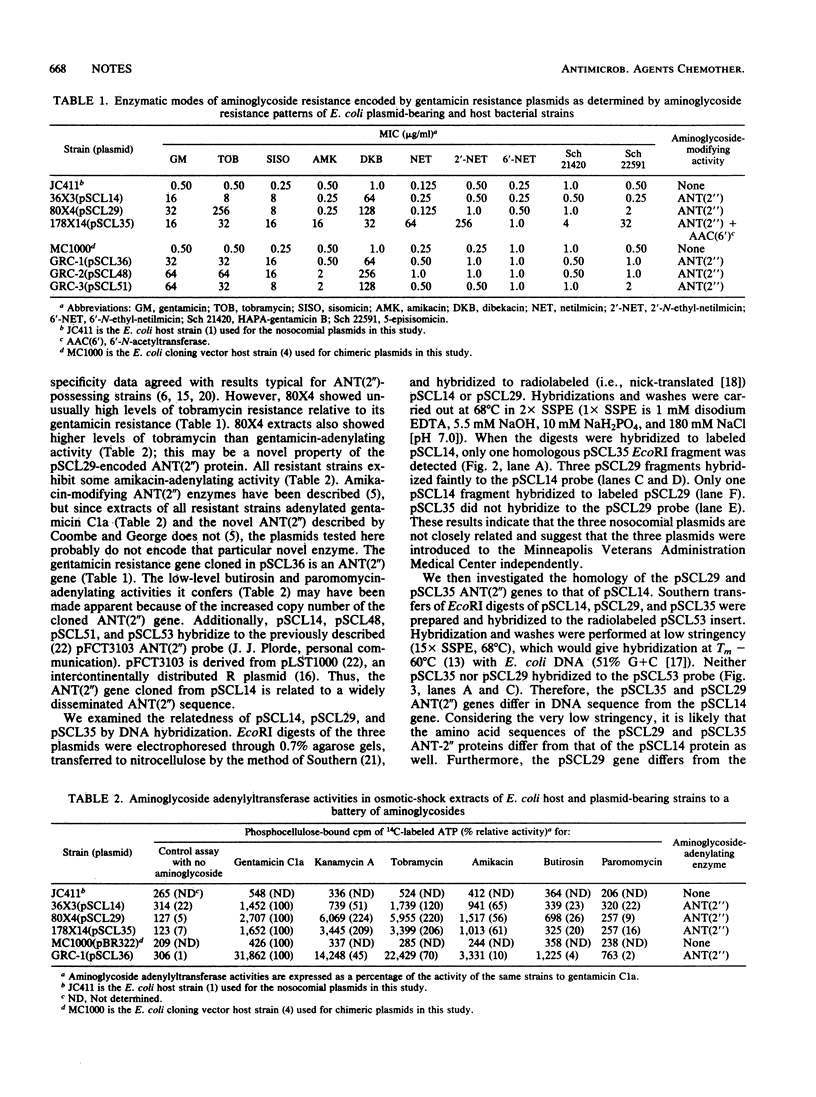
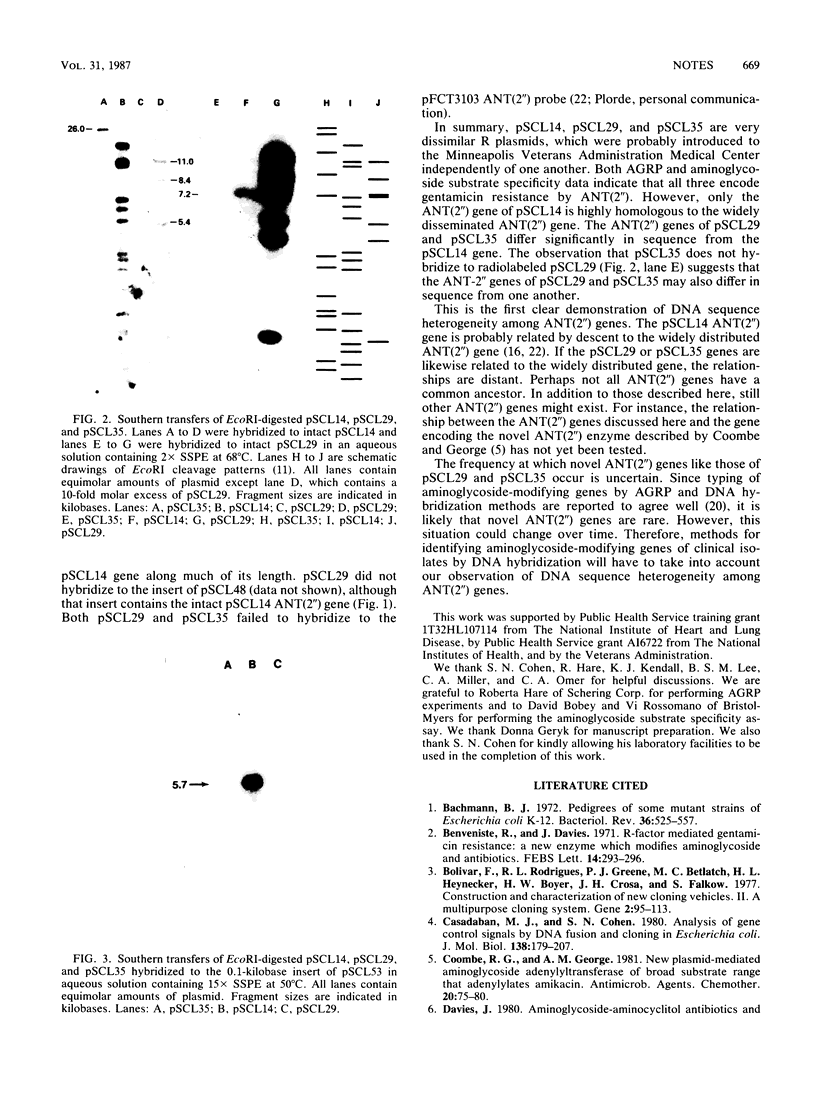
Biochemical and phenotypic assays indicate that three enterobacterial R plasmids isolated in a single hospital encode 2''-O-adenylyltransferase [ANT(2'')], and an ANT(2'')-specific probe was developed from one plasmid. Southern hybridization revealed the three plasmids to be unrelated and, further, showed their ANT(2'')-encoding genes to be different.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R., Davies J. R-factor mediated gentamicin resistance: A new enzyme which modifies aminoglycoside antibiotics. FEBS Lett. 1971 May 20;14(5):293–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombe R. G., George A. M. New plasmid-mediated aminoglycoside adenylyltransferase of broad substrate range that adenylylates amikacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):75–80. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Smith D. I. Plasmid-determined resistance to antimicrobial agents. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:469–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.002345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerding D. N., Buxton A. E., Hughes R. A., Cleary P. P., Arbaczawski J., Stamm W. E. Nosocomial multiply resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: epidemiology of an outbreak of apparent index case origin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):608–615. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. J., Dowding J. E. Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:611–628. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Gerding D. N., Cleary P. P. Hospital distribution, persistence, and reintroduction of related gentamicin R plasmids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):654–659. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Gerding D. N., Cleary P. P. Plasmid macroevolution in a nosocomial environment: demonstration of a persistent molecular polymorphism and construction of a cladistic phylogeny on the basis of restriction data. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;194(1-2):173–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00383513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. F., Pla M. P., Mayer K. H., Kishi H., Gilleece E., Syvanen M., Hopkins J. D. Intercontinental spread of a new antibiotic resistance gene on an epidemic plasmid. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):87–88. doi: 10.1126/science.2994226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski P. L., Peterson B. C., Gerding D. N., Cleary P. P. Physical characterization of ten R plasmids obtained from an outbreak of nosocomial Klebsiella pneumoniae infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):616–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Kumada T., Hsieh W. C., Chung H. Y., Chong Y., Hare R. S., Miller G. H., Sabatelli F. J., Howard J. Comparison of aminoglycoside resistance patterns in Japan, Formosa, and Korea, Chile, and the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):282–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C., Gootz T. D., Gordon K. P., Tompkins L. S., Young S. A., Plorde J. J. Development of a DNA probe for the structural gene of the 2"-O-adenyltransferase aminoglycoside-modifying enzyme. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):678–687. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]