Abstract
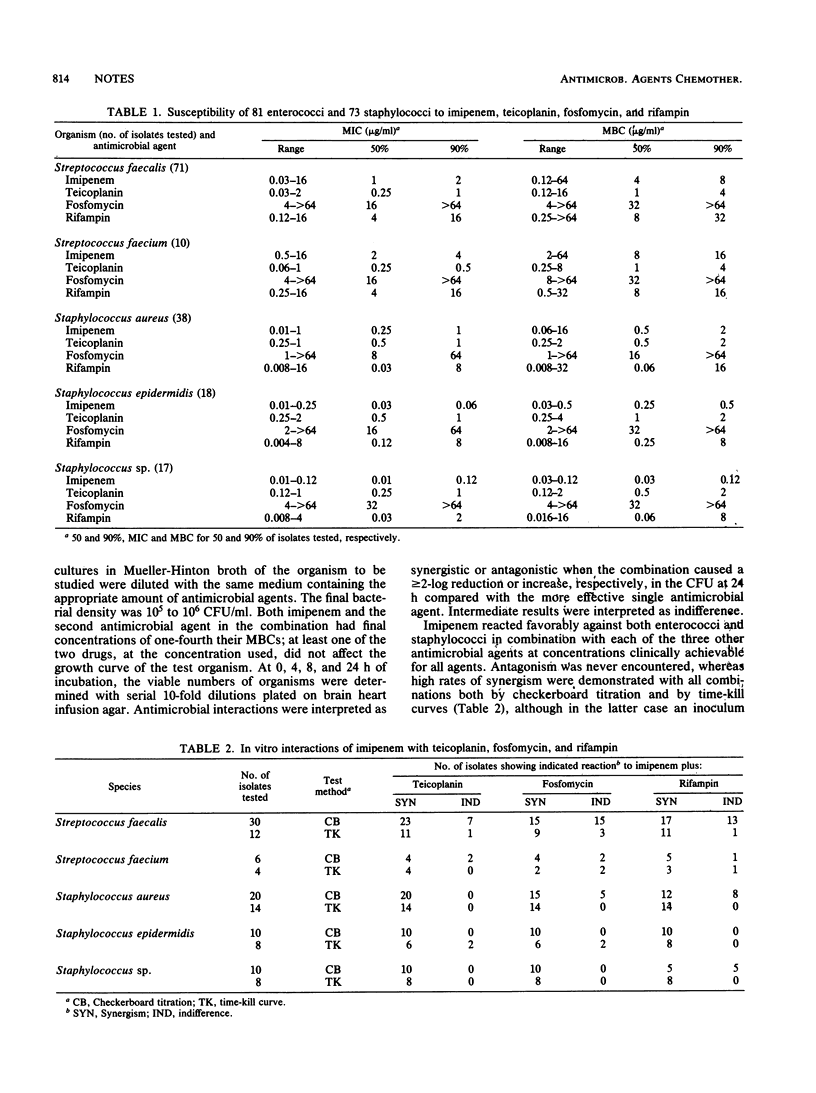
The in vitro activities of imipenem alone and in combination with teicoplanin, fosfomycin, and rifampin were tested against clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci. In both groups of organisms, the three combinations demonstrated high rates of synergism in both checkerboard and time-kill studies.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ampel N. M., Moon-McDermott L., Keating M., Zinner S. H. In-vitro activity of aztreonam in combination with four other antibiotics against gram-negative bacilli and Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Apr;13(4):398–399. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.4.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auckenthaler R., Wilson W. R., Wright A. J., Washington J. A., 2nd, Durack D. T., Geraci J. E. Lack of in vivo and in vitro bactericidal activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin against enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):448–452. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aznar J., García Iglesias M. C., Perea E. J. Comparative activity of imipenem (N-formimidoyl thienamycin) on enterococci and its interactions with aminoglycosides. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Feb;13(2):129–132. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertram M. A., Young L. S. Imipenem antagonism of the in vitro activity of piperacillin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):272–274. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braveny I. In vitro activity of imipenem--a review. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;3(5):456–462. doi: 10.1007/BF02017375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., Alford R. H. Antagonism by chloramphenicol of broad-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotics against Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):405–407. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díez Enciso M., Mateos Lindemann M., Gutiérrez Altés A. In vitro evaluation of N-formimidoyl thienamycin (MK0787) combined with amikacin against gram-negative bacilli and Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Dec;22(6):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.6.1064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Moellering R. C., Jr Susceptibility of enterococci and Listeria monocytogenes to N-Formimidoyl thienamycin alone and in combination with an aminoglycoside. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):789–793. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Walder M. Antimicrobial activity of fosfomycin in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 May;11(5):467–471. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.5.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gombert M. E., Berkowitz L. B., Cummings M. C. Synergistic effect of N-formimidoyl thienamycin with gentamicin and amikacin against Streptococcus faecalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Feb;23(2):245–247. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooton T. M., Blair A. D., Turck M., Counts G. W. Synergism at clinically attainable concentrations of aminoglycoside and beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Oct;26(4):535–538. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.4.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N. Review of the in vitro spectrum of activity of imipenem. Am J Med. 1985 Jun 7;78(6A):22–32. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan F. M., Kropp H., Sundelof J. G., Birnbaum J. Thienamycin: development of imipenen-cilastatin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Dec;12 (Suppl 500):1–35. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_d.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. A., Finan M., Yousuf M. In-vitro antagonism by N-formimidoyl thienamycin and cefoxitin of second and third generation cephalosporins in Aeromonas hydrophila and Serratia marcescens. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Apr;11(4):311–318. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.4.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. Comparative in vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic species and its beta-lactamase stability. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):180–187. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes M. P., Lerner A. M. Current problems in the treatment of infective endocarditis due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):314–321. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varaldo P. E., Debbia E., Schito G. C. In vitro activities of rifapentine and rifampin, alone and in combination with six other antibiotics, against methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant staphylococci of different species. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):615–618. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varaldo P. E., Debbia E., Schito G. C. In vitro activity of teichomycin and vancomycin alone and in combination with rifampin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Mar;23(3):402–406. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.3.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varaldo P. E., Grazi G., Soro O., Cisani G., Satta G. Simplified lyogroup system, a new method for routine identification of staphylococci: description and comparison with three other methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):63–68. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.63-68.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C., Tisone J. C. Synergism between N-formimidoyl thienamycin and gentamicin or tobramycin against enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Dec;22(6):1082–1083. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.6.1082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


