Abstract
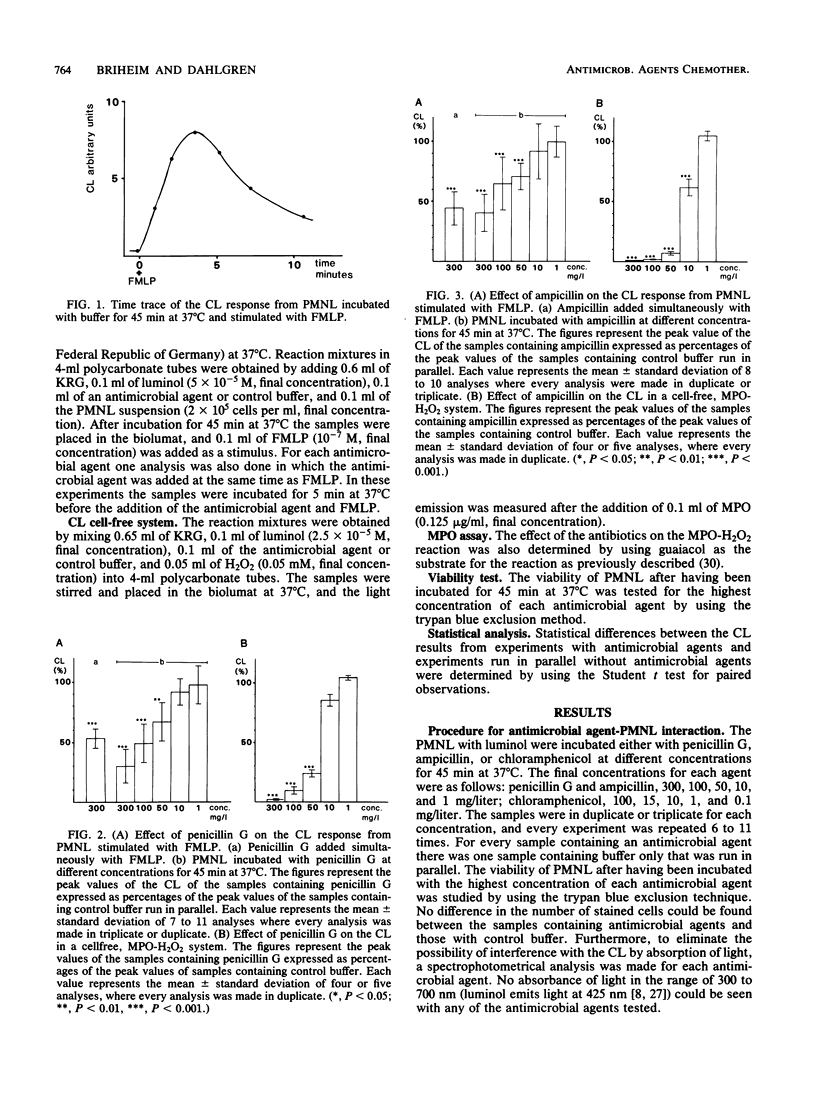
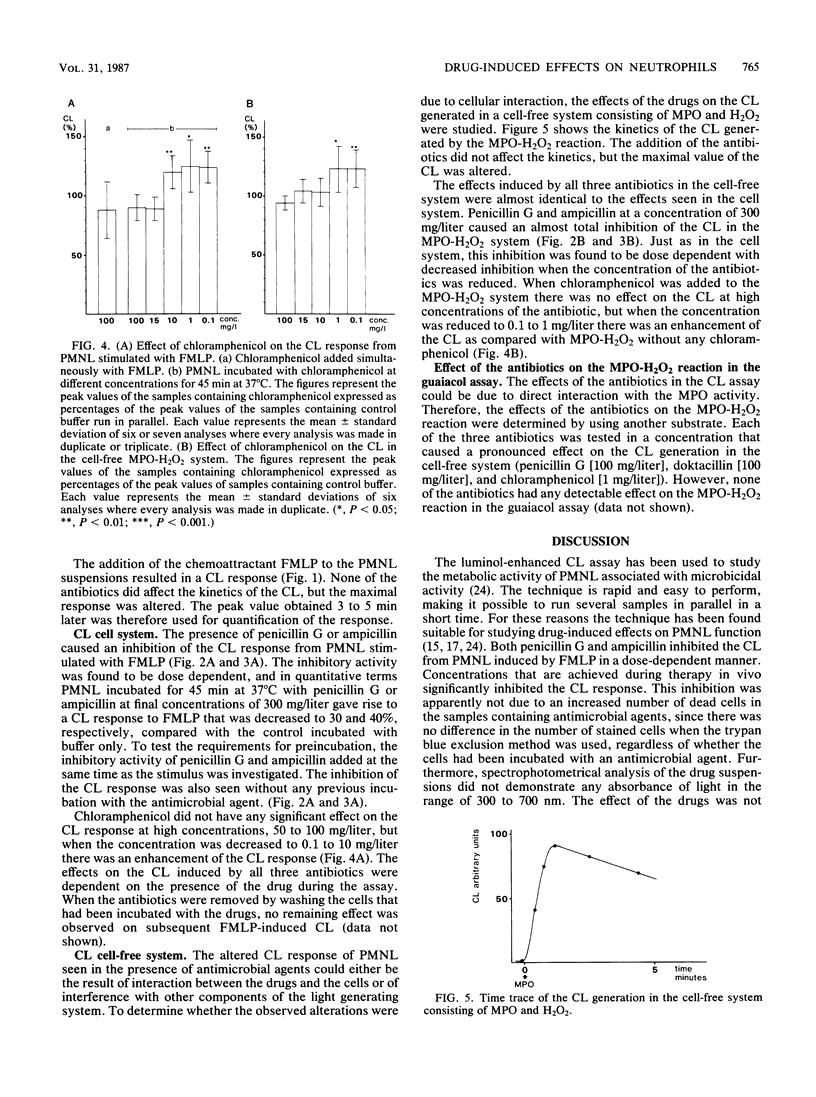
The effect of three antimicrobial agents, penicillin G, ampicillin, and chloramphenicol, on luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence of polymorphonuclear leukocytes stimulated by the chemoattractant formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine was studied. An inhibitory effect of penicillin G and of ampicillin was demonstrated, whereas chloramphenicol gave rise to an enhancement of the chemiluminescence response from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. These effects could be due to interaction between the drugs and the polymorphonuclear leukocytes, but they could also be the result of interference with the generation of light without any effect on the cells. Therefore, the effects of the same antimicrobial agents on the chemiluminescence generated from a cell-free system consisting of myeloperoxidase and hydrogen peroxide were investigated in parallel. The results obtained in the cell-free system were almost identical to those obtained in the cell system; i.e., penicillin G and ampicillin caused an inhibition and chloramphenicol caused an enhancement of the light emission. These results indicate that observed effects induced by drugs in a chemiluminescence assay are not necessarily due to interaction between the drug and polymorphonuclear leukocytes but may be caused by interference with other components of the assay. In view of these findings, the conflicting data reported in the literature on the effects of antimicrobial agents on phagocyte function are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C., Loose L. D. Phagocytic activation of a luminol-dependent chemiluminescence in rabbit alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C., Stjernholm R. L., Steele R. H. Evidence for the generation of an electronic excitation state(s) in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and its participation in bactericidal activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):679–684. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aniansson H., Stendahl O., Dahlgren C. Comparison between luminol- and lucigenindependent chemiluminescence of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1984 Dec;92(6):357–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb00100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender J. G., Van Epps D. E. Analysis of the bimodal chemiluminescence pattern stimulated in human neutrophils by chemotactic factors. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1062–1070. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1062-1070.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkstén B., Ray C., Quie P. G. Inhibition of human neutrophil chemotaxis and chemiluminescence by amphotericin B. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):315–317. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.315-317.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briheim G., Stendahl O., Dahlgren C. Intra- and extracellular events in luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.1-5.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. S., Shirley P. S., DeChatelet L. R. Further evaluation of luminol-enhanced luminescence in the diagnosis of disorders of leukocyte oxidative metabolism: role of myeloperoxidase. Clin Chem. 1983 Mar;29(3):513–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlgren C., Briheim G. Comparison between the luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and of the myeloperoxidase-HOOH system: influence of pH, cations and protein. Photochem Photobiol. 1985 May;41(5):605–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1985.tb03533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlgren C., Stendahl O. Effect of in vitro preincubation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes on formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced chemiluminescence. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):34–39. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.34-39.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlgren C., Stendahl O. Role of myeloperoxidase in luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):736–741. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.736-741.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R., Long G. D., Shirley P. S., Bass D. A., Thomas M. J., Henderson F. W., Cohen M. S. Mechanism of the luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1589–1593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R., Shirley P. S. Evaluation of chronic granulomatous disease by a chemiluminescence assay of microliter quantities of whole blood. Clin Chem. 1981 Oct;27(10):1739–1741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncker D., Ullmann U. Influence of various antimicrobial agents on the chemiluminescence of phagocytosing human granulocytes. Chemotherapy. 1986;32(1):18–24. doi: 10.1159/000238384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Cole P. J., Williams A. J., Hastings M. The measurement of opsonic and phagocytic function by Luminol-dependent chemiluminescence. Immunology. 1980 Sep;41(1):67–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden H., Hong J. J., Ogra P. L. In-vivo effects of clindamycin on neutrophil function--a preliminary report. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Oct;12 (Suppl 100):29–34. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_c.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glette J., Sandberg S., Hopen G., Solberg C. O. Influence of tetracyclines on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):354–357. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnarpe H., Belsheim J., Blomqvist C., Lundbäck A., Svensson A. C. The in-vitro influence of ceftazidime on host defence mechanisms. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Apr;13(4):369–375. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.4.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings M. J., Petricevic I., Williams A. J., Cole P. J., Easmon C. S. The effect of culture media on the production and measurement of luminol-dependent chemiluminescence. Br J Exp Pathol. 1982 Apr;63(2):147–153. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser W. E., Jr, Remington J. S. Effect of antibiotics on the immune response. Am J Med. 1982 May;72(5):711–716. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90534-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt M. E., Ryall M. E., Campbell A. K. Albumin inhibits human polymorphonuclear leucocyte luminol-dependent chemiluminescence: evidence for oxygen radical scavenging. Br J Exp Pathol. 1984 Apr;65(2):231–241. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horan T. D., English D., McPherson T. A. Association of neutrophil chemiluminescence with microbicidal activity. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Feb;22(2):259–269. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höger P. H., Vosbeck K., Seger R., Hitzig W. H. Uptake, intracellular activity, and influence of rifampin on normal function of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):667–674. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Wokalek H., Schöpf E., Eggert H., Ernst M., Rietschel E. T., Fischer H. Measurement of chemiluminescence in freshly drawn human blood. I. Role of granulocytes, platelets, and plasma factors in zymosan-induced chemiluminescence. Klin Wochenschr. 1981 Mar 2;59(5):203–221. doi: 10.1007/BF01476577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell L. A. Effects of antimicrobial and antineoplastic drugs on the phagocytic and microbicidal function of the polymorphonuclear leukocyte. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 May-Jun;4(3):683–697. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.3.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. R., Putman M., Greenberg S. B., Wallace R. J., Jr, Wilson S. Z. Serial studies of leukocyte chemiluminescence: lack of effect of macrolide antibiotic therapy. J Med. 1980;11(1):39–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRipley R. J., Sbarra A. J. Role of the phagocyte in host-parasite interactions. XII. Hydrogen peroxide-myeloperoxidase bactericidal system in the phagocyte. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1425–1430. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1425-1430.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleske J. M., de la Cruz A., Ahdieh H., Sorvino D., La Braico J., Cooper R., Singh R., Lin R., Minnefor A. Effects of antibiotics on polymorphonuclear leukocyte chemiluminescence and chemotaxis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Oct;12 (Suppl 100):35–38. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_c.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scevola D., Concia E., Tinelli M., Benzi R., Monzillo V., Cremonesi G. Chemiluminescence, phagocytosis, chemotaxis and killing activity of human leukocytes exposed to Clindamycin. Microbiologica. 1986 Apr;9(2):209–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. P., Remington J. S. Effect of antimicrobial agents on chemiluminescence of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes in response to phagocytosis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Dec;10(6):505–515. doi: 10.1093/jac/10.6.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Winston D. J., Van Dyke K. In vitro evaluation of opsonic and cellular granulocyte function by luminol-dependent chemiluminescence: utility in patients with severe neutropenia and cellular deficiency states. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):41–51. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.41-51.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. D., Davis D., Thrupp L. D. Effect of antimicrobial agents on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte microbicidal function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):15–20. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



