Abstract
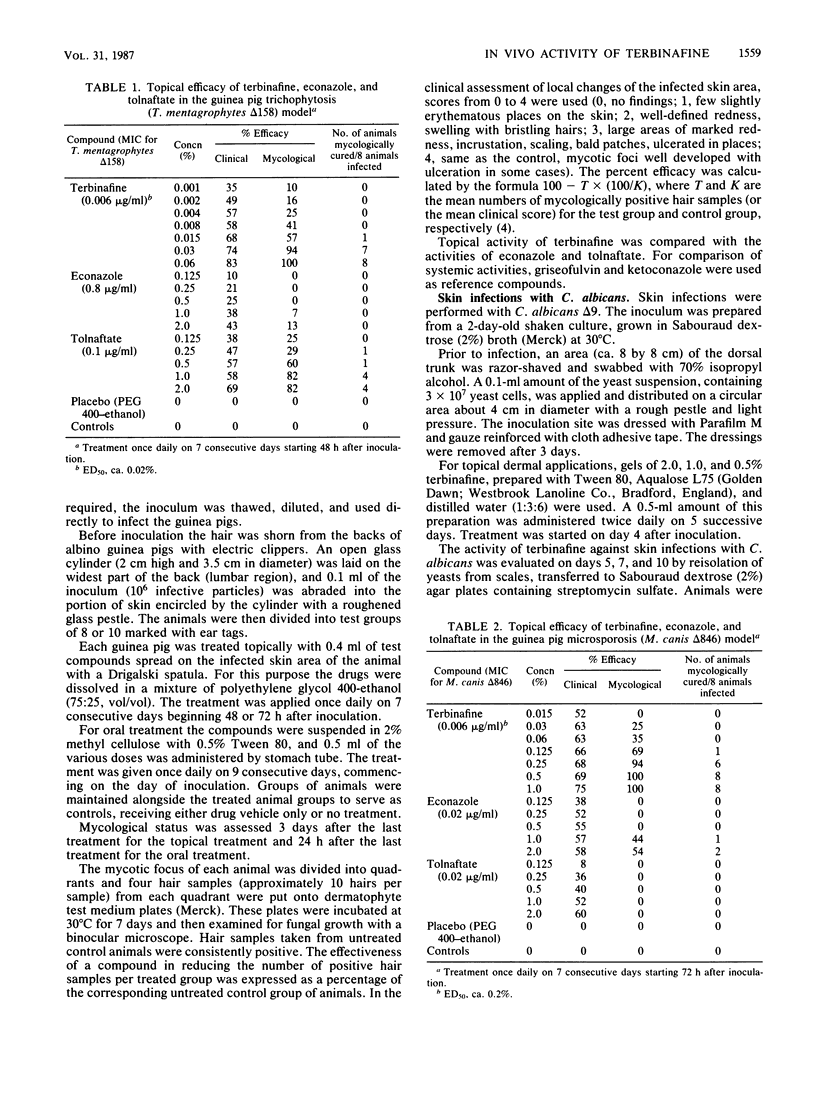
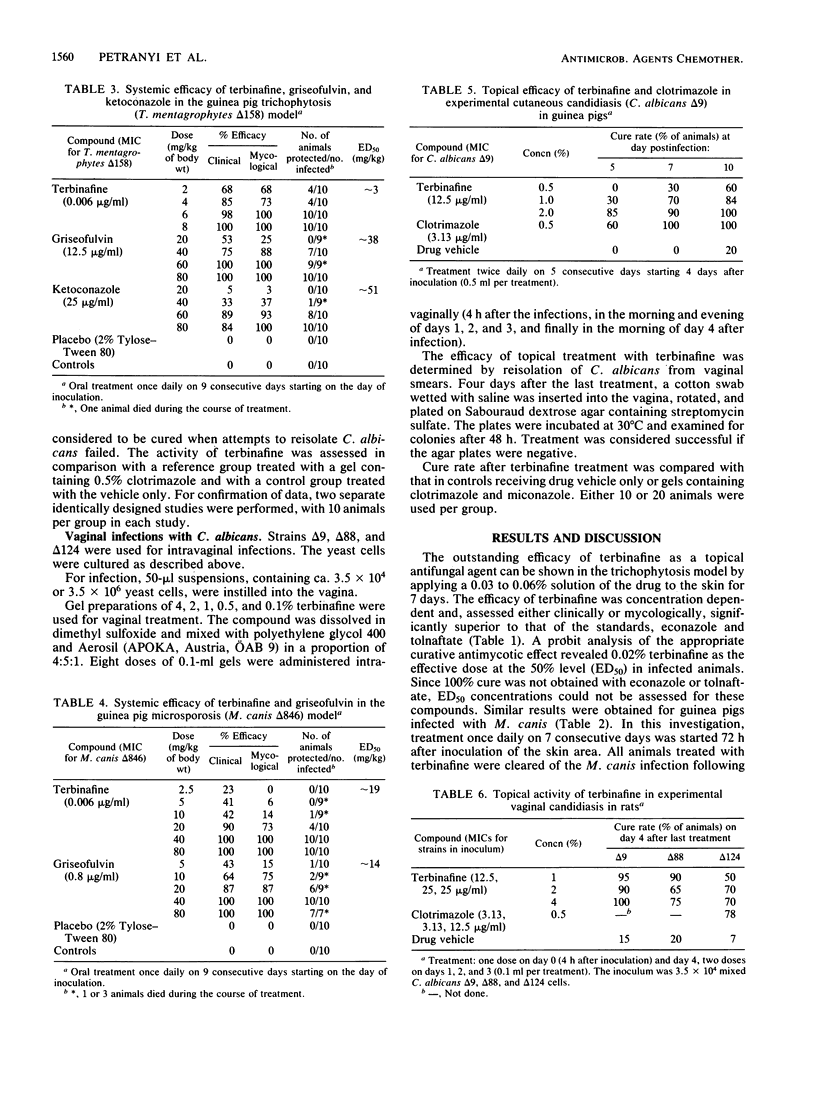
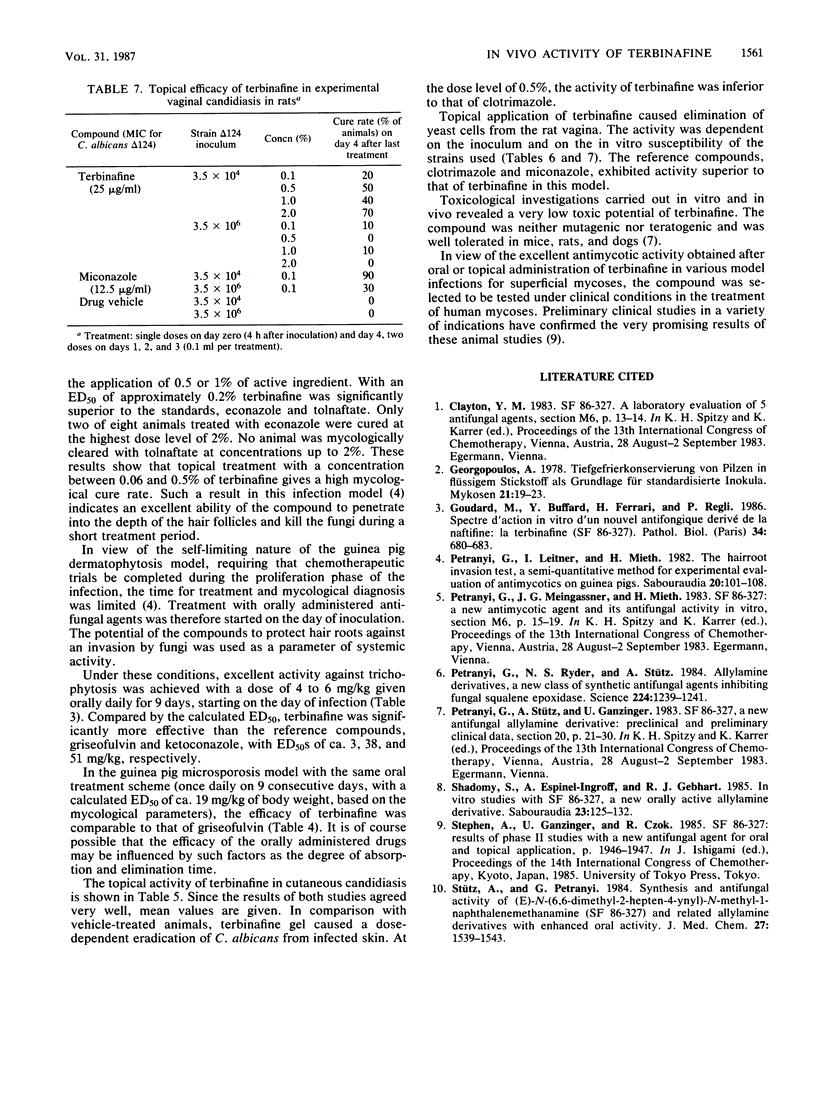
The allylamine derivative terbinafine is the first antifungal agent with primary fungicidal properties against dermatophytes which acts systemically after oral application as well as locally after topical application. Comparative oral studies carried out with griseofulvin and ketoconazole in model infections such as guinea pig trichophytosis and microsporosis revealed terbinafine to be superior to the reference compounds both clinically and mycologically. An excellent antimycotic activity of terbinafine was also demonstrable after topical treatment of guinea pig dermatophytoses caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes or Microsporum canis. Results of comparative chemotherapeutic studies carried out with econazole and tolnaftate demonstrated superior efficacy of terbinafine in the treatment of both trichophytosis and microsporosis. Skin infections of guinea pigs caused by Candida albicans and vaginal candidiasis in rats proved to be responsive to a topical application of terbinafine also. However, the reference compounds, clotrimazole and miconazole, exhibited activity superior to that of terbinafine in both models.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Georgopoulos A. Tiefgefriekonservierung von Pilzen in flüssigem Stickstoff als Grundlage für standardisierte Inokula. Mykosen. 1978 Jan;21(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudard M., Buffard Y., Ferrari H., Regli P. Spectre d'action in vitro d'un nouvel antifongique dérivé de la naftifine: la terbinafine (SF 86-327). Pathol Biol (Paris) 1986 Jun;34(5 Pt 2):680–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petranyi G., Leitner I., Mieth H. The "hair root invasion test", a semi-quantitative method for experimental evaluation of antimycotics in guinea-pigs. Sabouraudia. 1982 Jun;20(2):101–108. doi: 10.1080/00362178285380171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petranyi G., Ryder N. S., Stütz A. Allylamine derivatives: new class of synthetic antifungal agents inhibiting fungal squalene epoxidase. Science. 1984 Jun 15;224(4654):1239–1241. doi: 10.1126/science.6547247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadomy S., Espinel-Ingroff A., Gebhart R. J. In-vitro studies with SF 86-327, a new orally active allylamine derivative. Sabouraudia. 1985 Apr;23(2):125–132. doi: 10.1080/00362178585380201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stütz A., Petranyi G. Synthesis and antifungal activity of (E)-N-(6,6-dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ynyl)-N-methyl-1-naphtha lenemethanamine (SF 86-327) and related allylamine derivatives with enhanced oral activity. J Med Chem. 1984 Dec;27(12):1539–1543. doi: 10.1021/jm00378a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


