Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether expression of the four members of the neurotrophin (NT) family and their four corresponding receptors is related to synovial inflammation in patients with spondyloarthritis (SpA).
Material and Methods: Synovial fluid (SF) and serum NTs and their receptors were measured by ELISA. Immunohistochemistry was used for synovial tissue biopsy specimens from patients with SpA, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoarthritis (OA). In SpA synovium, immunoreactivity of the receptors trkA and NGFRp75 was also assessed before and after 12 weeks of treatment with the monoclonal anti-tumour necrosis factor α antibody, infliximab.
Results: mRNA transcripts of all NTs and receptors were expressed in the inflamed synovium. At the protein level, brain derived neurotrophic factor and NT-3 were significantly higher in the SF of patients with SpA than in those with OA. In contrast, ELISA of serum samples showed that the highest member in SpA was NT-4. Immunohistochemistry demonstrated that the NT receptors trkA and NGFRp75 were highly expressed in the inflamed synovium of patients with SpA, correlating with vascularity and lymphoid aggregates, respectively. Additionally, immunoreactivity of both receptors was significantly decreased after infliximab treatment.
Conclusions: NTs and their receptors are expressed in inflamed peripheral joints of patients with SpA. Their expression is not constitutive but related to inflammation and they may be involved in the local disease processes.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (486.1 KB).
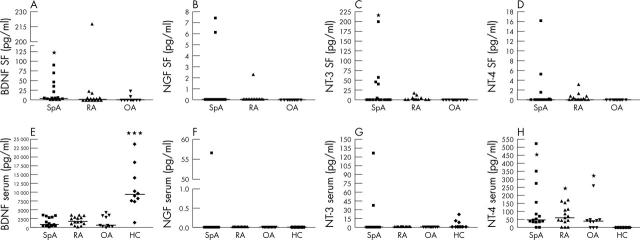
Figure 1.
Neurotrophins were measured by quantitative immunoassay in the SF of 15 patients with SpA, 15 with RA, and 10 with OA (A-D) and in the serum of these patients and 10 healthy controls (HC) (E–H). The scatter plots of all four neurotrophins indicate the individual values. Bold horizontal lines represent the median. Detectable concentrations (median, range; always given for the total group of patients) of SF BDNF were measured in 11/15 (73%) patients with SpA (4.5 pg/ml, 0–90), in 8/15 (53%) patients with RA (1.7 pg/ml, 0–218), and in 2/10 (20%) patients with OA (0 pg/ml, 0–24). SF BDNF concentrations were significantly higher in the SpA group than in patients with OA (A), *p = 0.025. SF NT-3 was detected in 5/15 (33%) patients with SpA (0 pg/ml, 0–200) and in 4/15 (27%) patients with RA (0 pg/ml, 0–17). SF NT-3 levels were also significantly higher in SpA than in OA (C), *p = 0.047). Serum BDNF (E) was detectable in all 50 subjects showing significantly higher levels in HC than all the other groups (SpA, *p<0.0001; RA, *p<0.0001; and OA, *p = 0.001), whereas serum NT-4 (H) was significantly higher in SpA (*p<0.001), RA (*p = 0.001), and OA (*p = 0.008) than in HC.
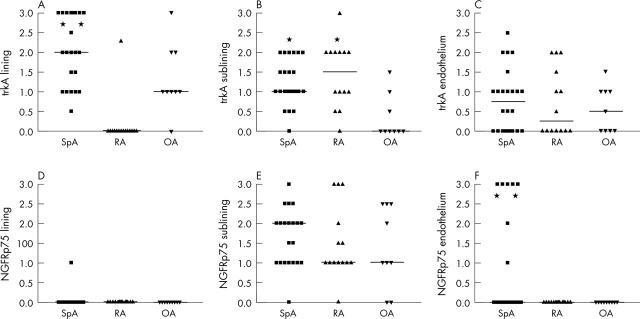
Figure 2.
Immunoreactivity of trkA (A–C) and NGFRp75 (D–F) in the lining layer, sublining layer, and endothelium of synovial tissue biopsy specimens obtained from clinically affected knee joints of 24 patients with SpA, 15 with RA, and 10 with OA. The results represent the individual scores on a semiquantitative 0 (no expression) to 3 (high expression) scale, with bars representing the median score. As indicated (*), the immunoreactivity of trkA was significantly higher in SpA lining than in RA lining (p = 0.047) and OA lining (p = 0.034). Similarly, trkA was more highly expressed in SpA and RA sublining than in OA (p = 0.001 and p = 0.003, respectively). NGFRp75 was almost absent in the lining layer and was equally expressed across disease groups in the sublining layer. However, some patients with SpA showed high endothelial expression, resulting in a significant difference in comparison with RA (p = 0.012) and OA (p = 0.041).
Figure 3.
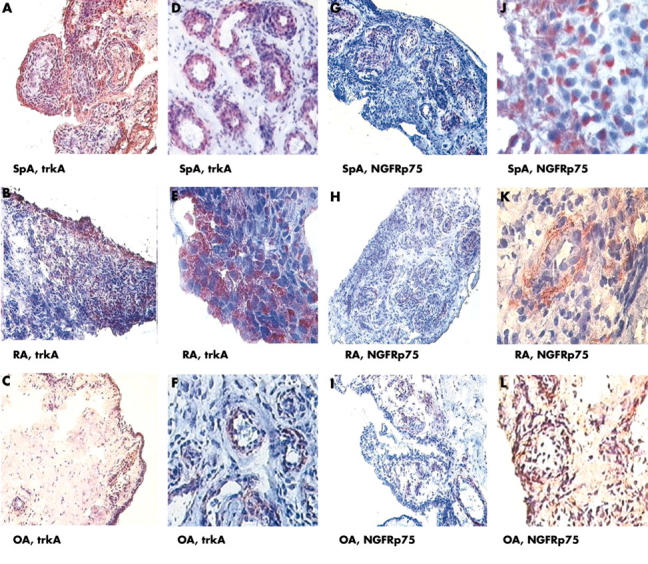
Microscopic pictures of ST sections from 12 different patients are depicted. (A–F) immunostaining of synovial tissue samples of two different patients with SpA, RA, and OA each at low (A, B, C, x160) and high magnification (D, E, F, x320). In patients with SpA, intensive trkA staining predominantly in the lining layer (A) and less intense staining in the sublining layer and the endothelium (D) is seen. In patients with RA, a similar pattern for trkA staining is seen (B, x160 and E, x320) and correspondingly for patients with OA (C, F). (G-L) NGFRp75 immunoreactivity showing an intense staining in the sublining layer (G, J) of patients with SpA. However, immunoreactivity for NGFRp75 is less intense in RA (H, K) and OA (I, L) than in SpA. In all three groups, NGFRp75 staining is not seen in the lining layer, but it is found in the endothelium of patients with SpA.
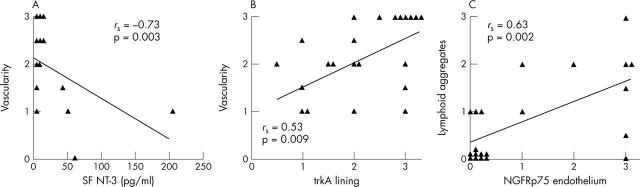
Figure 4.
Significant correlations as determined by Spearman's test in patients with SpA between NT expression and measures of synovial inflammation were found for (A) NT-3 in SF and the degree of vascularisation; (B) immunoreactivity of trkA in the lining layer and the degree of vascularisation; and (C) immunoreactivity of NGFRp75 in the endothelium and the number of lymphoid aggregates.
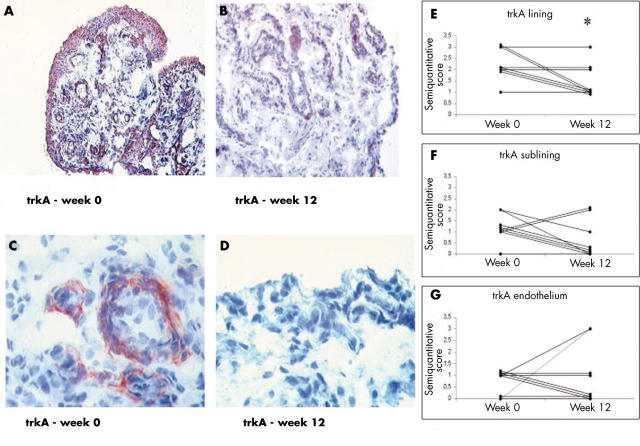
Figure 5.
Immunohistochemistry on ST biopsy samples of selected patients with SpA before and after 12 weeks of infliximab treatment (original magnification is x160 in A, B and x320 in C, D). (A, C) show trkA staining at baseline (week 0) with a predominance of immunoreactivity in the lining and sublining layer. (B, D) Staining of synovial samples obtained in the same patients after 12 weeks of treatment with infliximab. (E–G) indicate the semiquantitative scores (0–3) for trkA expression in the lining and sublining layer and in the endothelium of all nine patients with SpA who were analysed before and 12 weeks after TNFα blocking treatment with infliximab. (E) The trkA reduction in the lining layer was significant at p = 0.03 (*).
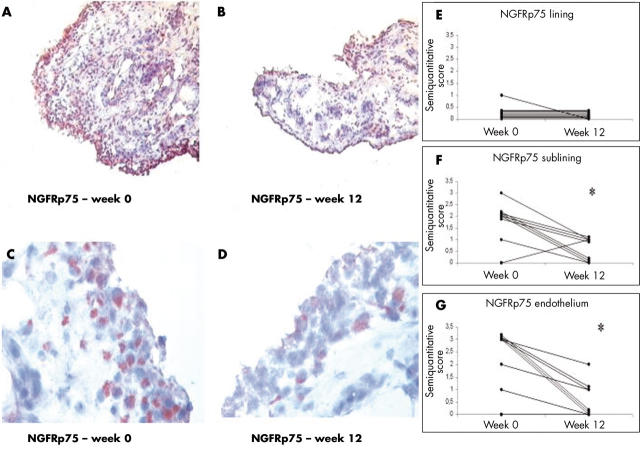
Figure 6.
Immunohistochemistry on ST biopsy specimens of selected patients with SpA before and after 12 weeks of infliximab treatment (original magnification is x160 in A, B and x320 in C, D). (A, C) NGFRp75 staining at baseline, with a predominance in the sublining layer and the endothelium. (B, D) Synovial sections of the same patients stained after 12 weeks of anti-TNFα treatment with infliximab, showing clearly a less intense or even absent staining in both the lining and the sublining layer as well as in the endothelium. (E–G) indicate the semiquantitative scores (0–3) of NGFRp75 expression in the lining and sublining layer and in the endothelium of the nine patients with SpA before and 12 weeks after TNFα blocking treatment with infliximab. (F, G) NGFRp75 is significantly reduced in the sublining layer and in the endothelium (both at *p = 0.004).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloe L., Tuveri M. A., Carcassi U., Levi-Montalcini R. Nerve growth factor in the synovial fluid of patients with chronic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Mar;35(3):351–355. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeten D., Demetter P., Cuvelier C., Van Den Bosch F., Kruithof E., Van Damme N., Verbruggen G., Mielants H., Veys E. M., De Keyser F. Comparative study of the synovial histology in rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthropathy, and osteoarthritis: influence of disease duration and activity. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Dec;59(12):945–953. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.12.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeten D., Van den Bosch F., Elewaut D., Stuer A., Veys E. M., De Keyser F. Needle arthroscopy of the knee with synovial biopsy sampling: technical experience in 150 patients. Clin Rheumatol. 1999;18(6):434–441. doi: 10.1007/s100670050134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeten Dominique, Demetter Pieter, Cuvelier Claude A., Kruithof Elli, Van Damme Nancy, De Vos Martine, Veys Eric M., De Keyser Filip. Macrophages expressing the scavenger receptor CD163: a link between immune alterations of the gut and synovial inflammation in spondyloarthropathy. J Pathol. 2002 Mar;196(3):343–350. doi: 10.1002/path.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeten Dominique, Kruithof Elli, De Rycke Leen, Boots Anemieke M., Mielants Herman, Veys Eric M., De Keyser Filip. Infiltration of the synovial membrane with macrophage subsets and polymorphonuclear cells reflects global disease activity in spondyloarthropathy. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005 Jan 21;7(2):R359–R369. doi: 10.1186/ar1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeten Dominique, Kruithof Elli, De Rycke Leen, Vandooren Bernard, Wyns Bart, Boullart Luc, Hoffman Ilse E. A., Boots Annemieke M., Veys Eric M., De Keyser Filip. Diagnostic classification of spondylarthropathy and rheumatoid arthritis by synovial histopathology: a prospective study in 154 consecutive patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Sep;50(9):2931–2941. doi: 10.1002/art.20476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracci-Laudiero Luisa, Celestino Domenico, Starace Giuseppe, Antonelli Alessia, Lambiase Alessandro, Procoli Annabella, Rumi Carlo, Lai Marco, Picardi Alessandra, Ballatore Giovanna. CD34-positive cells in human umbilical cord blood express nerve growth factor and its specific receptor TrkA. J Neuroimmunol. 2003 Mar;136(1-2):130–139. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(03)00007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroleo M. C., Costa N., Bracci-Laudiero L., Aloe L. Human monocyte/macrophages activate by exposure to LPS overexpress NGF and NGF receptors. J Neuroimmunol. 2001 Feb 15;113(2):193–201. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(00)00441-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Rycke Leen, Baeten Dominique, Foell Dirk, Kruithof Elli, Veys Eric M., Roth Johannes, De Keyser Filip. Differential expression and response to anti-TNFalpha treatment of infiltrating versus resident tissue macrophage subsets in autoimmune arthritis. J Pathol. 2005 May;206(1):17–27. doi: 10.1002/path.1758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demetter P., De Vos M., Van Huysse J. A., Baeten D., Ferdinande L., Peeters H., Mielants H., Veys E. M., De Keyser F., Cuvelier C. A. Colon mucosa of patients both with spondyloarthritis and Crohn's disease is enriched with macrophages expressing the scavenger receptor CD163. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 May 27;64(2):321–324. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.018382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., van der Linden S., Juhlin R., Huitfeldt B., Amor B., Calin A., Cats A., Dijkmans B., Olivieri I., Pasero G. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Oct;34(10):1218–1227. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhard P. B., Erb P., Graumann U., Otten U. Expression of nerve growth factor and nerve growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase Trk in activated CD4-positive T-cell clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):10984–10988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.10984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhard P. B., Ganter U., Stalder A., Bauer J., Otten U. Expression of functional trk protooncogene in human monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5423–5427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont A. J., Watkins A., Le Maitre C., Baird P., Jeziorska M., Knight M. T. N., Ross E. R. S., O'Brien J. P., Hoyland J. A. Nerve growth factor expression and innervation of the painful intervertebral disc. J Pathol. 2002 Jul;197(3):286–292. doi: 10.1002/path.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garaci E., Caroleo M. C., Aloe L., Aquaro S., Piacentini M., Costa N., Amendola A., Micera A., Caliò R., Perno C. F. Nerve growth factor is an autocrine factor essential for the survival of macrophages infected with HIV. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Nov 23;96(24):14013–14018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.24.14013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iannone F., De Bari C., Dell'Accio F., Covelli M., Patella V., Lo Bianco G., Lapadula G. Increased expression of nerve growth factor (NGF) and high affinity NGF receptor (p140 TrkA) in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002 Dec;41(12):1413–1418. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/41.12.1413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karege Félicien, Perret Guillaume, Bondolfi Guido, Schwald Michèle, Bertschy Gilles, Aubry Jean-Michel. Decreased serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in major depressed patients. Psychiatry Res. 2002 Mar 15;109(2):143–148. doi: 10.1016/s0165-1781(02)00005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto K., Okada T., Kannan Y., Ushio H., Matsumoto M., Matsuda H. Nerve growth factor prevents apoptosis of rat peritoneal mast cells through the trk proto-oncogene receptor. Blood. 1995 Dec 15;86(12):4638–4644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E., Baeten D., Van den Bosch F., Mielants H., Veys E. M., De Keyser F. Histological evidence that infliximab treatment leads to downregulation of inflammation and tissue remodelling of the synovial membrane in spondyloarthropathy. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Sep 23;64(4):529–536. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.018549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labouyrie E., Dubus P., Groppi A., Mahon F. X., Ferrer J., Parrens M., Reiffers J., de Mascarel A., Merlio J. P. Expression of neurotrophins and their receptors in human bone marrow. Am J Pathol. 1999 Feb;154(2):405–415. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65287-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labouyrie E., Parrens M., de Mascarel A., Bloch B., Merlio J. P. Distribution of NGF receptors in normal and pathologic human lymphoid tissues. J Neuroimmunol. 1997 Aug;77(2):161–173. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(97)00055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambiase A., Manni L., Bonini S., Rama P., Micera A., Aloe L. Nerve growth factor promotes corneal healing: structural, biochemical, and molecular analyses of rat and human corneas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000 Apr;41(5):1063–1069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang Undine E., Hellweg Rainer, Gallinat Jürgen. BDNF serum concentrations in healthy volunteers are associated with depression-related personality traits. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004 Apr;29(4):795–798. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micera A., Vigneti E., Pickholtz D., Reich R., Pappo O., Bonini S., Maquart F. X., Aloe L., Levi-Schaffer F. Nerve growth factor displays stimulatory effects on human skin and lung fibroblasts, demonstrating a direct role for this factor in tissue repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 May 8;98(11):6162–6167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.101130898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller Luitpold E., Weidler Claudia, Falk Werner, Angele Peter, Schaumburger Jens, Schölmerich Jürgen, Straub Rainer H. Increased prevalence of semaphorin 3C, a repellent of sympathetic nerve fibers, in the synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Apr;50(4):1156–1163. doi: 10.1002/art.20110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassenstein Christina, Braun Armin, Erpenbeck Veit Johannes, Lommatzsch Marek, Schmidt Stephanie, Krug Norbert, Luttmann Werner, Renz Harald, Virchow Johann Christian., Jr The neurotrophins nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neurotrophin-3, and neurotrophin-4 are survival and activation factors for eosinophils in patients with allergic bronchial asthma. J Exp Med. 2003 Aug 4;198(3):455–467. doi: 10.1084/jem.20010897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassenstein Christina, Kerzel Sebastian, Braun Armin. Neurotrophins and neurotrophin receptors in allergic asthma. Prog Brain Res. 2004;146:347–367. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(03)46022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozza M., Guerra M., Manzini E., Calza L. A histochemical study of the rheumatoid synovium: focus on nitric oxide, nerve growth factor high affinity receptor, and innervation. J Rheumatol. 2000 May;27(5):1121–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri Siba P., Sanyal Mrinmoy, Weltman Helena, Kundu-Raychaudhuri Smriti. K252a, a high-affinity nerve growth factor receptor blocker, improves psoriasis: an in vivo study using the severe combined immunodeficient mouse-human skin model. J Invest Dermatol. 2004 Mar;122(3):812–819. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2003.12602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinshagen M., Rohm H., Steinkamp M., Lieb K., Geerling I., Von Herbay A., Flämig G., Eysselein V. E., Adler G. Protective role of neurotrophins in experimental inflammation of the rat gut. Gastroenterology. 2000 Aug;119(2):368–376. doi: 10.1053/gast.2000.9307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinshagen Max, von Boyen Georg, Adler Guido, Steinkamp Martin. Role of neurotrophins in inflammation of the gut. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2002 Apr;3(4):565–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rihl M., Baeten D., Seta N., Gu J., De Keyser F., Veys E. M., Kuipers J. G., Zeidler H., Yu D. T. Y. Technical validation of cDNA based microarray as screening technique to identify candidate genes in synovial tissue biopsy specimens from patients with spondyloarthropathy. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 May;63(5):498–507. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.008052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld R. D., Zeni L., Haniu M., Talvenheimo J., Radka S. F., Bennett L., Miller J. A., Welcher A. A. Purification and identification of brain-derived neurotrophic factor from human serum. Protein Expr Purif. 1995 Aug;6(4):465–471. doi: 10.1006/prep.1995.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisz A. M., Stanisz J. A. Nerve growth factor and neuroimmune interactions in inflammatory diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;917:268–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb05392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessarollo L. Pleiotropic functions of neurotrophins in development. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1998 Jun;9(2):125–137. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(98)00003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torcia M., Bracci-Laudiero L., Lucibello M., Nencioni L., Labardi D., Rubartelli A., Cozzolino F., Aloe L., Garaci E. Nerve growth factor is an autocrine survival factor for memory B lymphocytes. Cell. 1996 May 3;85(3):345–356. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touhami Amel, Grueterich Martin, Tseng Scheffer C. G. The role of NGF signaling in human limbal epithelium expanded by amniotic membrane culture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002 Apr;43(4):987–994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuveri M., Generini S., Matucci-Cerinic M., Aloe L. NGF, a useful tool in the treatment of chronic vasculitic ulcers in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2000 Nov 18;356(9243):1739–1740. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)03212-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandooren Bernard, Kruithof Elli, Yu David T. Y., Rihl Markus, Gu Jieruo, De Rycke Leen, Van Den Bosch Filip, Veys Eric M., De Keyser Filip, Baeten Dominique. Involvement of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in peripheral synovitis and down-regulation by tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade in spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Sep;50(9):2942–2953. doi: 10.1002/art.20477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidler C., Holzer C., Harbuz M., Hofbauer R., Angele P., Schölmerich J., Straub R. H. Low density of sympathetic nerve fibres and increased density of brain derived neurotrophic factor positive cells in RA synovium. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005 Jan;64(1):13–20. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.016154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z., Nagata K., Iijima T. Immunohistochemical study of NGF and its receptors in the synovial membrane of the ankle joint of adjuvant-induced arthritic rats. Histochem Cell Biol. 2000 Dec;114(6):453–459. doi: 10.1007/s004180000222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Chunhua, Gu Jieruo, Rihl Markus, Baeten Dominique, Huang Feng, Zhao Miansong, Zhang Hanwei, Maksymowych Walter P., De Keyser Filip, Veys Eric M. Serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase 3 and macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 correlate with disease activity in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Oct 15;51(5):691–699. doi: 10.1002/art.20696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]