Abstract
Kinetoplastid hemoflagellates are sensitive to growth inhibition by various purine analogs. In this study the activities of 9-deazainosine (9-DINO), formycin B, and sinefungin were compared in experimental murine Trypanosoma brucei subsp. brucei infections, both singly and in combination with the ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor DL-alpha-difluoromethylornithine (DFMO, eflornithine). Used singly, all of the purine analogs were able to suppress an acute T. brucei subsp. brucei infection. 9-DINO and formycin B were the most active. None of the purine analogs was curative when used singly against a strain causing chronic central nervous system infection. 9-DINO was highly effective when used in combination with DFMO in curing this central nervous system infection and another more stringent experimental infection. Neither sinefungin nor formycin B was active in combination with DFMO in curing the central nervous system experimental infection. 9-DINO was metabolized to phosphorylated derivatives of 9-deazaadenosine and 9-deazaguanosine by bloodstream trypomastigotes, but not by murine erythrocyte suspensions or kidney or liver homogenates--a potential rationale for the selectivity of the analog. These studies indicate that 9-DINO is a potent, nontoxic purine analog which, in combination with DFMO, is capable of late-stage cures of African trypanosomiasis.
Full text
PDF
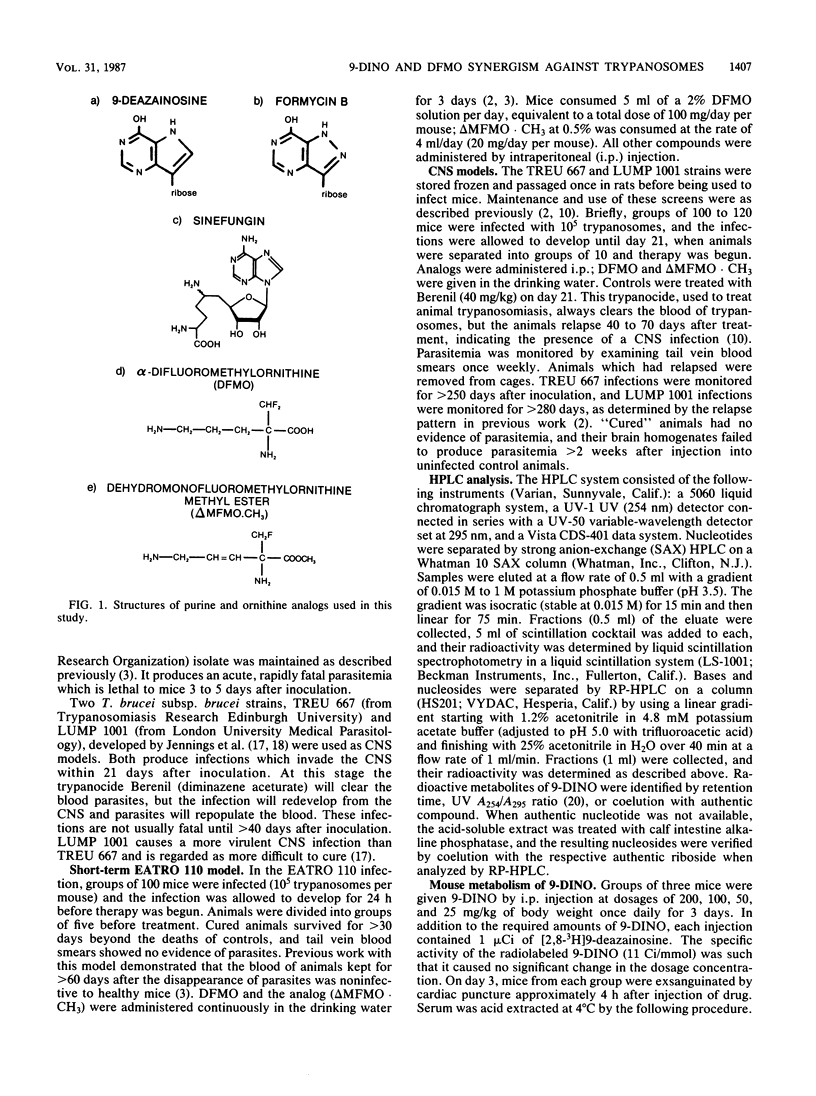
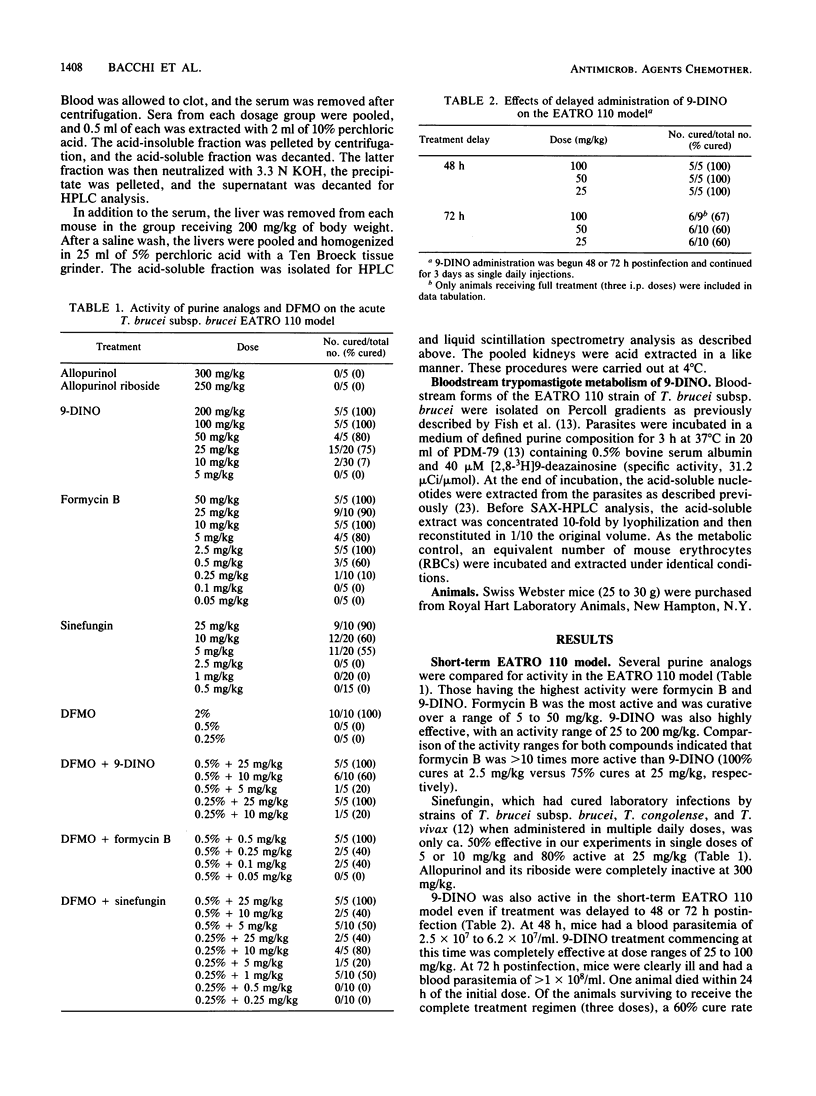
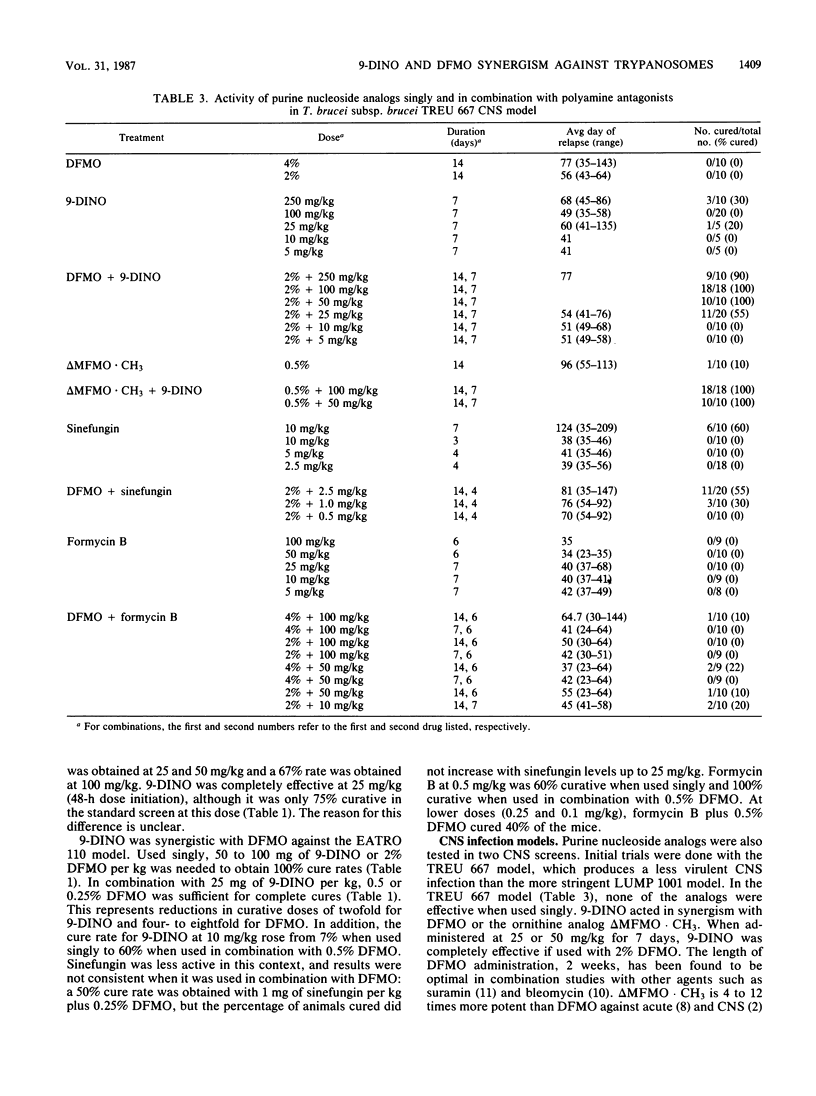
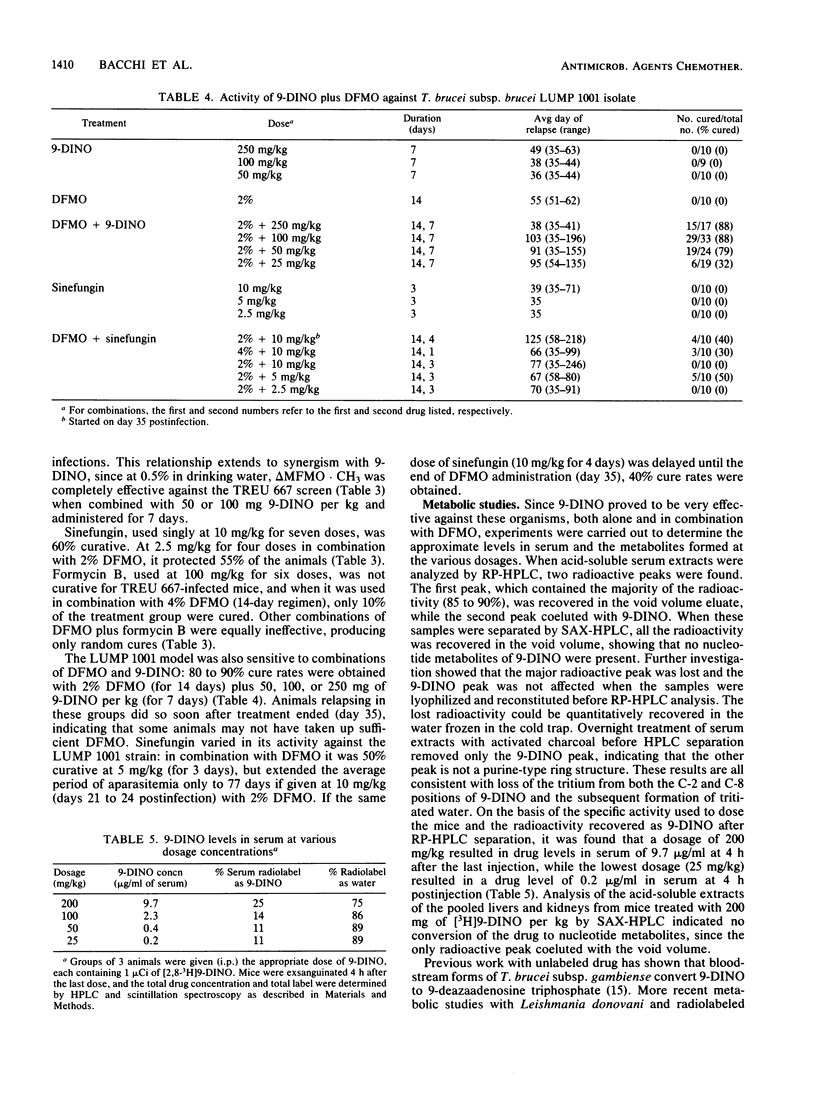



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacchi C. J., Garofalo J., Mockenhaupt D., McCann P. P., Diekema K. A., Pegg A. E., Nathan H. C., Mullaney E. A., Chunosoff L., Sjoerdsma A. In vivo effects of alpha-DL-difluoromethylornithine on the metabolism and morphology of Trypanosoma brucei brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Mar;7(3):209–225. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacchi C. J., Nathan H. C., Hutner S. H., McCann P. P., Sjoerdsma A. Polyamine metabolism: a potential therapeutic target in trypanosomes. Science. 1980 Oct 17;210(4467):332–334. doi: 10.1126/science.6775372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berens R. L., Marr J. J., Brun R. Pyrazolopyrimidine metabolism in African trypanosomes: metabolic similarities to Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania spp. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1980 Apr;1(2):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(80)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman J. D., Hanson W. L., Lovelace J. K., Waits V. B., Jackson J. E., Chapman W. L., Jr, Klein R. S. Activity of purine analogs against Leishmania donovani in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jan;31(1):111–113. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman J. D., Lee L. S., Robins R. K., Revankar G. R. Activity of purine analogs against Leishmania tropica within human macrophages in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):233–236. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman J. D., Rainey P., Santi D. V. Metabolism of formycin B by Leishmania amastigotes in vitro. Comparative metabolism in infected and uninfected human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):252–257. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitonti A. J., Bacchi C. J., McCann P. P., Sjoerdsma A. Catalytic irreversible inhibition of Trypanosoma brucei brucei ornithine decarboxylase by substrate and product analogs and their effects on murine trypanosomiasis. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 May 15;34(10):1773–1777. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90648-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Chang K. P. Phosphorylation and anti-leishmanial activity of formycin B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun 16;100(3):1377–1383. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91976-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson A. B., Jr, Bacchi C. J., Mellow G. H., Nathan H. C., McCann P. P., Sjoerdsma A. Efficacy of combinations of difluoromethylornithine and bleomycin in a mouse model of central nervous system African trypanosomiasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5729–5733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson A. B., Jr, Bienen E. J., Bacchi C. J., McCann P. P., Nathan H. C., Hutner S. H., Sjoerdsma A. New drug combination for experimental late-stage African trypanosomiasis: DL-alpha-difluoromethylornithine (DFMO) with suramin. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Nov;33(6):1073–1077. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.1073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube D. K., Mpimbaza G., Allison A. C., Lederer E., Rovis L. Antitrypanosomal activity of sinefungin. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Jan;32(1):31–33. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish W. R., Looker D. L., Marr J. J., Berens R. L. Purine metabolism in the bloodstream forms of Trypanosoma gambiense and Trypanosoma rhodesiense. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 24;719(2):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish W. R., Marr J. J., Berens R. L., Looker D. L., Nelson D. J., LaFon S. W., Balber A. E. Inosine analogs as chemotherapeutic agents for African trypanosomes: metabolism in trypanosomes and efficacy in tissue culture. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):33–36. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer R. I., Lloyd L. S. Effects of 8-azaadenosine and formycin on cell lethality and the synthesis and methylation of nucleic acids in human colon carcinoma cells in culture. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Oct 15;31(20):3207–3214. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90551-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. W., Krenitsky T. A. Aldehyde oxidase from rabbit liver: specificity toward purines and their analogs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Nov 15;251(1):36–46. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings F. W., Gray G. D. Relapsed parasitaemia following chemotherapy of chronic T. brucei infections in mice and its relation to cerebral trypanosomes. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1983;7:147–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings F. W., Whitelaw D. D., Urquhart G. M. The relationship between duration of infection with Trypanosoma brucei in mice and the efficacy of chemotherapy. Parasitology. 1977 Oct;75(2):143–153. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000062284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenitsky T. A., Tuttle J. V., Cattau E. L., Jr, Wang P. A comparison of the distribution and electron acceptor specificities of xanthine oxidase and aldehyde oxidase. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1974 Dec 15;49(4):687–703. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(74)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFon S. W., Nelson D. J., Berens R. L., Marr J. J. Inosine analogs. Their metabolism in mouse L cells and in Leishmania donovani. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9660–9665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr J. J., Berens R. L., Cohn N. K., Nelson D. J., Klein R. S. Biological action of inosine analogs in Leishmania and Trypanosoma spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Feb;25(2):292–295. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.2.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr J. J., Berens R. L., Nelson D. J. Purine metabolism in Leishmania donovani and Leishmania braziliensis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 1;544(2):360–371. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann P. P., Bacchi C. J., Clarkson A. B., Jr, Bey P., Sjoerdsma A., Schecter P. J., Walzer P. D., Barlow J. L. Inhibition of polyamine biosynthesis by alpha-difluoromethylornithine in African trypanosomes and Pneumocystis carinii as a basis of chemotherapy: biochemical and clinical aspects. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Nov;35(6):1153–1156. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann P. P., Bacchi C. J., Clarkson A. B., Jr, Seed J. R., Nathan H. C., Amole B. O., Hutner S. H., Sjoerdsma A. Further studies on difluoromethylornithine in African trypanosomes. Med Biol. 1981 Dec;59(5-6):434–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal R. A., Croft S. L., Nelson D. J. Anti-leishmanial effect of allopurinol ribonucleoside and the related compounds, allopurinol, thiopurinol, thiopurinol ribonucleoside, and of formycin B, sinefungin and the lepidine WR6026. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1985;79(1):122–128. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(85)90255-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. J., Lafon S. W., Jones T. E., Spector T., Berens R. L., Marr J. J. The metabolism of formycin B in Leishmania donovani. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 16;108(1):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91873-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainey P., Garrett C. E., Santi D. V. The metabolism and cytotoxic effects of Formycin B in Trypanosoma cruzi. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Feb 15;32(4):749–752. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90511-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romijn J. C., Verkoelen C. F., Splinter T. A. Problems of pharmacokinetic studies on alpha-difluoromethylornithine in mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1987;19(1):30–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00296251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter P. J., Sjoerdsma A. Difiuoromethylornithine in the treatment of African trypanosomiasis. Parasitol Today. 1986 Aug;2(8):223–224. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(86)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjoerdsma A., Schechter P. J. Chemotherapeutic implications of polyamine biosynthesis inhibition. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1984 Mar;35(3):287–300. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1984.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T., Jones T. E., LaFon S. W., Nelson D. J., Berens R. L., Marr J. J. Monophosphates of formycin B and allopurinol riboside. Interactions with leishmanial and mammalian succino-AMP synthetase and GMP reductase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 May 15;33(10):1611–1617. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nieuwenhove S., Schechter P. J., Declercq J., Boné G., Burke J., Sjoerdsma A. Treatment of gambiense sleeping sickness in the Sudan with oral DFMO (DL-alpha-difluoromethylornithine), an inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase; first field trial. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1985;79(5):692–698. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(85)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


