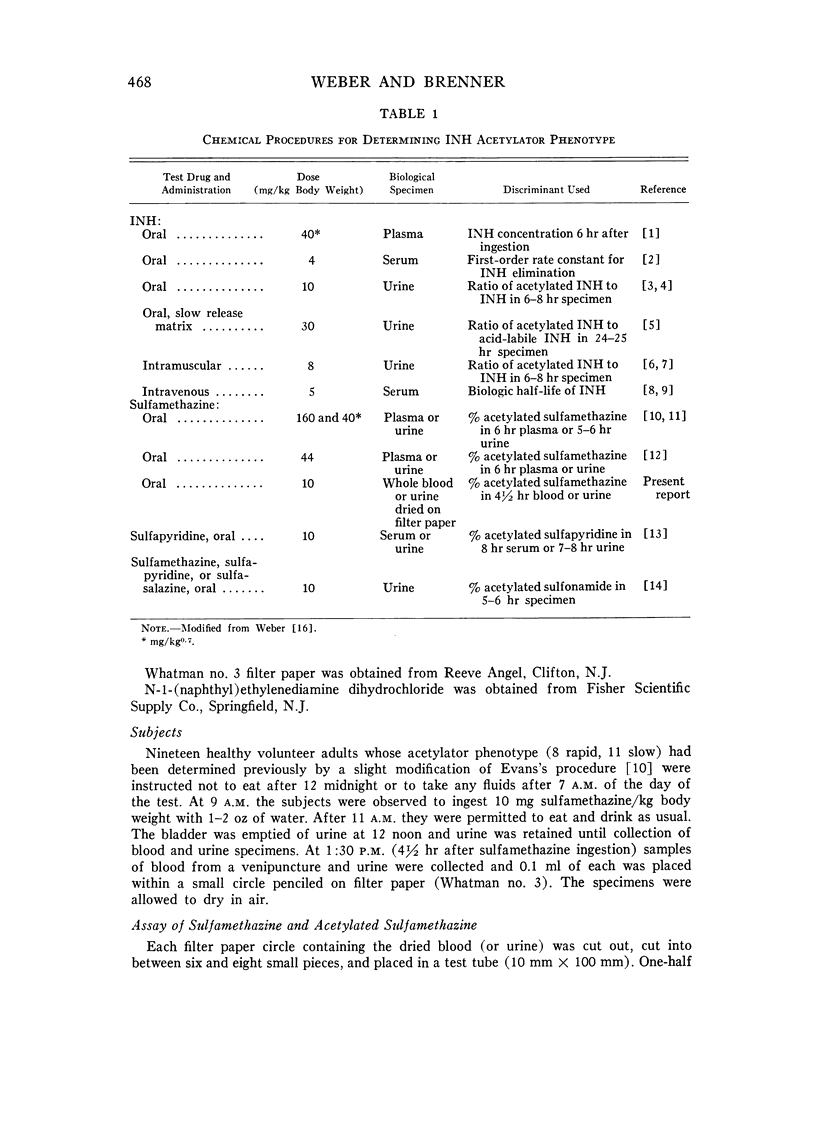
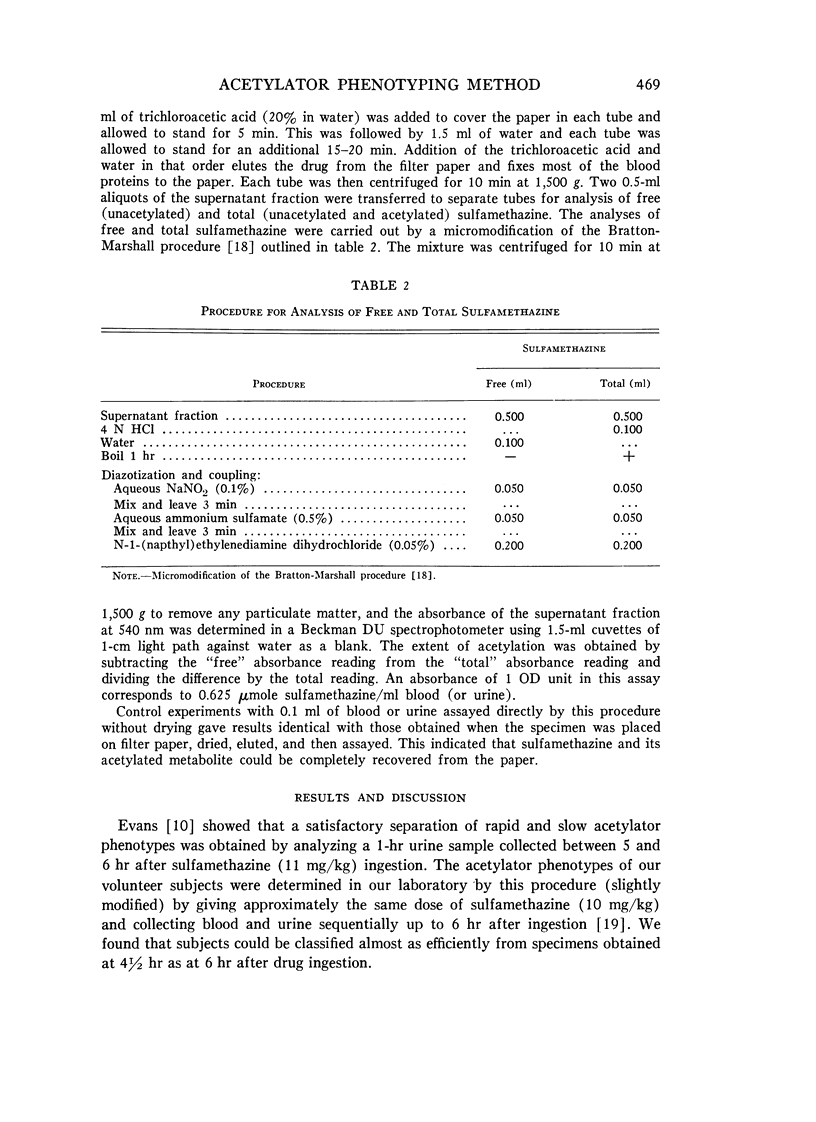
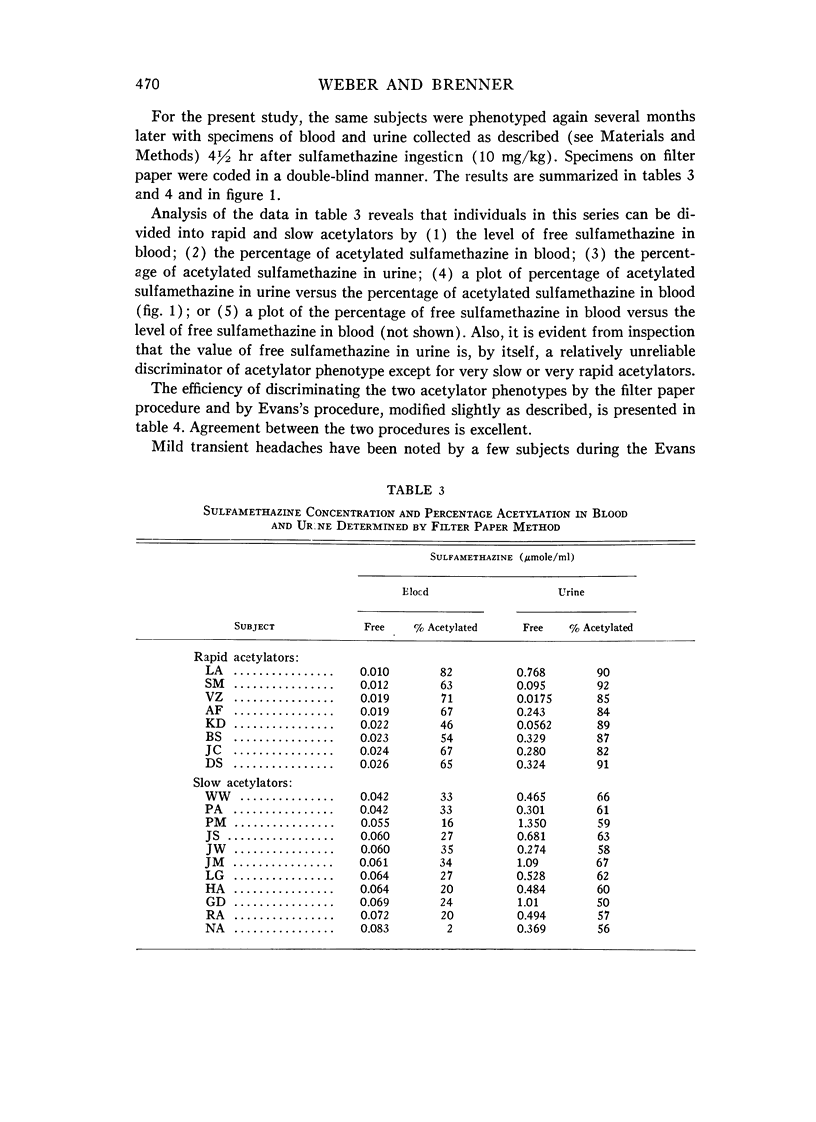
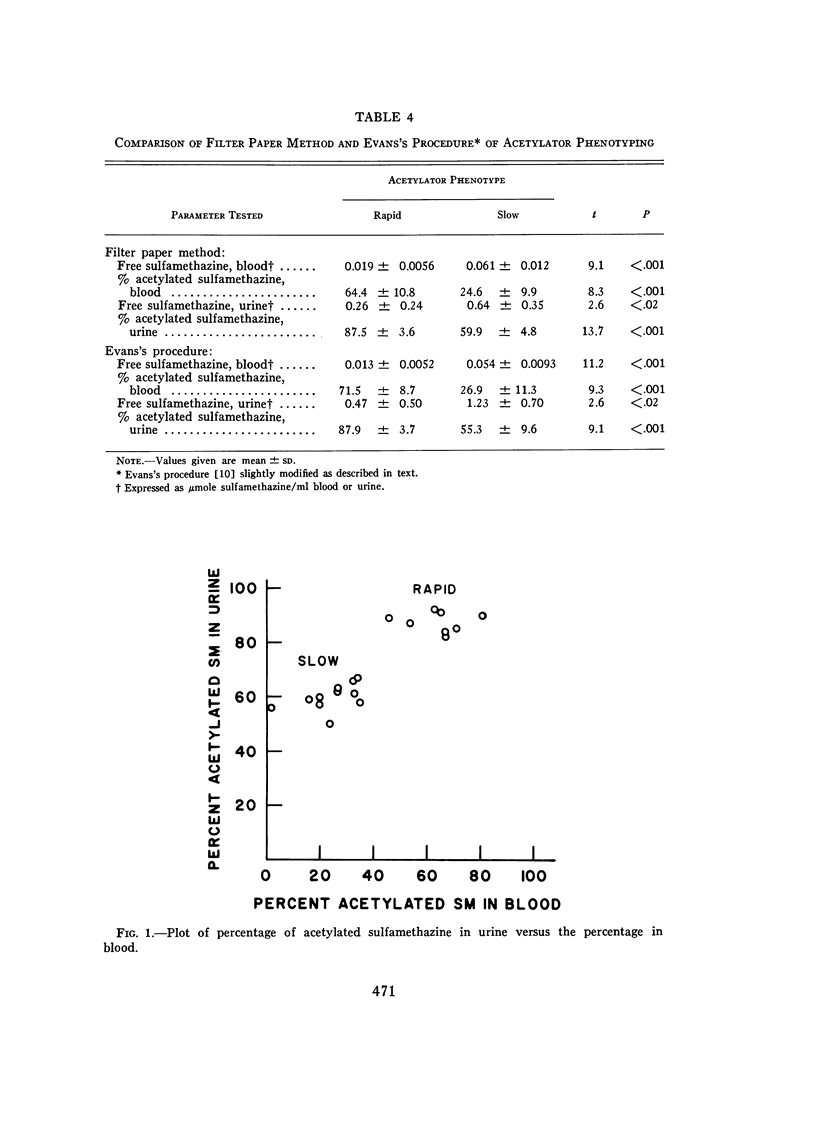
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EVANS D. A., MANLEY K. A., McKUSICK V. A. Genetic control of isoniazid metabolism in man. Br Med J. 1960 Aug 13;2(5197):485–491. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5197.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidus L., Hodgkin M. M. Screening of isoniazid inactivators. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jan;3(1):130–133. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.1.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidus L., Hodgkin M. M. Simplified screening test for phenotyping of isoniazid inactivators. Int J Clin Pharmacol. 1973 Feb;7(1):82–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellard G. A., Gammon P. T., Polansky F., Víznerová A., Havlík I., Fox W. Further studies on the pharmacology of a slow-release matrix preparation of isoniazid (Smith and Nephew HS 82) of potential use in the intermittent treatment of tuberculosis. Tubercle. 1973 Mar;54(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(73)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. A. An improved and simplified method of detecting the acetylator phenotype. J Med Genet. 1969 Dec;6(4):405–407. doi: 10.1136/jmg.6.4.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eze L. C., Evans D. A. The use of the autoanalyzer to determine the acetylator phenotype. J Med Genet. 1972 Mar;9(1):57–59. doi: 10.1136/jmg.9.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearse D. J., Weber W. W. Multiple N-acetyltransferases and drug metabolism. Tissue distribution, characterization and significance of mammalian N-acetyltransferase. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;132(3):519–526. doi: 10.1042/bj1320519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENNE J. W. Studies of human patterns of isoniazid metabolism using an intravenous fall-off technique with a chemical method. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1960 Jan;81:1–8. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1960.81.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanes C. W., Schaefer O., Eidus L. Inactivation of isoniazid by Canadian Eskimos and Indians. Can Med Assoc J. 1972 Feb 19;106(4):331–335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila M. J., Tiitinen H. The rate of isoniazid inactivation in Finnish diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1967;45(4):423–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. M. Human variability in the metabolism of sulfamethazine. Hum Hered. 1969;19(4):402–409. doi: 10.1159/000152245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao K. V., Mitchison D. A., Nair N. G., Prema K., Tripathy S. P. Sulphadimidine acetylation test for classification of patients as slow or rapid inactivators of isoniazid. Br Med J. 1970 Aug 29;3(5721):495–497. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5721.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H., Evans D. A. The polymorphic acetylation of sulphapyridine in man. J Med Genet. 1972 Jun;9(2):168–171. doi: 10.1136/jmg.9.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. Simplified method for determining acetylator phenotype. Br Med J. 1972 Aug 26;3(5825):506–507. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5825.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E. M., Wright R. C., Weaver D. D. The discrimination of phenotypes for rate of disappearance of isonicotinoyl hydrazide from serum. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jul;48(7):1173–1176. doi: 10.1172/JCI106081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


