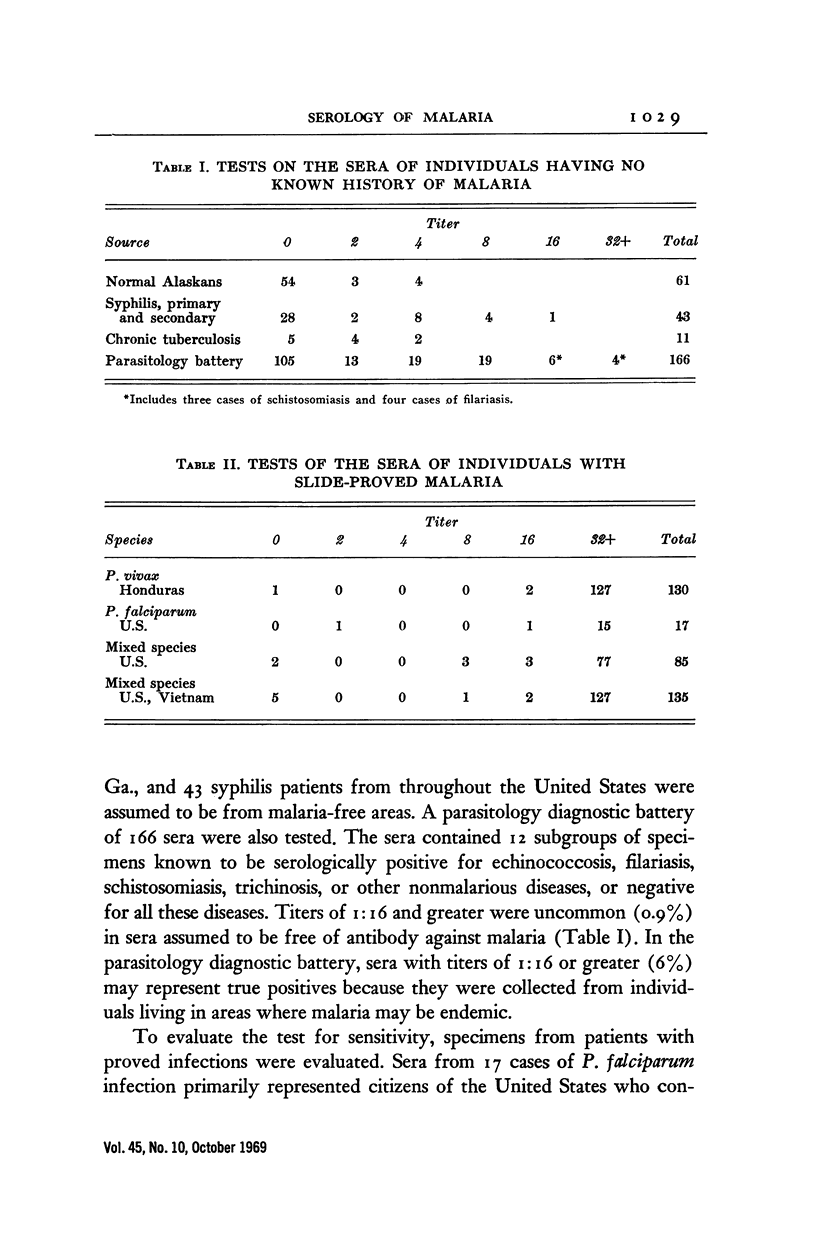
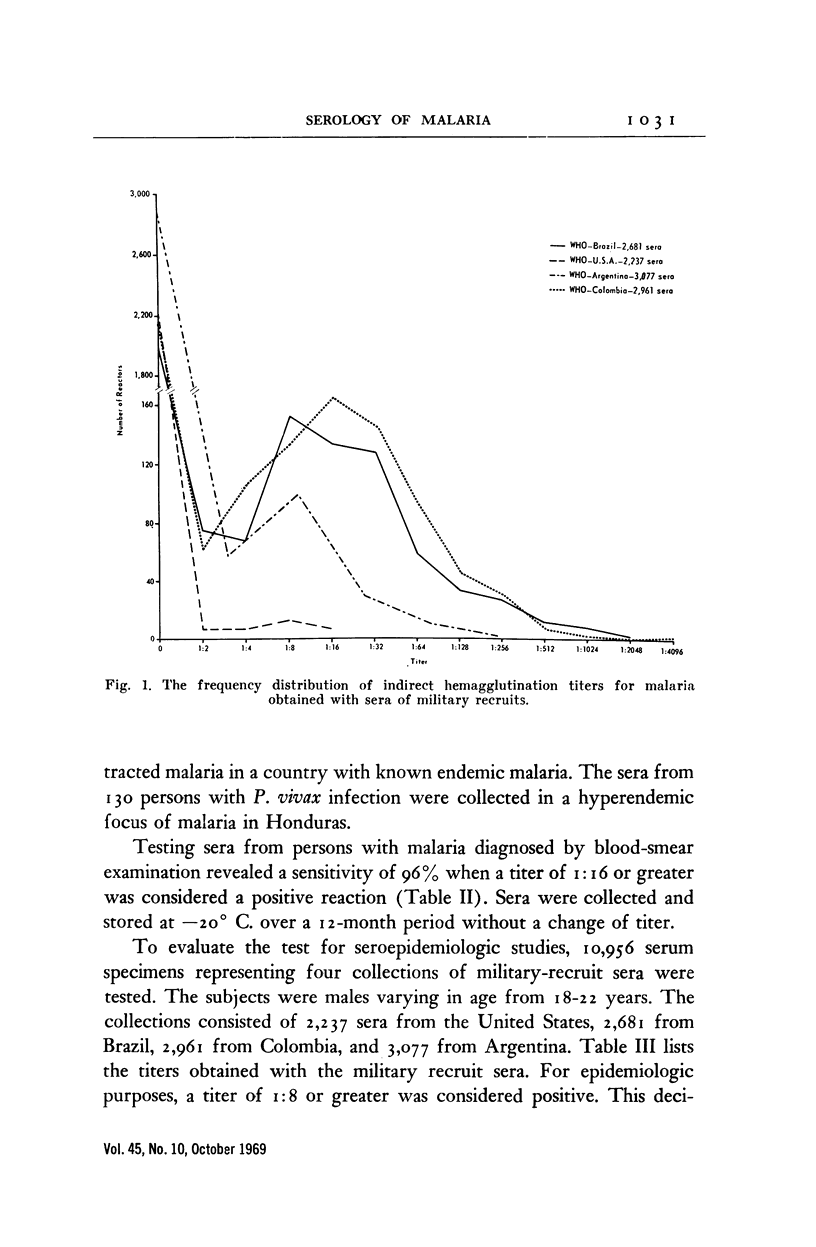
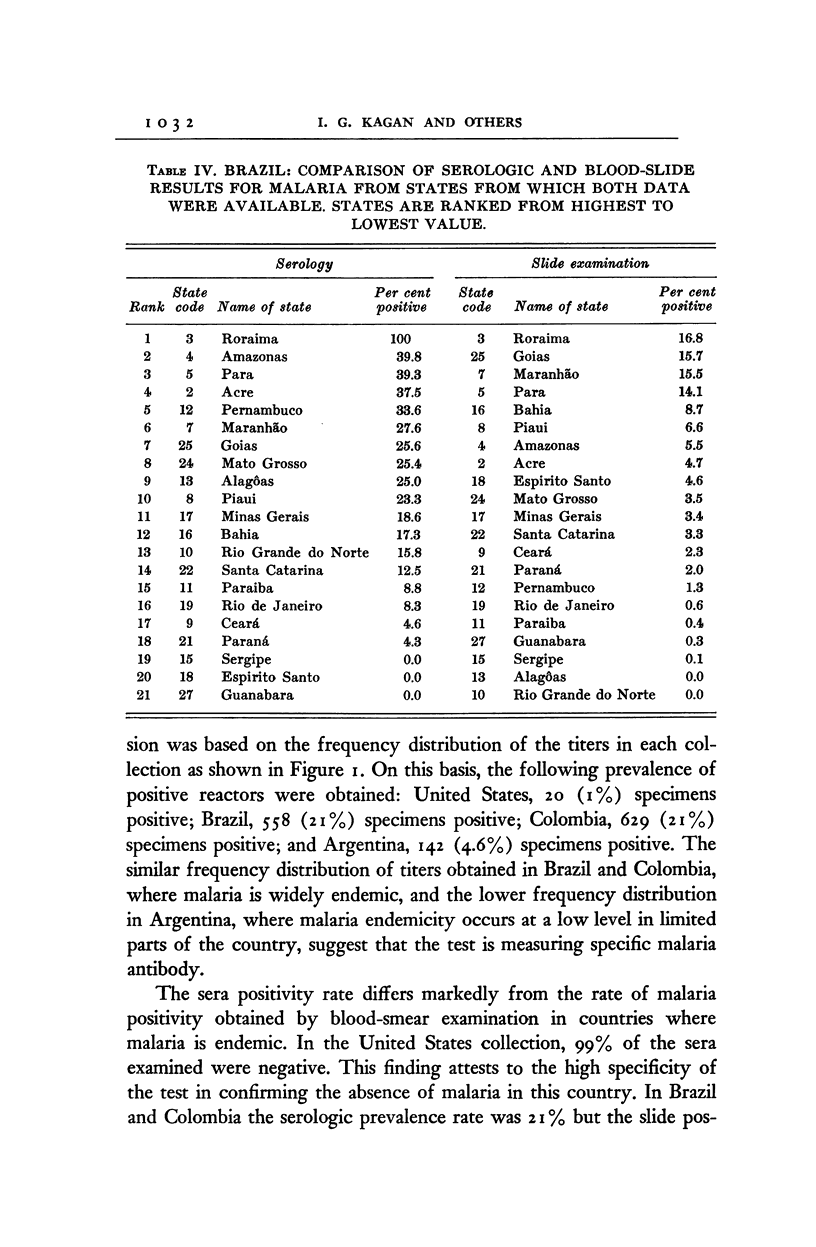
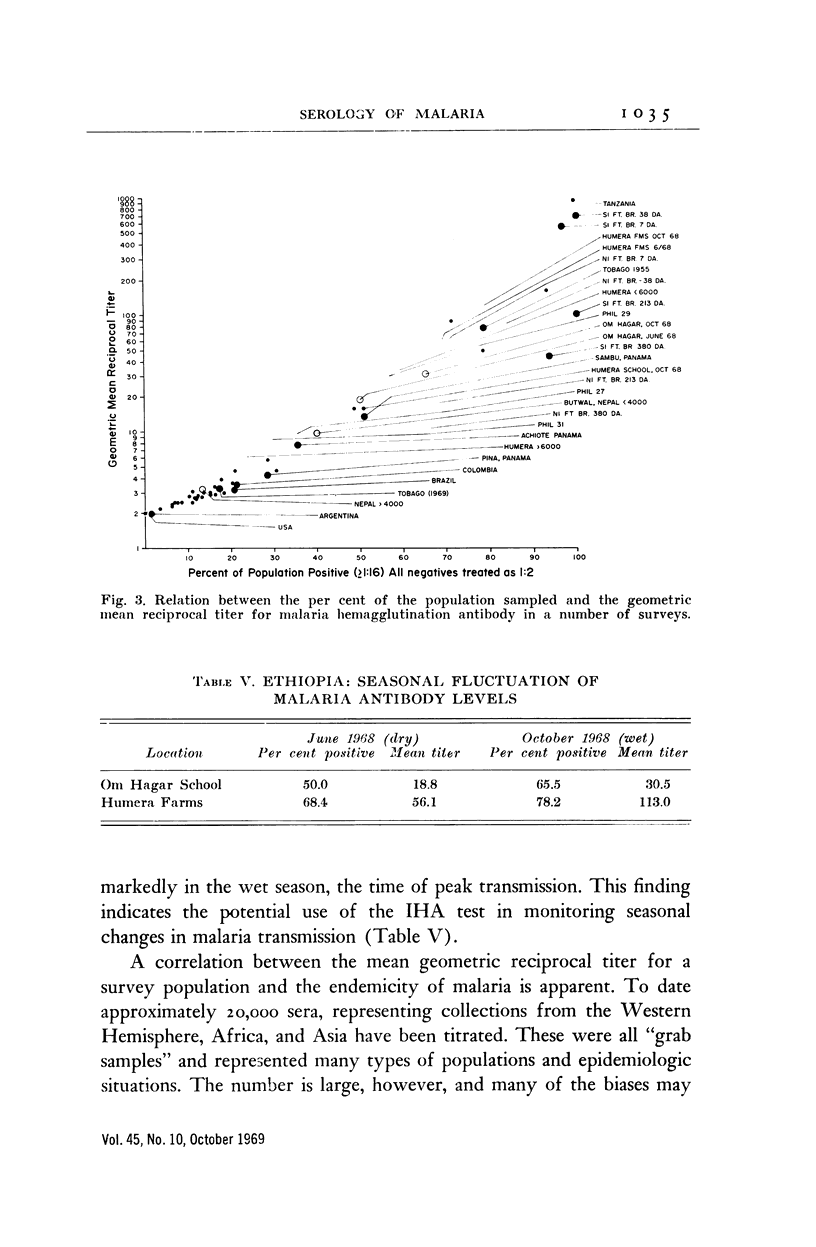
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bray R. S., el-Nahal H. M. Indirect haemagglutination test for malarial antibody. Nature. 1966 Oct 1;212(5057):83–83. doi: 10.1038/212083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS W. E., SKINNER J. C., GUINN E. G., DOBROVOLNY C. G., JONES F. E. FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY REACTIONS AGAINST SIX SPECIES OF SIMIAN MALARIA IN MONKEYS FROM INDIA AND MALAYSIA. J Parasitol. 1965 Feb;51:81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins W. E., Jeffery G. M., Guinn E., Skinner J. C. Fluorescent antibody studies in human malaria. IV. Cross-reactions between human and simian malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Jan;15(1):11–15. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins W. E., Skinner J. C., Coifman R. E. Fluorescent antibody studies in human malaria. V. Response of sera from Nigerians to five Plasmodium antigens. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1967 Sep;16(5):568–571. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1967.16.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuadrado R. R., Kagan I. G. The prevalence of antibodies to parasitic diseases in sera of young army recruits from the United States and Brazil. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Sep;86(2):330–340. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DESOWITZ R. S., SAAVE J. J. THE APPLICATION OF THE HAEMAGGLUTINATION TEST TO A STUDY OF THE IMMUNITY TO MALARIA IN PROTECTED AND UNPROTECTED POPULATION GROUPS IN AUSTRALIAN NEW GUINEA. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32:149–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desowitz R. S., Saave J. J., Stein B. The application of the indirect haemagglutination test in recent studies on the immuno-epidemiology of human malaria and the immune response in experimental malaria. Mil Med. 1966 Sep;131(9):1157–1166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUVIN S. F., TOBIE J. E., EVANS C. B., COATNEY G. R., CONTACOS P. G. Antibody production in human malaria as determined by the fluorescent antibody technique. Science. 1962 Mar 30;135(3509):1130–1131. doi: 10.1126/science.135.3509.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUVIN S. F., TOBIE J. E., EVANS C. B., COATNEY G. R., CONTACOS P. G. Fluorescent antibody studies on the course of antibody production and serum gamma globulin levels in normal volunteers infected with human and simian malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1962 Jul;11:429–436. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1962.11.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunn J. S., Chin W., Contacos P. G., Coatney G. R. Changes in antibody titers and serum protein fractions during the course of prolonged infections with vivax or with falciparum malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Jan;15(1):3–10. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGREGOR I. A., WILLIAMS K., VOLLER A., BILLEWICZ W. Z. IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE AND THE MEASUREMENT OF IMMUNE RESPONSE TO HYPERENDEMIC MALARIA. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1965 Jul;59:395–414. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(65)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney D. F., Redington B. C., Schoenbechler M. J. The preparation and serologic activity of plasmodial fractions. Mil Med. 1966 Sep;131(9 Suppl):1141–1151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers W. A., Jr, Fried J. A., Kagan I. G. A modified, indirect microhemagglutination test for malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1968 Nov;17(6):804–809. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1968.17.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEIN B., DESOWITZ R. S. THE MEASUREMENT OF ANTIBODY IN HUMAN MALARIA BY A FORMOLIZED TANNED SHEEP CELL HAEMAGGLUTINATION TEST. Bull World Health Organ. 1964;30:45–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadun E. H., Gore R. W. Mass diagnostic test using Plasmodium falciparum and chimpanzee erythrocyte lysate. Exp Parasitol. 1968 Oct;23(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(68)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
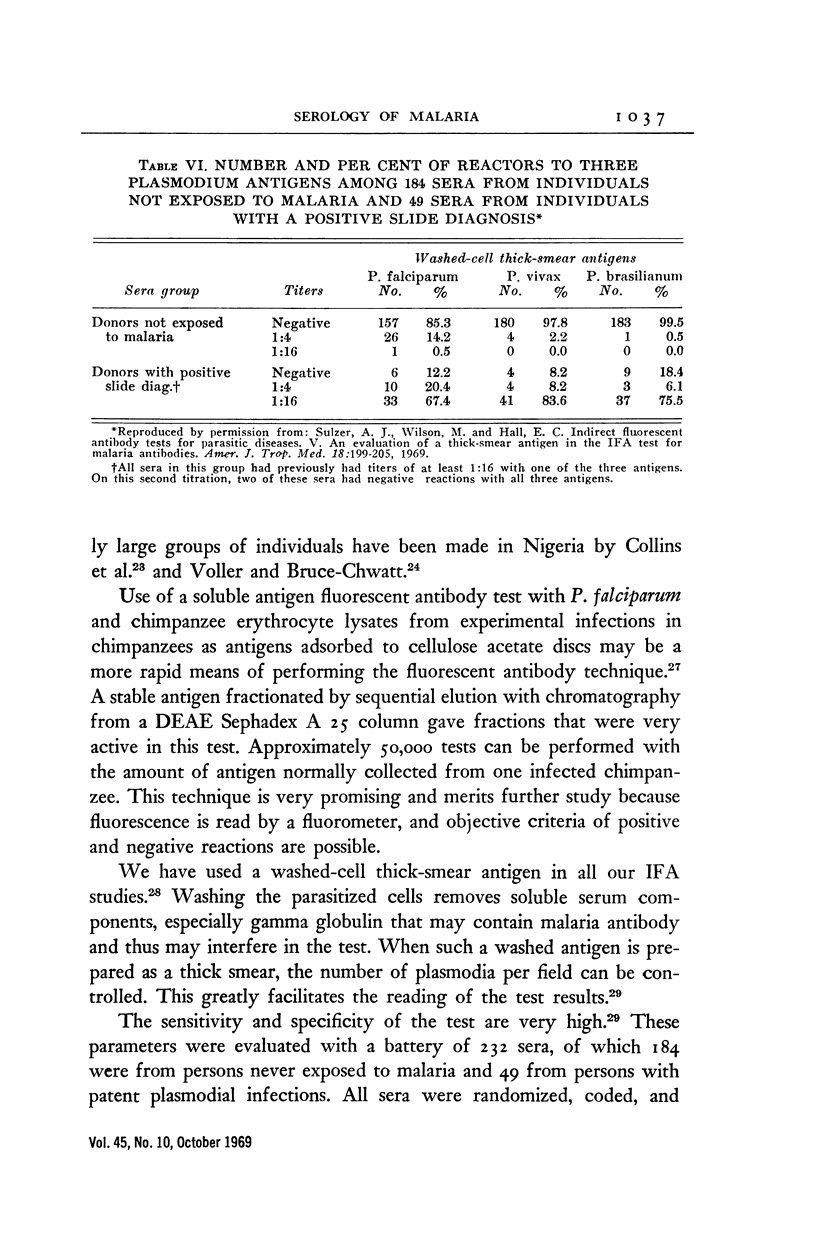
- Sulzer A. J., Wilson M., Hall E. C. Indirect fluorescent-antibody tests for parasitic diseases. V. An evaluation of a thick-smear antigen in the IFA test for malaria antibodies. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1969 Mar;18(2):199–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulzer A. J., Wilson M. The use of thick-smear antigen slides in the malaria indirect fluorescent antibody test. J Parasitol. 1967 Oct;53(5):1110–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOBIE J. E., COATNEY G. R. Fluorescent antibody staining of human malaria parasites. Exp Parasitol. 1961 Sep;11:128–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(61)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLLER A., BRAY R. S. Fluorescent antibody staining as a measure of malarial antibody. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Aug-Sep;110:907–910. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLLER A. FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY METHODS AND THEIR USE IN MALARIA RESEARCH. Bull World Health Organ. 1964;30:343–354. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bruce-Chwatt L. J. Serological malaria surveys in Nigeria. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(6):883–897. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walls K. W., Kagan I. G. Studies on the prevalence of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. 2. Brazil. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Sep;86(2):305–313. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walls K. W., Kagan I. G., Turner A. Studies on the prevalence of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. 1. U. S. military recruits. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Jan;85(1):87–92. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


