Abstract
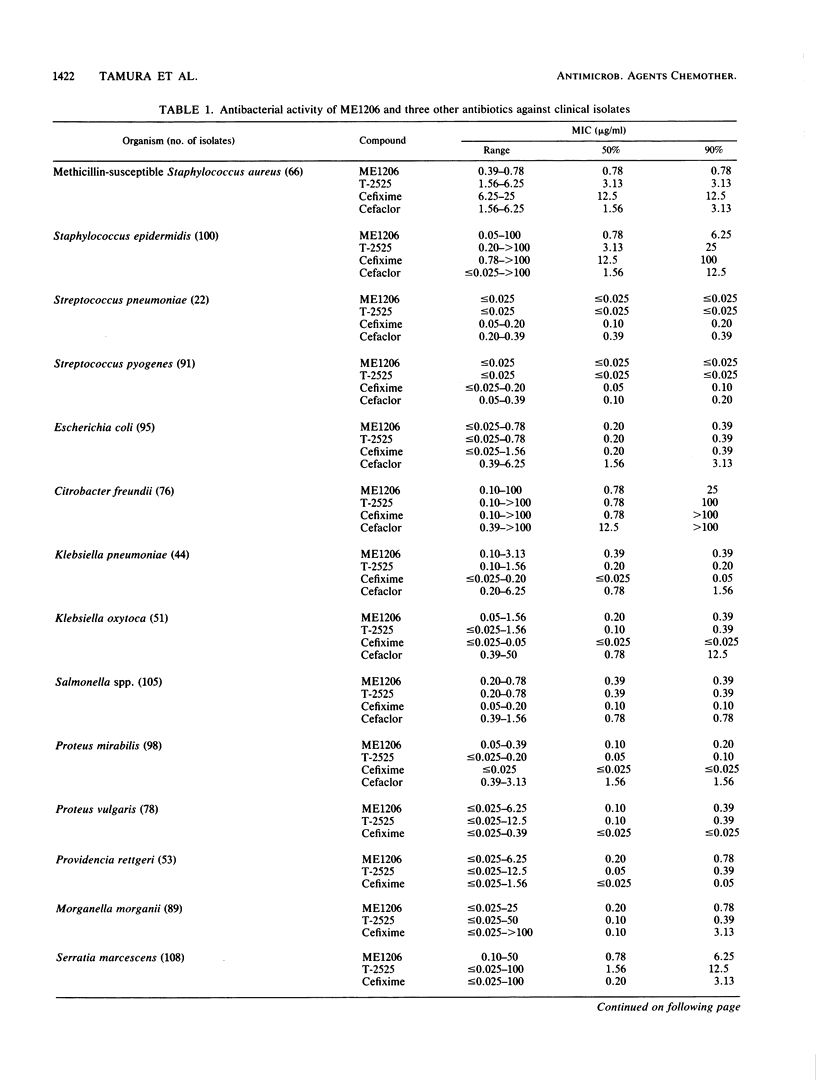
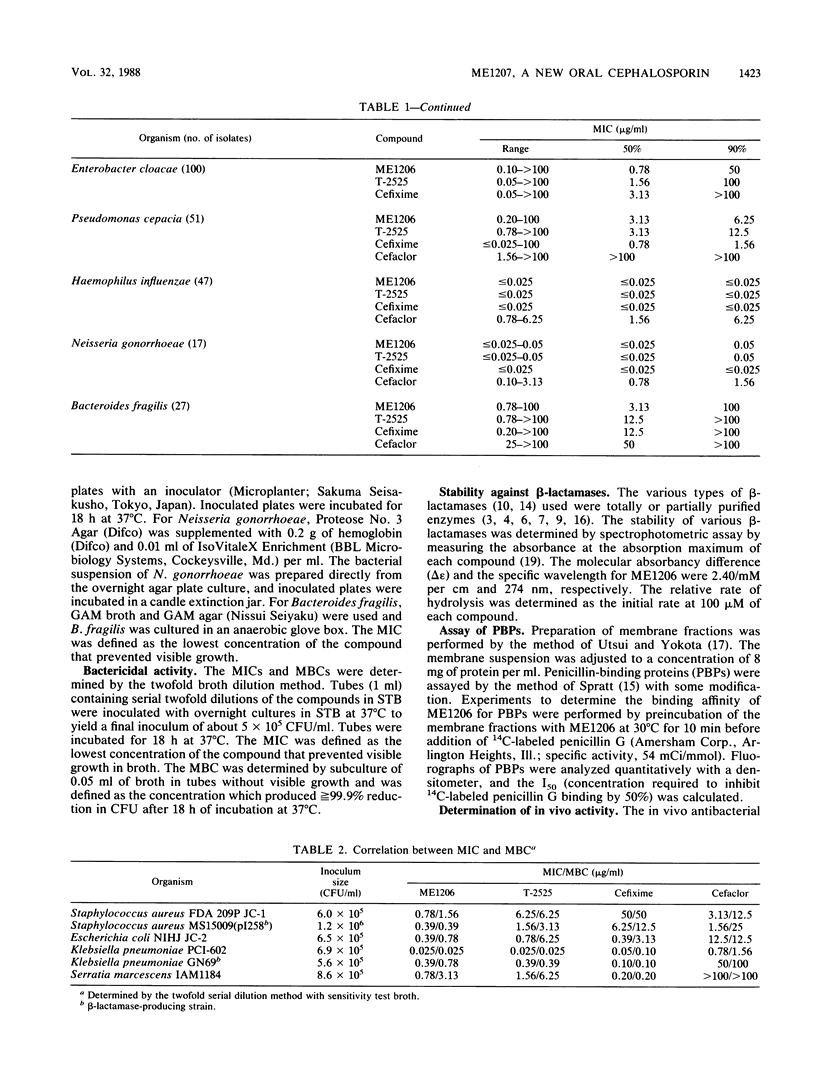
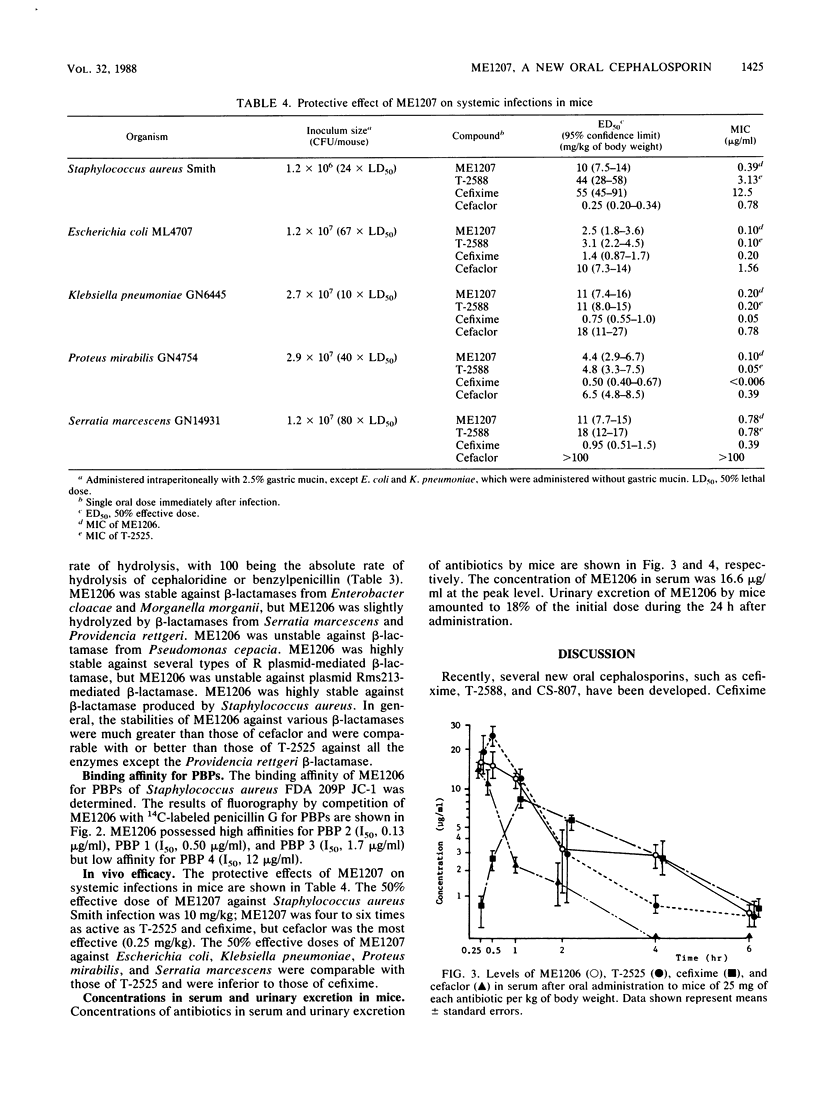
ME1207 (pivaloyloxymethyl ester of ME1206) is a new oral cephalosporin. ME1206 is (6R,7R)-7-[(Z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)- acetamido]-3-[(Z)-2-(4-methylthiazol-5-yl)-ethyl]-cephem-4-carboxy lic acid. The susceptibilities of about 1,600 clinical isolates to ME1206 were determined by the agar dilution method. ME1206 showed a broad spectrum of activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. ME1206 was more active than cefaclor, T-2525, and cefixime against Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Against gram-negative bacteria, the activity of ME1206 was comparable with that of T-2525, but ME1206 was less active than cefixime. Against Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, ME1206 had high activity (MIC, less than or equal to 0.05 microgram/ml). ME1206 was stable against various beta-lactamases, except beta-lactamases from Providencia rettgeri, Pseudomonas cepacia, and Escherichia coli W3630 (Rms213). The 50% effective doses of ME1207 after oral administration against systemic infections in mice were comparable with those of T-2588 against gram-negative bacteria and about one-fourth that of T-2588 against Staphylococcus aureus Smith.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bill N. J., Washington J. A., 2nd Comparison of in vitro activity of cephalexin, cephradine, and cefaclor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):470–474. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau P. Y., Leung Y. K., Ng W. W., Arnold K. Comparative in vitro antibacterial activities of two new oral cephalosporins, ceftetrame (Ro 19-5247) and cefetamet (Ro 15-8074). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Mar;31(3):473–476. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Iyobe S., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of a new beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas cepacia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):355–358. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamimura T., Kojo H., Matsumoto Y., Mine Y., Goto S., Kuwahara S. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial properties of FK 027, a new orally active cephem antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jan;25(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara N., Yotsuji A., Kumano K., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and some properties of a cephalosporinase from Proteus vulgaris. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):185–187. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura M., Nakazawa H., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and biochemical properties of beta-lactamase produced by Proteus rettgeri. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):687–690. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami S., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of a cephalosporinase from Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Dec;18(6):853–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.6.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Chin N. X., Labthavikul P. In vitro activity and beta-lactamase stability of two oral cephalosporins, ceftetrame (Ro 19-5247) and cefetamet (Ro 15-8074). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Sep;30(3):423–428. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Fu K. P. Cefaclor: in vitro spectrum of activity and beta-lactamase stability. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):584–588. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto S., Hamana Y., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of T-2588, a new oral cephalosporin, compared with those of other oral beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1111–1116. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda M., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Properties of cephalosporinase from Proteus morganii. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1981 Nov;34(11):1469–1475. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.34.1469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsui Y., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of CS-807, a new oral cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1085–1092. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsui Y., Yokota T. Role of an altered penicillin-binding protein in methicillin- and cephem-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):397–403. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waley S. G. A spectrophotometric assay of beta-lactamase action on penicillins. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):789–790. doi: 10.1042/bj1390789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]