Abstract
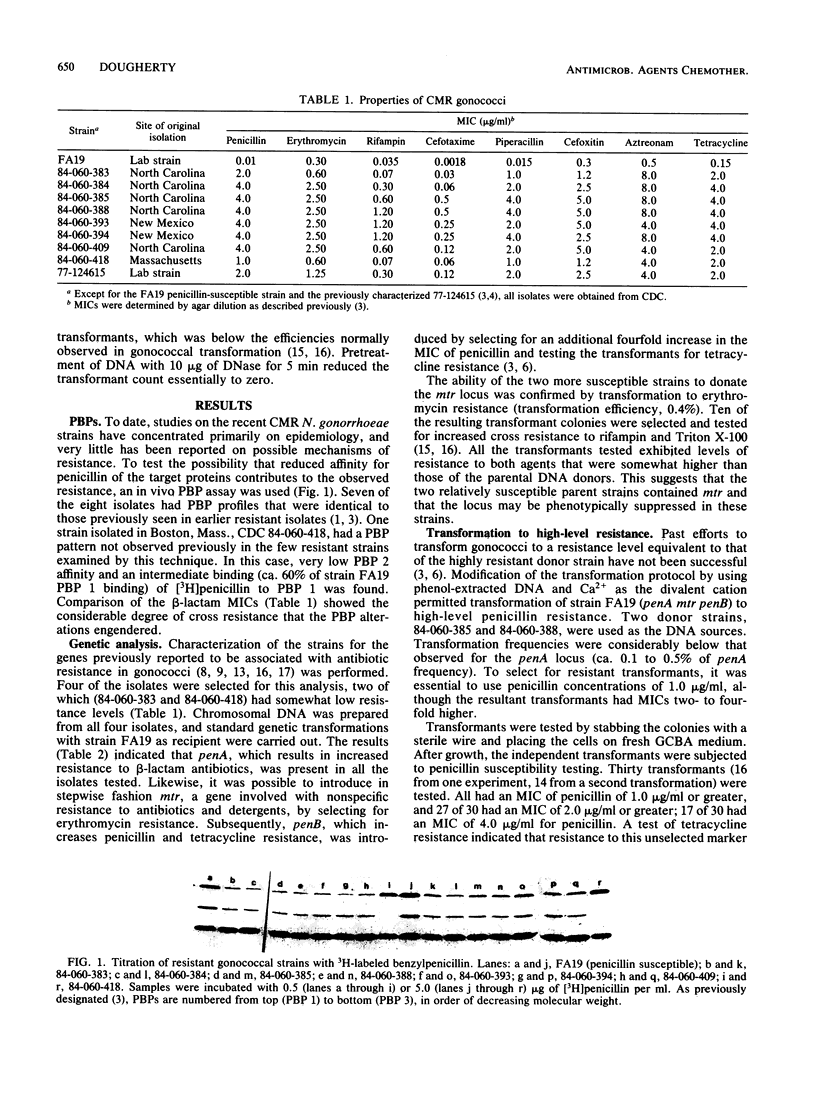
Eight recent isolates of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with high-level non-beta-lactamase-mediated penicillin resistance were investigated. The penicillin-binding proteins of these strains were found to have reduced affinity for radiolabeled penicillin. Testing for known resistance genes showed that these were present in the resistant isolates. Genetic transformation was used to construct strains with increasing levels of antibiotic resistance. Modification of the transformation protocol made it possible to isolate transformants at the highest (penicillin-resistant DNA donor) level of resistance. These transformants unexpectedly yielded two distinct penicillin-binding protein patterns when tested.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G. Properties of penicillin-binding proteins in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):316–322. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Asmus A., Tomasz A. Specificity of DNA uptake in genetic transformation of gonococci. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jan 15;86(1):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Koller A. E., Tomasz A. Competition of beta-lactam antibiotics for the penicillin-binding proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):109–114. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Koller A. E., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins of penicillin-susceptible and intrinsically resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):730–737. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faruki H., Kohmescher R. N., McKinney W. P., Sparling P. F. A community-based outbreak of infection with penicillin-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae not producing penicillinase (chromosomally mediated resistance). N Engl J Med. 1985 Sep 5;313(10):607–611. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198509053131004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier T. W., Zubrzycki L., Coyle M. B., Chila M., Warner P. Genetic analysis of drug resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: production of increased resistance by the combination of two antibiotic resistance loci. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):834–842. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.834-842.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier T. W., Zubrzycki L., Coyle M. B. Genetic analysis of drug resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: identification and linkage relationships of loci controlling drug resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 May;7(5):676–681. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.5.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. J., Biddle J. W., JeanLouis Y. A., DeWitt W. E., Blount J. H., Morse S. A. Chromosomally mediated resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the United States: results of surveillance and reporting, 1983-1984. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):340–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. J., Blount J. H., Biddle J. W., JeanLouis Y., Morse S. A. Changing trends in gonococcal antibiotic resistance in the United States, 1983-1984. MMWR CDC Surveill Summ. 1984;33(4):11SS–15SS. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarubbi F. A., Jr, Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Genetic mapping of linked antibiotic resistance loci in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1284–1292. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1284-1292.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarubbi F. A., Jr, Sparling P. F., Blackman E., Lewis E. Loss of low-level antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae due to env mutations. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):750–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.750-756.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F., Sarubbi F. A., Jr, Blackman E. Inheritance of low-level resistance to penicillin, tetracycline, and chloramphenicol in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):740–749. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.740-749.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner P. F., Zubrzycki L. J., Chila M. Polygenes and modifier genes for tetracycline and penicillin resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Mar;117(1):103–110. doi: 10.1099/00221287-117-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]