Abstract
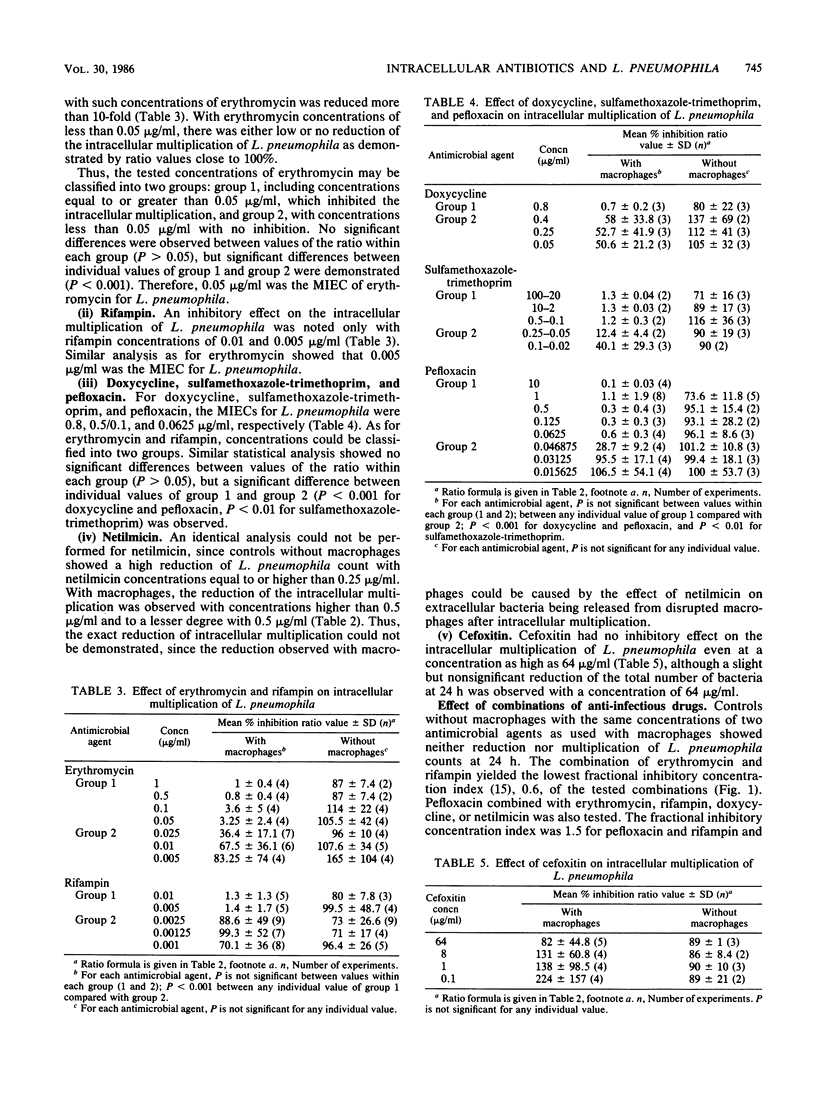
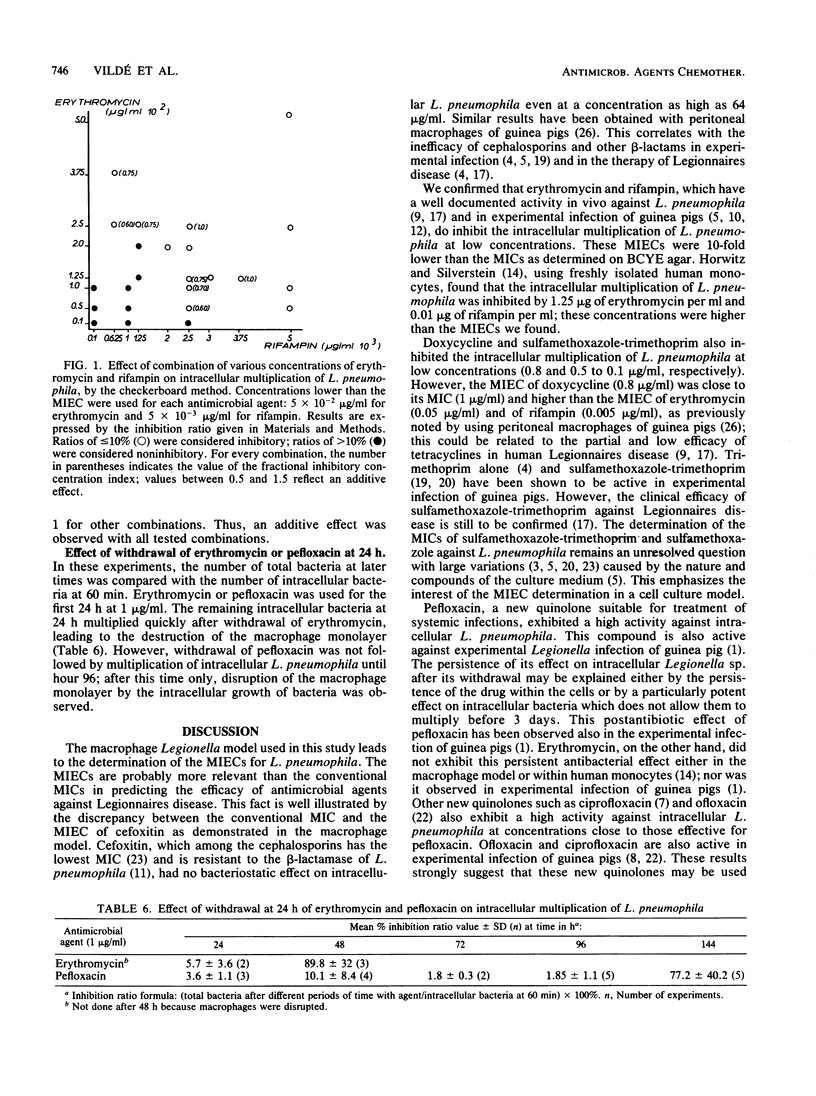
The activity of serial concentrations of different antimicrobial agents on the multiplication of Legionella pneumophila within human monocyte-derived macrophages was studied. The results led to the definition of a minimal extracellular concentration inhibiting intracellular multiplication (MIEC). According to the MIECs, the antimicrobial agents tested were classified in three groups: very active (MIEC less than or equal to 0.06 microgram/ml), such as erythromycin, rifampin, and pefloxacin; active (1 microgram/ml greater than or equal to MIEC greater than or equal to 0.1 microgram/ml), such as sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim or doxycycline; and ineffective, such as cefoxitin, which was not active within macrophages at as high as 64 micrograms/ml despite a low MIC (0.2 microgram/ml) on bacterial charcoal-yeast extract agar. The activity of netilmicin was difficult to assess because of its effect on extracellular legionellae. Combinations of erythromycin with rifampin and pefloxacin with erythromycin, rifampin, doxycycline, or netilmicin showed an additive effect and no antagonism. These results obtained in a cellular model are in agreement with the efficacy of antimicrobial agents in experimental infections and in Legionnaires disease. They sustain clinical interest in the new quinolones, such as pefloxacin, and in combinations of antimicrobial agents for the treatment of Legionnaires disease.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dournon E., Rajagopalan P., Vilde J. L., Pocidalo J. J. Efficacy of pefloxacin in comparison with erythromycin in the treatment of experimental guinea pig legionellosis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17 (Suppl B):41–48. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.suppl_b.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. N., Kroboth F. J., Karpf M., Yee R. B., Pasculle A. W. Pneumonia and multiple lung abscesses caused by dual infection with Legionella micdadei and Legionella pneumophila. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Jan;127(1):121–125. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.1.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. N., McDevitt D. A., Pasculle A. W. Disk diffusion antimicrobial susceptibility testing of members of the family Legionellaceae including erythromycin-resistant variants of Legionella micdadei. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):723–729. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.723-729.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Calarco K., Yasui V. K. Antimicrobial therapy of experimentally induced Legionnaires' disease in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Nov;130(5):849–856. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.5.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Imipenem in Legionnaires' disease. Lancet. 1984 Sep 29;2(8405):757–757. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92669-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Meyer R. D. Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila to twenty antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Sep;18(3):403–408. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.3.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgeorge R. B., Gibson D. H., Jepras R., Baskerville A. Studies on ciprofloxacin therapy of experimental Legionnaires' disease. J Infect. 1985 May;10(3):194–203. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(85)92438-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgeorge R. B. The effect of antibiotics on the growth of Legionella pneumophila in guinea-pig alveolar phagocytes infected in vivo by an aerosol. J Infect. 1985 May;10(3):189–193. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(85)92413-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W., Tsai T. R., Orenstein W., Parkin W. E., Beecham H. J., Sharrar R. G., Harris J., Mallison G. F., Martin S. M., McDade J. E. Legionnaires' disease: description of an epidemic of pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1189–1197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W., Wachsmuth I., Bopp C., Feeley J. C., Tsai T. F. Antibiotic treatment of guinea-pigs infected with agent of Legionnaires' disease. Lancet. 1978 Jan 28;1(8057):175–178. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90611-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. Inactivation of beta-lactam antibiotics by Legionella pneumophila. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):561–564. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. H., Fitzgeorge R. B., Baskerville A. Antibiotic therapy of experimental airborne Legionnaires' disease. J Infect. 1983 Nov;7(3):210–217. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(83)97034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Intracellular multiplication of Legionnaires' disease bacteria (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes is reversibly inhibited by erythromycin and rifampin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):15–26. doi: 10.1172/JCI110744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) multiples intracellularly in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):441–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI109874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis V. J., Thacker W. L., Shepard C. C., McDade J. E. In vivo susceptibility of the Legionnaires disease bacterium to ten antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):419–422. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D. Legionella infections: a review of five years of research. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):258–278. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. M., Macher A. M., Shelhamer J. H., Balow J. E., Gill V., Parrillo J. E. Unresponsiveness of Legionella bozemanii pneumonia to erythromycin administration despite in vitro sensitivity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Nov;128(5):955–956. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.5.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Dowling J. N., Frola F. N., McDevitt D. A., Levi M. A. Antimicrobial therapy of experimental Legionella micdadei pneumonia in guinea pigs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Dec;28(6):730–734. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.6.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plouffe J. F., Para M. F., Bollin G. E. Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim treatment of guinea pigs infected with Legionella pneumophila. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):780–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudin J. E., Evans T. L., Wing E. J. Failure of erythromycin in treatment of Legionella micdadei pneumonia. Am J Med. 1984 Feb;76(2):318–320. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90793-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Sawatari K., Fukuda Y., Nagasawa M., Koga H., Tomonaga A., Nakazato H., Fujita K., Shigeno Y., Suzuyama Y. Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila to ofloxacin in vitro and in experimental Legionella pneumonia in guinea pigs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):15–20. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Baker C. N., Kirven L. A. In vitro activity of antimicrobial agents on Legionnaires disease bacterium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):78–80. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Mizuguchi Y. Antibiotic susceptibility of Legionella pneumophia Philadelphia-1 in cultured guinea-pig peritoneal macrophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Apr;130(4):901–906. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-4-901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


