Abstract
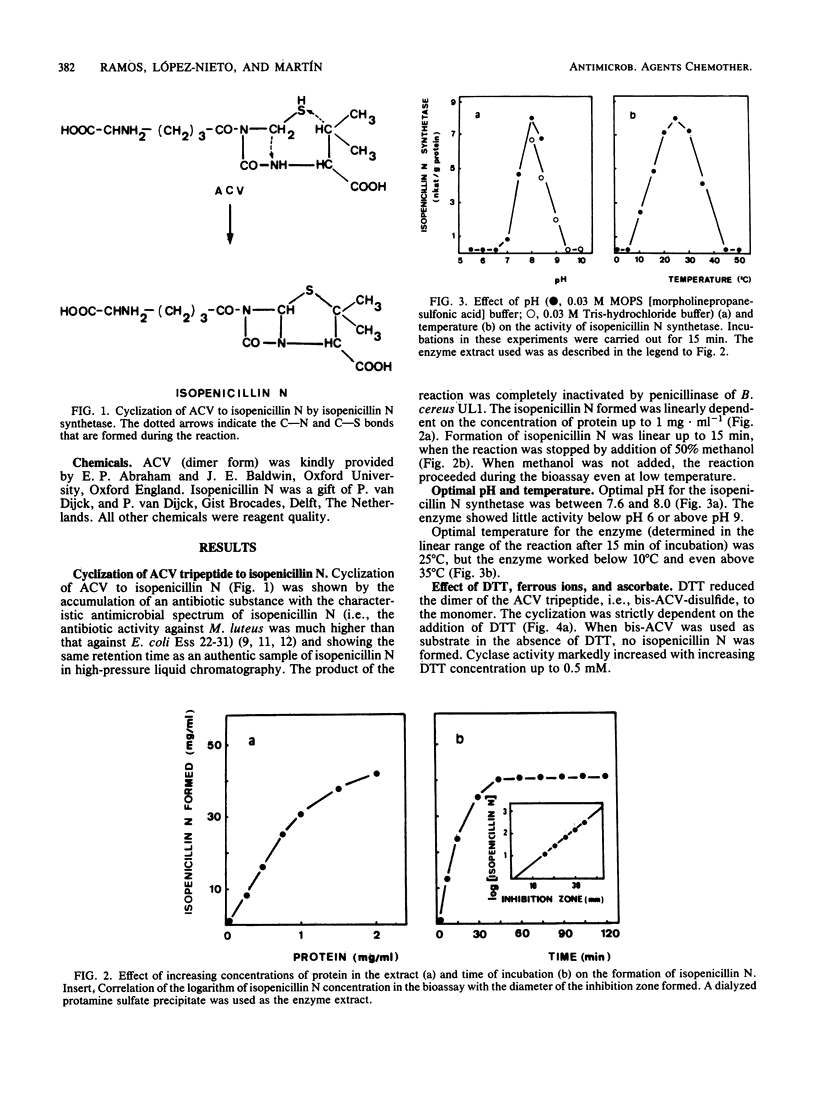
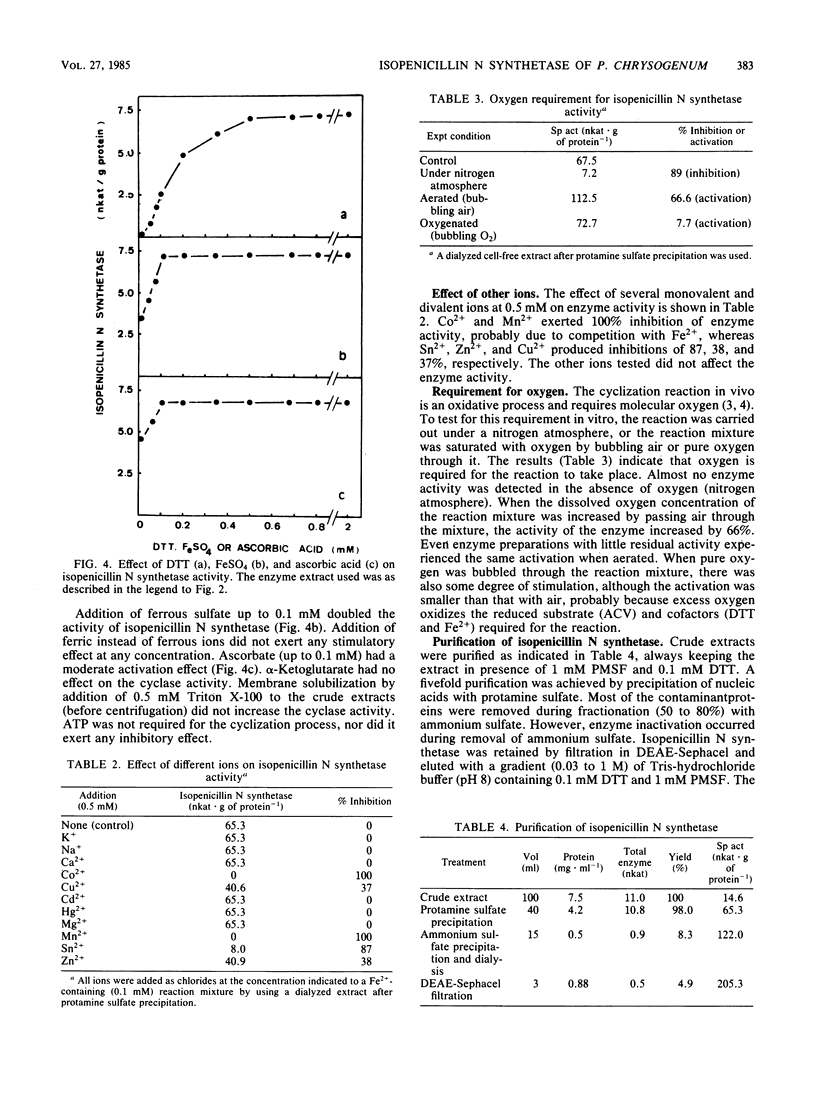
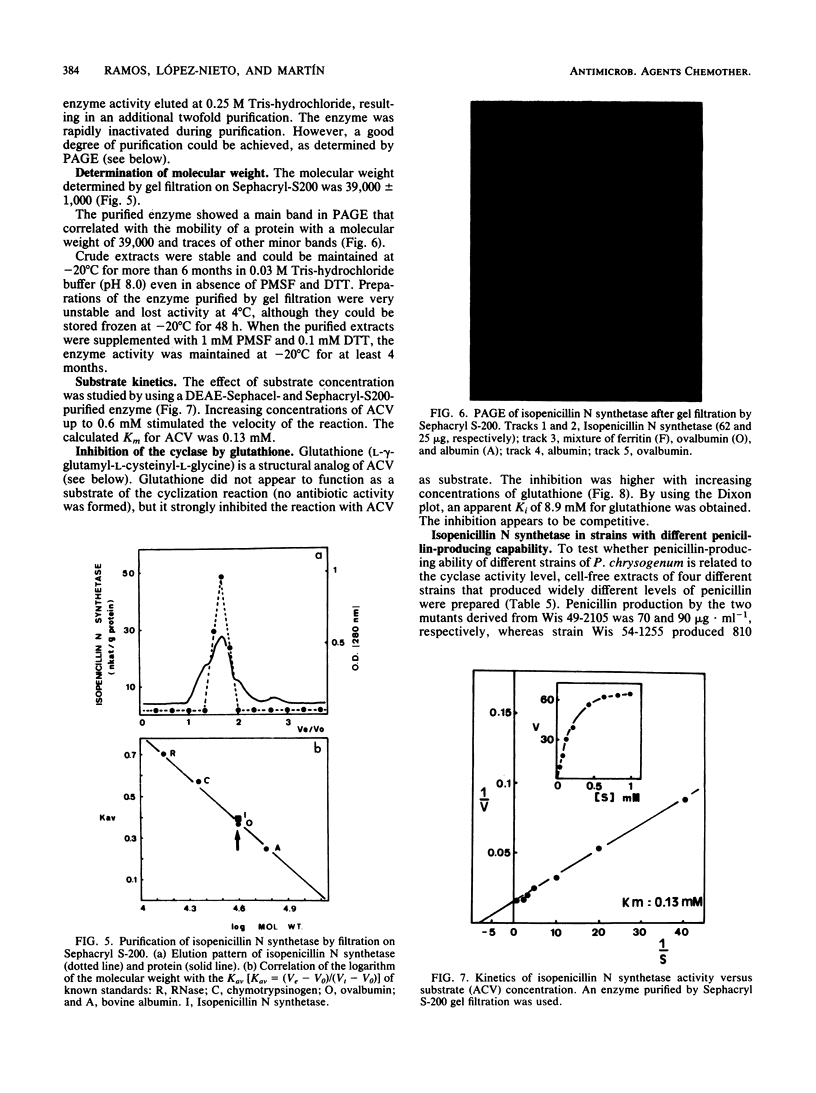
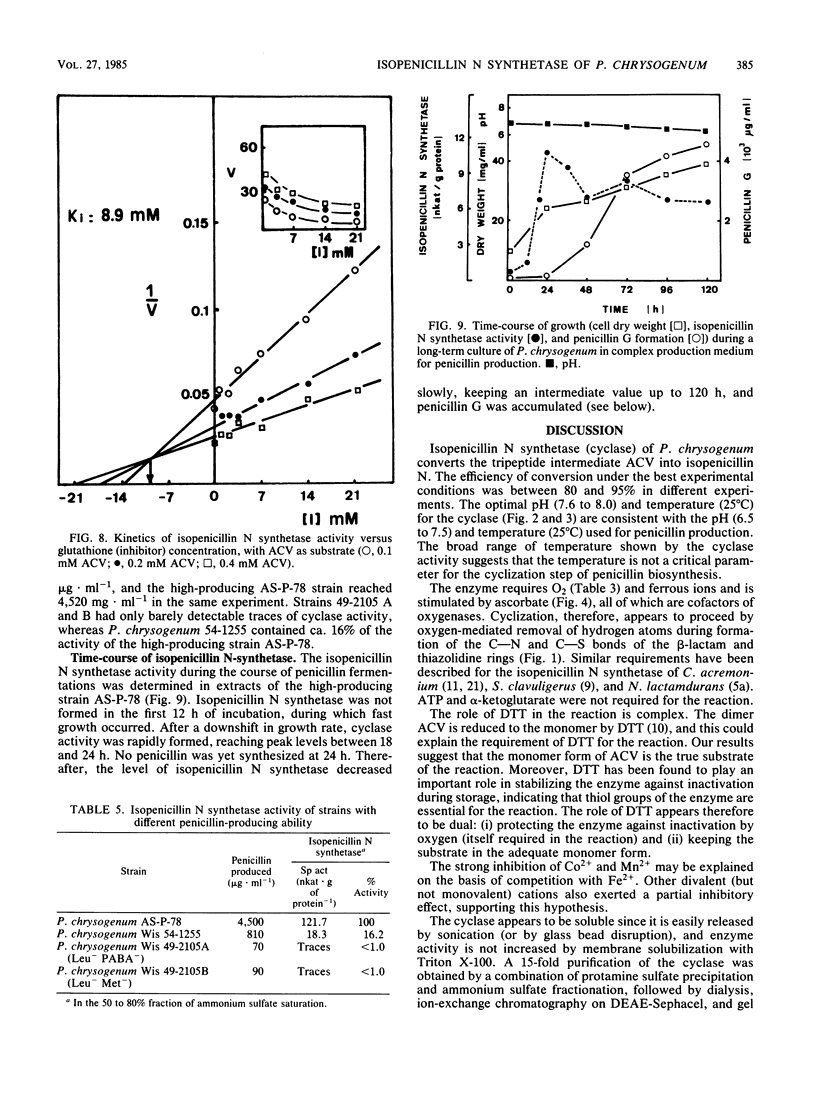
The tripeptide delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine, an intermediate in the penicillin biosynthetic pathway, is converted to isopenicillin N by isopenicillin N synthetase (cyclase) of Penicillium chrysogenum. The cyclization required dithiothreitol and was stimulated by ferrous ions and ascorbate. Co2+ and Mn2+ completely inhibited enzyme activity. Optimal temperature and pH were 25 degrees C and 7.8, respectively. The reaction required O2 and was stimulated by increasing the dissolved oxygen concentration of the reaction mixture. Purification of the enzyme to a single major band in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis was achieved by protamine sulfate precipitation, ammonium sulfate fractionation (50 to 80% of saturation), DEAE-Sephacel chromatography, and gel filtration on Sephacryl S-200. The estimated molecular weight was 39,000 +/- 1,000. The apparent Km of isopenicillin N synthetase for delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine was 0.13 mM. The enzyme activity was strongly inhibited by glutathione, which acts as a competitive inhibitor. A good correlation was observed between the isopenicillin N synthetase activity in extracts of four different strains of P. chrysogenum (with widely different penicillin-producing capability) and the amount of penicillin production by these strains.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adriaens P., Meesschaert B., Wuyts W., Vanderhaeghe H., Eyssen H. Presence of delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine in fermentations of Penicillium chrysogenum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Dec;8(6):638–642. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.6.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anné J., Peberdy J. F. Induced fusion of fungal protoplasts following treatment with polyethylene glycol. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Feb;92(2):413–417. doi: 10.1099/00221287-92-2-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. A., Huang F. C., Sih C. J. The absolute configuration of the amino acids in delta-(alpha-aminoadipyl)cysteinylvaline from Penicillium chrysogenum. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 13;15(1):177–180. doi: 10.1021/bi00646a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander I. J., Shen Y. Q., Heim J., Demain A. L., Wolfe S. A pure enzyme catalyzing penicillin biosynthesis. Science. 1984 May 11;224(4649):610–612. doi: 10.1126/science.6546810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. E., Westlake D. W., Wolfe S. Cyclization of delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine to penicillins by cell-free extracts of Streptomyces clavuligerus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Apr;35(4):483–490. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. E., Westlake D. W., Wolfe S. High performance liquid chromatographic assay of cyclization activity in cell-free systems from Streptomyces clavuligerus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Aug;35(8):1026–1032. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konomi T., Herchen S., Baldwin J. E., Yoshida M., Hunt N. A., Demain A. L. Cell-free conversion of delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine into an antibiotic with the properties of isopenicillin N in Cephalosporium acremonium. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 15;184(2):427–430. doi: 10.1042/bj1840427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupka J., Shen Y. Q., Wolfe S., Demain A. L. Studies on the ring-cyclization and ring-expansion enzymes of beta-lactam biosynthesis in Cephalosporium acremonium. Can J Microbiol. 1983 May;29(5):488–496. doi: 10.1139/m83-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luengo J. M., Revilla G., López M. J., Villanueva J. R., Martín J. F. Inhibition and repression of homocitrate synthase by lysine in Penicillium chrysogenum. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):869–876. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.869-876.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luengo J. M., Revilla G., Villanueva J. R., Martín J. F. Lysine regulation of penicillin biosynthesis in low-producing and industrial strains of Penicillium chrysogenum. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Nov;115(1):207–211. doi: 10.1099/00221287-115-1-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D. M., Martín J. F. Carbon catabolite regulation of the conversion of penicillin N into cephalosporin C. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1983 Jun;36(6):700–708. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.36.700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meesschaert B., Adriaens P., Eyssen H. Studies on the biosynthesis of isopenicillin N with a cell-free preparation of Penicillium chrysogenum. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1980 Jul;33(7):722–730. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.33.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada Y., Baldwin J. E., Singh P. D., Solomon N. A., Demain A. L. Cell-free cyclization of delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine to isopenicillin N. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Sep;18(3):465–470. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]