Abstract
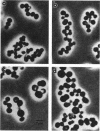
There are four penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) in Staphylococcus aureus, of which PBPs 2 and 3 are essential. Cefotaxime binds selectively to PBP 2, and cephalexin binds to PBP 3, each at its respective MIC. The morphology of S. aureus strains grown in the presence of the two antibiotics was examined by phase-contrast and scanning electron microscopy. Exposure of the cells to cefotaxime at concentrations at which it bound selectively to PBP 2 resulted in the extrusion of cytoplasm and cell lysis, whereas exposure to cephalexin at concentrations at which it bound exclusively to PBP 3 resulted in cell enlargement and the cessation of septation. The latter morphological response was very similar to that produced by norfloxacin. The results suggest that in S. aureus, PBP 2 may be the primary peptidoglycan transpeptidase, and PBP 3 may be involved in septation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amanuma H., Strominger J. L. Purification and properties of penicillin-binding proteins 5 and 6 from Escherichia coli membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11173–11180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHATTERJEE A. N., PARK J. T. BIOSYNTHESIS OF CELL WALL MUCOPEPTIDE BY A PARTICULATE FRACTION FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jan;51:9–16. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumplin G. C., Kenwright M., Hirst T. Investigations into the mechanism of action of the antibacterial agent norfloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 May;13 (Suppl B):9–23. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.suppl_b.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis N. A., Orr D., Ross G. W., Boulton M. G. Affinities of penicillins and cephalosporins for the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K-12 and their antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):533–539. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Koller A. E., Tomasz A. Competition of beta-lactam antibiotics for the penicillin-binding proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):109–114. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. Novobiocin and coumermycin inhibit DNA supercoiling catalyzed by DNA gyrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Liu F. Y. Binding of beta-lactam antibiotics to penicillin-binding proteins of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus faecalis: relation to antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):834–836. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Liu F. Y. Penicillin-binding proteins in bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):148–157. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Smith S. A., Sykes R. B. Penicillin-binding proteins in Bacteroides fragilis. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1983 Jul;36(7):907–910. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.36.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D., O'Grady F. Scanning electron microscopy of Staphyloccus aureus exposed to some common anti-staphylococcal agents. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Apr;70(2):263–270. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozarich J. W., Strominger J. L. A membrane enzyme from Staphylococcus aureus which catalyzes transpeptidase, carboxypeptidase, and penicillinase activities. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1272–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer M. J., Mauriz V. R. Correlation by scanning electron microscopy of in vitro and in vivo effects of amoxicillin and ampicillin on the morphology of Escherichia coli. Scan Electron Microsc. 1979;(3):33–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorian V., Atkinson B. Effects of subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics on cross walls of cocci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):1043–1055. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makover S. D., Wright R., Telep E. Penicillin-binding proteins in Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):584–588. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino T., Nakazawa S. Bacteriological study on effects of beta-lactam group antibiotics in high concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):1033–1042. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Drlica K. DNA gyrase on the bacterial chromosome: DNA cleavage induced by oxolinic acid. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):287–302. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suginaka H., Blumberg P. M., Strominger J. L. Multiple penicillin-binding components in Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 10;247(17):5279–5288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata K., Yamashita N., Konno M. Occurrence of a beta-lactam-inducible penicillin-binding protein in methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):851–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Hakenbeck R., Tomasz A. In vivo interaction of beta-lactam antibiotics with the penicillin-binding proteins of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Oct;18(4):629–637. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyke A. W., Ward J. B., Hayes M. V., Curtis N. A. A role in vivo for penicillin-binding protein-4 of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(2):389–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyke A. W., Ward J. B., Hayes M. V. Synthesis of peptidoglycan in vivo in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(3):553–558. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]