Abstract
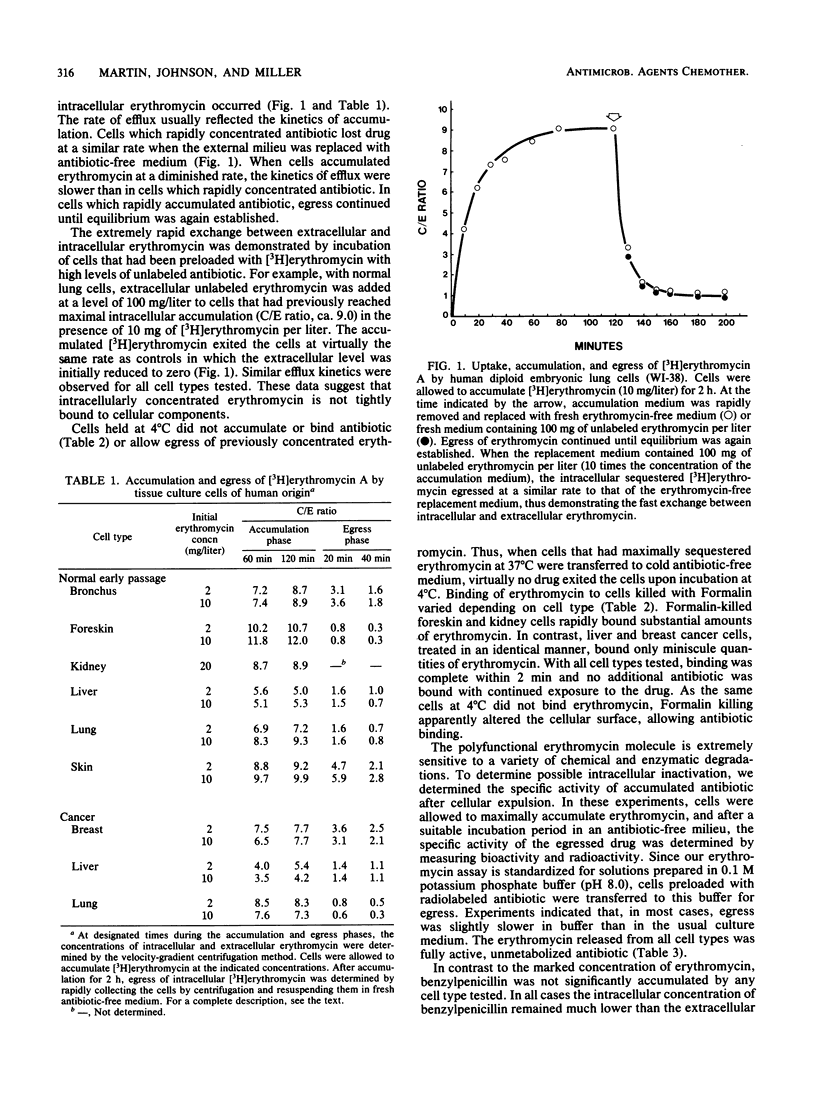
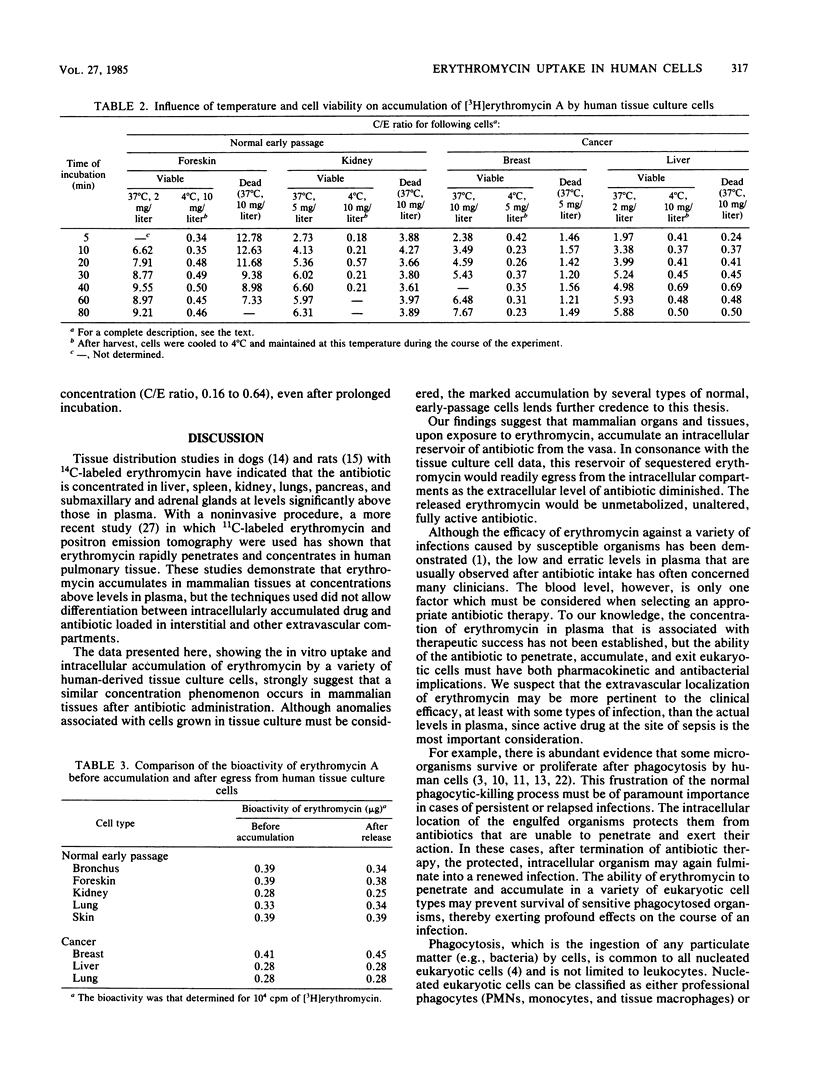
The ability of erythromycin A base to penetrate and accumulate in tissue culture cells of human origin was investigated. The antibiotic was highly concentrated by early passage cells of normal bronchus, kidney, liver, lung, and skin and by cancer cells derived from breast, liver, and lung. Intracellular levels 4 to 12 times that of the extracellular milieu were obtained in both early-passage and transformed cells. The total quantity of erythromycin accumulated depended on the extracellular concentration of antibiotic, but the cellular/extracellular ratios were, for the most part, independent of the initial extracellular drug concentration. In all cell types tested, the accumulated antibiotic rapidly egressed when cells were incubated in antibiotic-free medium. Bioactivity assays demonstrated that the expelled drug was unmetabolized, fully active antibiotic. The concentration of erythromycin by a variety of human cell types probably accounts, in part, for the effectiveness of the antibiotic against intracellular parasites such as Legionella and Chlamydia spp.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Easmon C. S. The effect of antibiotics on the intracellular survival of Staphylococcus aureus in vitro. Br J Exp Pathol. 1979 Feb;60(1):24–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelson P. J. Intracellular parasites and phagocytic cells: cell biology and pathophysiology. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):124–135. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.1.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogliani J., Domenget J. F., Hohn B., Merignargues G., Bornstein N. Maladie des légionnaires avec localisation digestive. Une observation. Nouv Presse Med. 1982 Sep 18;11(36):2699–2702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. H., Raff M. C. Induction of increased calcium uptake in mouse T lymphocytes by concanavalin A and its modulation by cyclic nucleotides. Nature. 1975 May 29;255(5507):378–382. doi: 10.1038/255378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatell J. M., Miro J. M., Sasal M., Ferrer O., Rodriguez M., Garcia San Miguel J. Legionella pneumophila antigen in brain. Lancet. 1981 Jul 25;2(8239):202–203. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., King-Thompson N. L., Steinberg T. H. Interactions of antibiotics and phagocytes. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Oct;12 (Suppl 100):1–11. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_c.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Quie P. G., Windhorst D. B., Pollara B., Good R. A. Protection of phagocytized bacteria from the killing action of antibiotics. Nature. 1966 Jun 11;210(5041):1131–1132. doi: 10.1038/2101131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of microorganisms. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):104–123. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humayun H. M., Bird T. J., Daugirdas J. T., Fruin R. C., Shawky M. M., Ing T. S. Legionnaires' disease bacillus in bone marrow. Can Med Assoc J. 1981 Nov 15;125(10):1084–1085. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Hand W. L., Francis J. B., King-Thompson N., Corwin R. W. Antibiotic uptake by alveolar macrophages. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Mar;95(3):429–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE C. C., ANDERSON R. C., CHEN K. K. Distribution and excretion of radioactivity in rats receiving N-methyl-C14-erythromycin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1956 Jul;117(3):265–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam C., Mathison G. E. Effect of low intraphagolysosomal pH on antimicrobial activity of antibiotics against ingested staphylococci. J Med Microbiol. 1983 Aug;16(3):309–316. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-3-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe R. E., Baldwin J. C., McGregor C. A., Miller D. C., Vosti K. L. Prosthetic valve endocarditis caused by Legionella pneumophila. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Apr;100(4):525–527. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-4-525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D. Legionella infections: a review of five years of research. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):258–278. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. F., Martin J. R., Johnson P., Ulrich J. T., Rdzok E. J., Billing P. Erythromycin uptake and accumulation by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and efficacy of erythromycin in killing ingested Legionella pneumophila. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):714–718. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesanti E. L. Protection of staphylococci ingested by macrophages from the bactericidal action of rifampin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):208–209. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokesch R. C., Hand W. L. Antibiotic entry into human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Mar;21(3):373–380. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts J. C., Hicklin M. D., Thomason B. M., Callaway C. S., Levine A. J. Fatal pneumonia caused by Legionella pneumophila, serogroup 3: demonstration of the bacilli in extrathoracic organs. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Feb;92(2 Pt 1):186–188. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-2-186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenburger D. D., Rappaport H., Ahluwalia M. S., Melvani R., Renner E. D. Legionnaires' disease. Am J Med. 1980 Sep;69(3):476–482. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. J., Felton W. W., Sun C. N. Extrapulmonary histopathologic manifestations of Legionnaires' disease: evidence for myocarditis and bacteremia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1980 Jun;104(6):287–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollmer P., Pride N. B., Rhodes C. G., Sanders A., Pike V. W., Palmer A. J., Silvester D. J., Liss R. H. Measurement of pulmonary erythromycin concentration in patients with lobar pneumonia by means of positron tomography. Lancet. 1982 Dec 18;2(8312):1361–1364. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Mizuguchi Y. Antibiotic susceptibility of Legionella pneumophia Philadelphia-1 in cultured guinea-pig peritoneal macrophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Apr;130(4):901–906. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-4-901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


