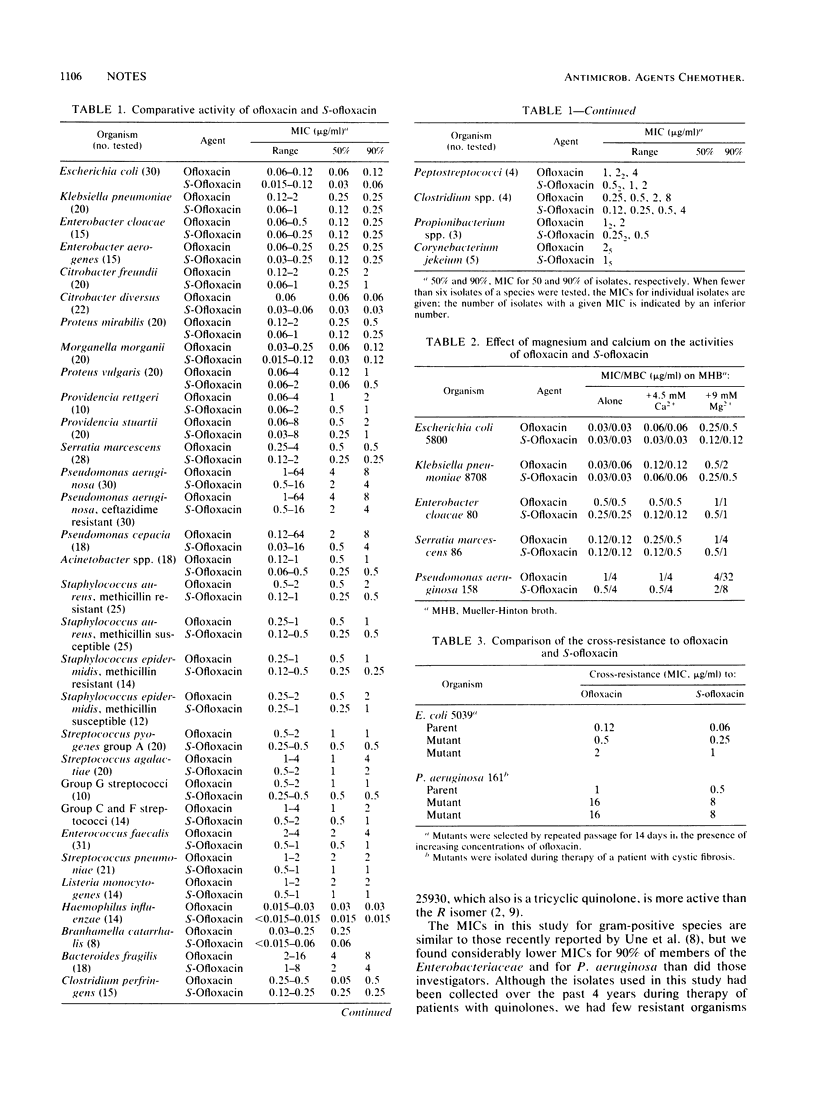
Abstract
S-Ofloxacin, the optically active form of ofloxacin, was twice as active as the S,R mixture of ofloxacin against members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and gram-positive species. Of the Enterobacteriaceae, 90% were inhibited by less than or equal to 1 microgram/ml and 90% of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes isolates were inhibited by 0.5 microgram/ml. Bacteroides fragilis was inhibited by 4 micrograms/ml. Organisms resistant to ofloxacin were resistant to S-ofloxacin. Like ofloxacin activity, the activity of S-ofloxacin was reduced by Mg2+ and by acid pH. Spontaneous mutational resistance to S-ofloxacin was similar to that to ofloxacin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Espinoza A. M., Chin N. X., Novelli A., Neu H. C. Comparative in vitro activity of a new fluorinated 4-quinolone, T-3262 (A-60969). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):663–670. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster J. F., Rohlfing S. R., Pecore S. E., Winandy R. M., Stern R. M., Landmesser J. E., Olsen R. A., Gleason W. B. Synthesis, absolute configuration, and antibacterial activity of 6,7-dihydro-5,8-dimethyl-9-fluoro-1-oxo-1H,5H- benzo[ij]quinolizine-2-carboxylic acid. J Med Chem. 1987 May;30(5):839–843. doi: 10.1021/jm00388a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa I., Atarashi S., Yokohama S., Imamura M., Sakano K., Furukawa M. Synthesis and antibacterial activities of optically active ofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):163–164. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn L., Neu H. C. Factors influencing the in vitro activity of two new aryl-fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agents, difloxacin (A-56619) and A-56620. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):143–146. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura M., Shibamura S., Hayakawa I., Osada Y. Inhibition of DNA gyrase by optically active ofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):325–327. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Fujimoto T., Sato K., Osada Y. In vitro activity of DR-3355, an optically active ofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Sep;32(9):1336–1340. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.9.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C., Ng E. Y., Souza K. S., McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Antagonism of wild-type and resistant Escherichia coli and its DNA gyrase by the tricyclic 4-quinolone analogs ofloxacin and S-25930 stereoisomers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1861–1863. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


