Abstract
Methods: Reports on two patients with severe manifestations of HCV related cryoglobulinaemia who failed to respond to interferon α are given. Both patients were treated with pulse cyclophosphamide (750–1000 mg/month for six and 11 months, respectively). HCV RNA was quantified and HCV quasispecies determined in cryoprecipitates and supernatants before and during treatment.
Results: Cryocrit and complement activation decreased in both patients with rebound of cryocrit in one case during continuing pulse cyclophosphamide treatment. Vasculitic symptoms improved. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels and HCV viral load (0.2–0.4 log) increased slightly and reached pretreatment levels after cyclophosphamide was stopped. A highly heterogeneous quasispecies was found in the cryoprecipitate and supernatant of one patient, whereas the viral population was homogeneous in the other patient. After six cycles of cyclophosphamide, viral distances decreased non-significantly. However, phylogenetic analysis showed the evolution of distinct viral strains in one patient and replacement of the main viral population by another population in the second patient.
Conclusions: Immunosuppressive treatment with pulse cyclophosphamide has a temporary limited effect on HCV associated cryoglobulinaemia and leads to a reversible increase of ALT levels and HCV viral load. Short term immunosuppression does not affect the viral heterogeneity as measured by amino acid and nucleotide distances in the hypervariable region 1 of HCV. A change of quasispecies was observed, but further studies are needed to evaluate if this does affect the outcome of IFNα treatment in such patients.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (176.6 KB).
Figure 1 .
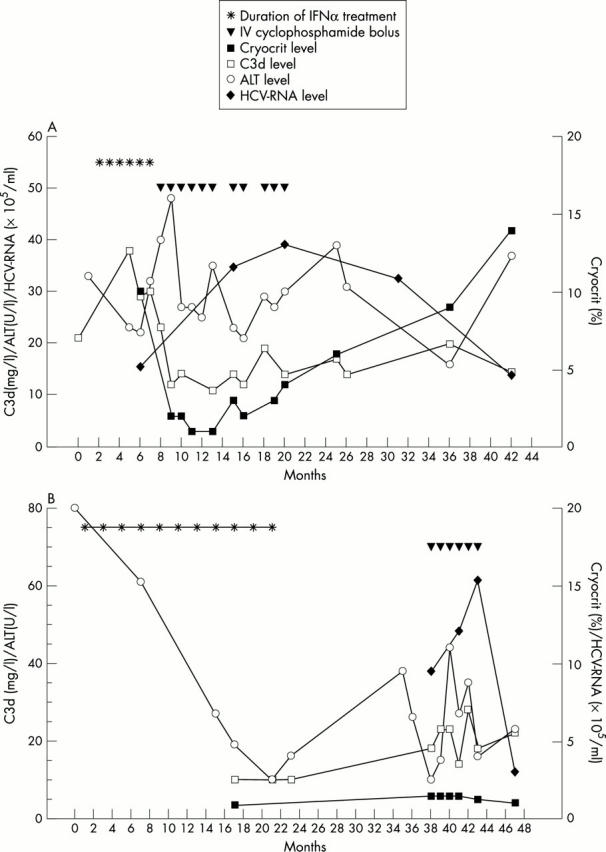
Response of mixed cryoglobulinaemia to pulse cyclophosphamide treatment and effect on virological parameters in patient A (A) and patient B (B). Normal values: C3d <10 mg/l; ALT <18 U/l. HCV-RNA level measured with an HCV Amplicor kit.
Figure 2 .
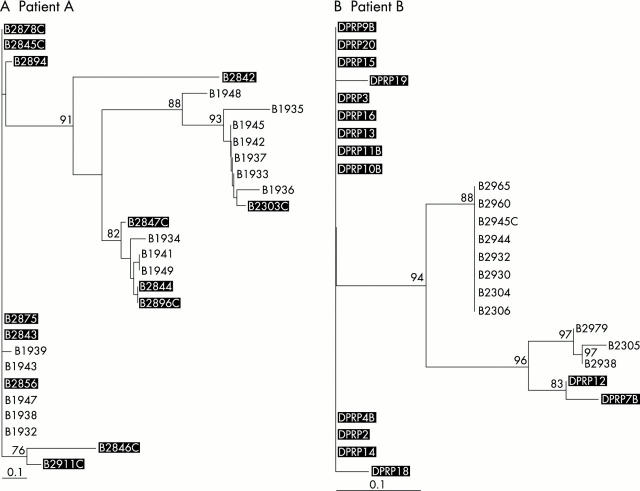
Phylogenetic tree of HCV isolates derived from alignments of amino acid sequences of the hypervariable region 1 in patient A (A) and patient B (B). Branch length is proportional to the evolutionary distances between sequences. Distance scale: 10% sequence dissimilarity. Bootstrap values greater than 70 are shown at the corresponding branch points. Clones derived from the cryoprecipitate after cyclophosphamide treatment are underlain (black), the others represent clones before treatment. The phylogenetic reconstruction showed sequential shifts in the viral population after six months.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.