Abstract
Background: In K/BxN mice, anti-glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI) antibodies (Abs) are arthritogenic, and their transfer into naïve mice induces arthritis. Anti-GPI Abs develop in many human patients with RA and are associated with more severe forms of the disease.
Objective: To elucidate the serum and synovial fluid (SF) anti-GPI IgG profiles among different patient groups with a variety of arthritides.
Methods: Blood and SF obtained concomitantly from 91 patients with clinically well defined arthritis were tested for concentrations of total anti-GPI IgG, anti-GPI IgG subclasses, B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS), and APRIL by ELISA.
Results: Anti-GPI IgG was detected in sera and SF of patients with many arthritic diseases, but was preferentially associated with inflammatory arthritis, in general, and RA, in particular. The anti-GPI IgG subclass usage was skewed and varied among the different arthritic disease groups. Inverse correlations between serum levels of BLyS and anti-GPI IgG and positive correlations between serum levels of APRIL and anti-GPI IgG were seen among immune based arthritic patients and patients with RA but not among non-immune based patients. No correlations were found in SF from any group of arthritic patients.
Conclusion: Raised circulating anti-GPI Abs are not unique to patients with RA but are present in many patients with inflammatory arthritis. The difference in anti-GPI IgG subclass usage among disease groups may influence effector function and disease outcome. The inverse correlation between serum BLyS and anti-GPI IgG levels suggests that anti-GPI B cells may be regulated differently from other autoantibody producing B cells. Anti-GPI Abs may serve a pathogenic function in humans by promoting the maintenance of existing disease.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (168.0 KB).
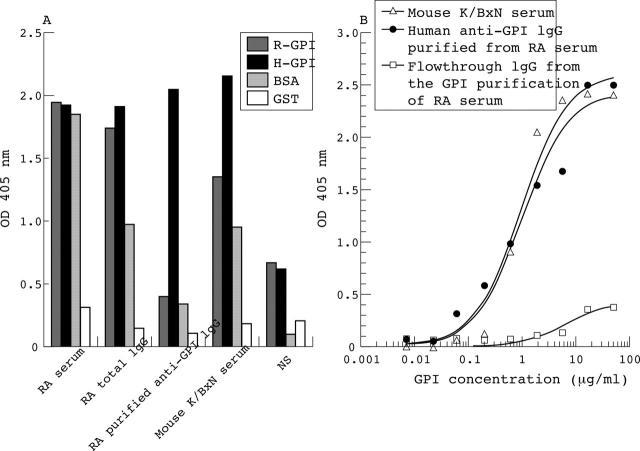
Figure 1.
Anti-GPI-specific IgG purified from the serum of a patient with RA with high anti-GPI titre. (A) Samples from different purification steps, including the RA serum before purification, the purified total IgG fraction, and the purified anti-GPI IgG fraction, were tested for their binding to rabbit GPI (rGPI), human GPI (hGPI), bovine serum albumin, and glutathione-S-transferase as control antigens in an ELISA. Mouse K/BxN serum and normal serum from a healthy subject (NS), were included as positive and negative controls. The fraction containing the purified anti-GPI IgG preparation was highly specific for hGPI and did not react with the other control antigens. (B) Titration of the human anti-GPI IgG fraction showed positive GPI reactivity down to 0.06 µg/ml of IgG, comparable to the mouse K/BxN serum, whereas no reactivity was found in the remaining RA IgG fraction after affinity purification.
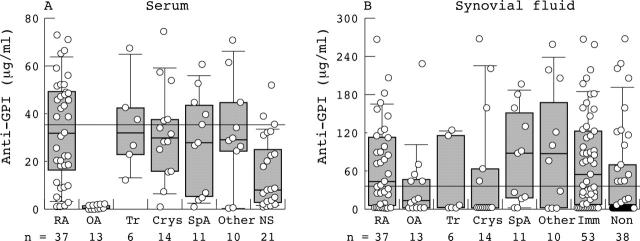
Figure 2.
Anti-GPI IgG concentration in sera and SF of patients with various arthritic diseases. Sera (A) and SF (B) obtained concomitantly from 37 patients with RA, 13 with OA, 6 with Tr, 14 with crystal induced arthritis (Crys), 11 with seronegative SpA, 10 with other forms of inflammatory arthritis (Other) and in 21 normal healthy control sera (NS) were tested for binding to recombinant hGPI by ELISA. Bound IgG was detected with an AP conjugated F(ab)2 goat antihuman IgG-Fc and the concentration calculated according to a standard serum with known concentration of IgG. The cut off points for positivity were calculated as the 95% centile of the concentrations in healthy control subjects (>35.4 µg/ml). Immune based arthritis (Imm) includes patients with RA, SpA, SLE, undifferentiated inflammatory polyarthritis, and polymyalgia rheumatica. Non-immune based arthritis (Non) includes patients with OA, Tr, Crys, infectious arthritis, and adenocarcinomatous arthritis. The lines inside the boxes indicate the medians, the outer boxes indicate the 25th and 75th centiles; the bars extending from the boxes indicate the 10th and 90th centiles.
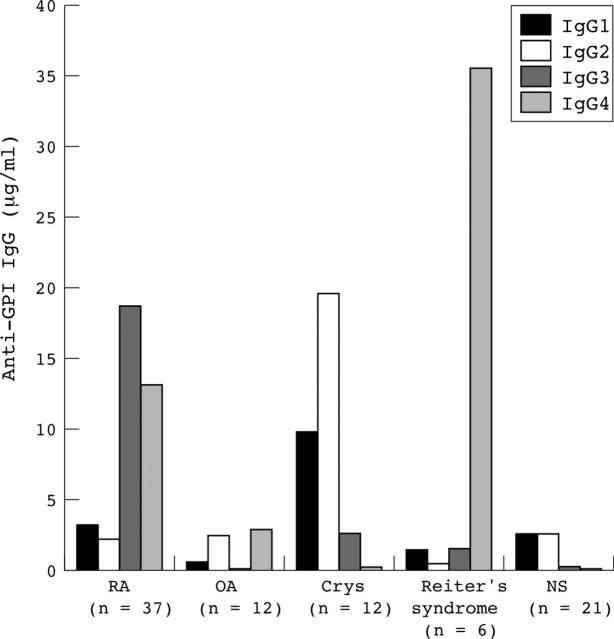
Figure 3.
Distinct anti-GPI IgG subclass composition observed for patients with different arthritic diseases. Serum samples from 37 patients with RA, 12 with OA, 12 with Crys, 6 with Reiter's syndrome, and 21 healthy subjects (NS) were tested for binding to hGPI in an ELISA. Bound anti-GPI IgG was detected with subclass-specific (IgG1–4) Ab, and the subclass concentration determined and expressed as the median concentration in µg/ml of the different anti-GPI IgG subclasses.
Figure 4.
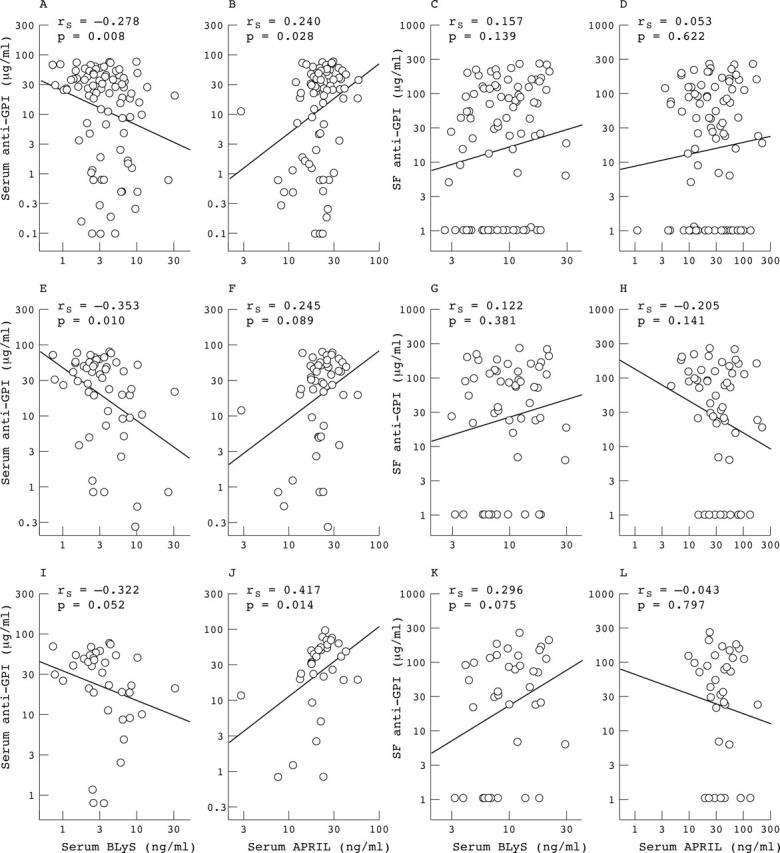
Correlation between BLyS or APRIL levels and anti-GPI IgG concentration in serum and SF samples of arthritic patients. Correlations representing all 91 patients with arthritis (A-D), only patients with immune based arthritis (E-H), or only patients with RA (I-L).
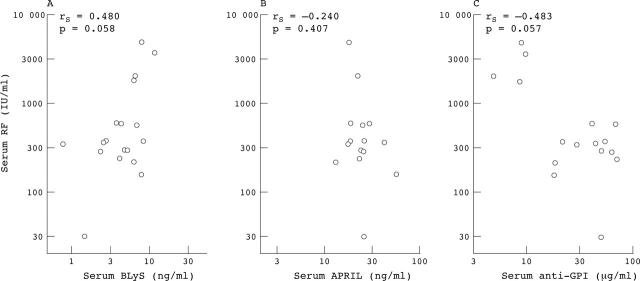
Figure 5.
Correlation between RF and BLyS, APRIL, or anti-GPI IgG levels in serum of patients with RA. Serum RF values plotted against serum BLyS (A), serum APRIL (B), and serum anti-GPI IgG (C) for the patients with RA for whom concurrent serum BLyS and RF levels were available.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P. The innate immune system in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Oct;44(10):2224–2234. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200110)44:10<2224::aid-art384>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avery Danielle T., Kalled Susan L., Ellyard Julia I., Ambrose Christine, Bixler Sarah A., Thien Marilyn, Brink Robert, Mackay Fabienne, Hodgkin Philip D., Tangye Stuart G. BAFF selectively enhances the survival of plasmablasts generated from human memory B cells. J Clin Invest. 2003 Jul;112(2):286–297. doi: 10.1172/JCI18025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batten M., Groom J., Cachero T. G., Qian F., Schneider P., Tschopp J., Browning J. L., Mackay F. BAFF mediates survival of peripheral immature B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 2000 Nov 20;192(10):1453–1466. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.10.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambridge G., Williams M., Leaker B., Corbett M., Smith C. R. Anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: prevalence, clinical correlates, and IgG subclass. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 Jan;53(1):24–29. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheema G. S., Roschke V., Hilbert D. M., Stohl W. Elevated serum B lymphocyte stimulator levels in patients with systemic immune-based rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Jun;44(6):1313–1319. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200106)44:6<1313::AID-ART223>3.0.CO;2-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook A. D., Mackay I. R., Cicuttini F. M., Rowley M. J. IgG subclasses of antibodies to type II collagen in rheumatoid arthritis differ from those in systemic lupus erythematosus and other connective tissue diseases. J Rheumatol. 1997 Nov;24(11):2090–2096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corr Maripat, Crain Brian. The role of FcgammaR signaling in the K/B x N serum transfer model of arthritis. J Immunol. 2002 Dec 1;169(11):6604–6609. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.11.6604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrigall Valerie M., Panayi Gabriel S. Autoantigens and immune pathways in rheumatoid arthritis. Crit Rev Immunol. 2002;22(4):281–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Do R. K., Hatada E., Lee H., Tourigny M. R., Hilbert D., Chen-Kiang S. Attenuation of apoptosis underlies B lymphocyte stimulator enhancement of humoral immune response. J Exp Med. 2000 Oct 2;192(7):953–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.7.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groom Joanna, Kalled Susan L., Cutler Anne H., Olson Carl, Woodcock Stephen A., Schneider Pascal, Tschopp Jurg, Cachero Teresa G., Batten Marcel, Wheway Julie. Association of BAFF/BLyS overexpression and altered B cell differentiation with Sjögren's syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2002 Jan;109(1):59–68. doi: 10.1172/JCI14121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. A., Johnston J., Mudri S., Enselman R., Dillon S. R., Madden K., Xu W., Parrish-Novak J., Foster D., Lofton-Day C. TACI and BCMA are receptors for a TNF homologue implicated in B-cell autoimmune disease. Nature. 2000 Apr 27;404(6781):995–999. doi: 10.1038/35010115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herve C. A., Wait R., Venables P. J. Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase is not a specific autoantigen in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003 Mar 31;42(8):986–988. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keg271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano Toshio. Revival of the autoantibody model in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Immunol. 2002 Apr;3(4):342–344. doi: 10.1038/ni0402-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu Benjamin L., Harless Susan M., Lindsley R. Coleman, Hilbert David M., Cancro Michael P. Cutting edge: BLyS enables survival of transitional and mature B cells through distinct mediators. J Immunol. 2002 Jun 15;168(12):5993–5996. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.12.5993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji Hong, Ohmura Koichiro, Mahmood Umar, Lee David M., Hofhuis Frans M. A., Boackle Susan A., Takahashi Kazue, Holers V. Michael, Walport Mark, Gerard Craig. Arthritis critically dependent on innate immune system players. Immunity. 2002 Feb;16(2):157–168. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(02)00275-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassahn Daniela, Kolb Cornelia, Solomon Samuel, Bochtler Petra, Illges Harald. Few human autoimmune sera detect GPI. Nat Immunol. 2002 May;3(5):411–413. doi: 10.1038/ni0502-411b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khare S. D., Sarosi I., Xia X. Z., McCabe S., Miner K., Solovyev I., Hawkins N., Kelley M., Chang D., Van G. Severe B cell hyperplasia and autoimmune disease in TALL-1 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Mar 28;97(7):3370–3375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.050580697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Ji-Yeon, Lee Mi-Hong, Jung Kyung-In, Na Hye Young, Cha Hoon-Suk, Ko Eun-Mi, Kim Tae Jin. Detection of antibodies against glucose 6-phosphate isomerase in synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis using surface plasmon resonance (BIAcore). Exp Mol Med. 2003 Aug 31;35(4):310–316. doi: 10.1038/emm.2003.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog Lars, Lorentzen Johnny, Padyukov Leonid, Alfredsson Lars. Genes and environment in arthritis: can RA be prevented? Arthritis Res. 2002 May 9;4 (Suppl 3):S31–S36. doi: 10.1186/ar566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maccioni Mariana, Zeder-Lutz Gabrielle, Huang Haochu, Ebel Claudine, Gerber Philippe, Hergueux Josiane, Marchal Patricia, Duchatelle Veronique, Degott Claude, van Regenmortel Marc. Arthritogenic monoclonal antibodies from K/BxN mice. J Exp Med. 2002 Apr 15;195(8):1071–1077. doi: 10.1084/jem.20011941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay F., Woodcock S. A., Lawton P., Ambrose C., Baetscher M., Schneider P., Tschopp J., Browning J. L. Mice transgenic for BAFF develop lymphocytic disorders along with autoimmune manifestations. J Exp Med. 1999 Dec 6;190(11):1697–1710. doi: 10.1084/jem.190.11.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariette X., Roux S., Zhang J., Bengoufa D., Lavie F., Zhou T., Kimberly R. The level of BLyS (BAFF) correlates with the titre of autoantibodies in human Sjögren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Feb;62(2):168–171. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto I., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. Arthritis provoked by linked T and B cell recognition of a glycolytic enzyme. Science. 1999 Nov 26;286(5445):1732–1735. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5445.1732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Isao, Lee David M., Goldbach-Mansky Raphaela, Sumida Takayuki, Hitchon Carol A., Schur Peter H., Anderson Ronald J., Coblyn Jonathan S., Weinblatt Michael E., Brenner Michael. Low prevalence of antibodies to glucose-6-phosphate isomerase in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and a spectrum of other chronic autoimmune disorders. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Apr;48(4):944–954. doi: 10.1002/art.10898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. A., Belvedere O., Orr A., Pieri K., LaFleur D. W., Feng P., Soppet D., Charters M., Gentz R., Parmelee D. BLyS: member of the tumor necrosis factor family and B lymphocyte stimulator. Science. 1999 Jul 9;285(5425):260–263. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5425.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee P., Wu B., Mayton L., Kim S-H, Robbins P. D., Wooley P. H. TNF receptor gene therapy results in suppression of IgG2a anticollagen antibody in collagen induced arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Aug;62(8):707–714. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.8.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay A., Ni J., Zhai Y., Yu G. L., Aggarwal B. B. Identification and characterization of a novel cytokine, THANK, a TNF homologue that activates apoptosis, nuclear factor-kappaB, and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. J Biol Chem. 1999 Jun 4;274(23):15978–15981. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.23.15978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli B., Belvedere O., Roschke V., Moore P. A., Olsen H. S., Migone T. S., Sosnovtseva S., Carrell J. A., Feng P., Giri J. G. Synthesis and release of B-lymphocyte stimulator from myeloid cells. Blood. 2001 Jan 1;97(1):198–204. doi: 10.1182/blood.v97.1.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayi G. S., Lanchbury J. S., Kingsley G. H. The importance of the T cell in initiating and maintaining the chronic synovitis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jul;35(7):729–735. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller M., Burton D. R., Ditzel H. J. Autoantibodies to GPI in rheumatoid arthritis: linkage between an animal model and human disease. Nat Immunol. 2001 Aug;2(8):746–753. doi: 10.1038/90696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider P., MacKay F., Steiner V., Hofmann K., Bodmer J. L., Holler N., Ambrose C., Lawton P., Bixler S., Acha-Orbea H. BAFF, a novel ligand of the tumor necrosis factor family, stimulates B cell growth. J Exp Med. 1999 Jun 7;189(11):1747–1756. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.11.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert David, Maier Bert, Morawietz Lars, Krenn Veit, Kamradt Thomas. Immunization with glucose-6-phosphate isomerase induces T cell-dependent peripheral polyarthritis in genetically unaltered mice. J Immunol. 2004 Apr 1;172(7):4503–4509. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.7.4503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert David, Schmidt Monika, Zaiss Dietmar, Jungblut Peter R., Kamradt Thomas. Autoantibodies to GPI and creatine kinase in RA. Nat Immunol. 2002 May;3(5):411–413. doi: 10.1038/ni0502-411a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seshasayee Dhaya, Valdez Patricia, Yan Minhong, Dixit Vishva M., Tumas Daniel, Grewal Iqbal S. Loss of TACI causes fatal lymphoproliferation and autoimmunity, establishing TACI as an inhibitory BLyS receptor. Immunity. 2003 Feb;18(2):279–288. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(03)00025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu H. B., Hu W. H., Johnson H. TALL-1 is a novel member of the TNF family that is down-regulated by mitogens. J Leukoc Biol. 1999 May;65(5):680–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohl William. B lymphocyte stimulator protein levels in systemic lupus erythematosus and other diseases. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2002 Aug;4(4):345–350. doi: 10.1007/s11926-002-0044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohl William, Cheema Gurtej S., Briggs William S., Xu Dong, Sosnovtseva Svetlana, Roschke Viktor, Ferrara Dardo E., Labat Kimberly, Sattler Fred R., Pierangeli Silvia S. B lymphocyte stimulator protein-associated increase in circulating autoantibody levels may require CD4+ T cells: lessons from HIV-infected patients. Clin Immunol. 2002 Aug;104(2):115–122. doi: 10.1006/clim.2002.5238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohl William, Metyas Samy, Tan Soon-Min, Cheema Gurtej S., Oamar Bonifacia, Xu Dong, Roschke Viktor, Wu Youmei, Baker Kevin P., Hilbert David M. B lymphocyte stimulator overexpression in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: longitudinal observations. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Dec;48(12):3475–3486. doi: 10.1002/art.11354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Soon-Min, Xu Dong, Roschke Viktor, Perry James W., Arkfeld Daniel G., Ehresmann Glenn R., Migone Thi-Sau, Hilbert David M., Stohl William. Local production of B lymphocyte stimulator protein and APRIL in arthritic joints of patients with inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Apr;48(4):982–992. doi: 10.1002/art.10860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. S., Schneider P., Kalled S. L., Wang L., Lefevre E. A., Cachero T. G., MacKay F., Bixler S. A., Zafari M., Liu Z. Y. BAFF binds to the tumor necrosis factor receptor-like molecule B cell maturation antigen and is important for maintaining the peripheral B cell population. J Exp Med. 2000 Jul 3;192(1):129–135. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todome Y., Ohkuni H., Mizuse M., Furuya M., Fujikawa S., Tanaka S., Watanabe N., Fujii K., Zabriskie J. B. Detection of antibodies against streptococcal peptidoglycan and the peptide subunit (synthetic tetra-D-alanyl-bovine serum albumin complex) in rheumatic-diseases. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1992;97(4):301–307. doi: 10.1159/000236137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribouley C., Wallroth M., Chan V., Paliard X., Fang E., Lamson G., Pot D., Escobedo J., Williams L. T. Characterization of a new member of the TNF family expressed on antigen presenting cells. Biol Chem. 1999 Dec;380(12):1443–1447. doi: 10.1515/BC.1999.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Roschke V., Baker K. P., Wang Z., Alarcón G. S., Fessler B. J., Bastian H., Kimberly R. P., Zhou T. Cutting edge: a role for B lymphocyte stimulator in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 2001 Jan 1;166(1):6–10. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Tong, Zhang Jun, Carter Robert, Kimberly Robert. BLyS and B cell autoimmunity. Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2003;6:21–37. doi: 10.1159/000066854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gaalen Floris A., Toes Rene E. M., Ditzel Henrik J., Schaller Monica, Breedveld Ferdinand C., Verweij Cor L., Huizinga Tom W. J. Association of autoantibodies to glucose-6-phosphate isomerase with extraarticular complications in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Feb;50(2):395–399. doi: 10.1002/art.20028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]