Abstract
1. Administration of prostaglandin E1 (1 mg/kg, i.p.) to rats induced sedation and a decrease in muscular tone. Prostaglandin E1-induced sedation was accompanied by the low voltage-high frequency E.E.G. pattern characteristic of the waking animal.
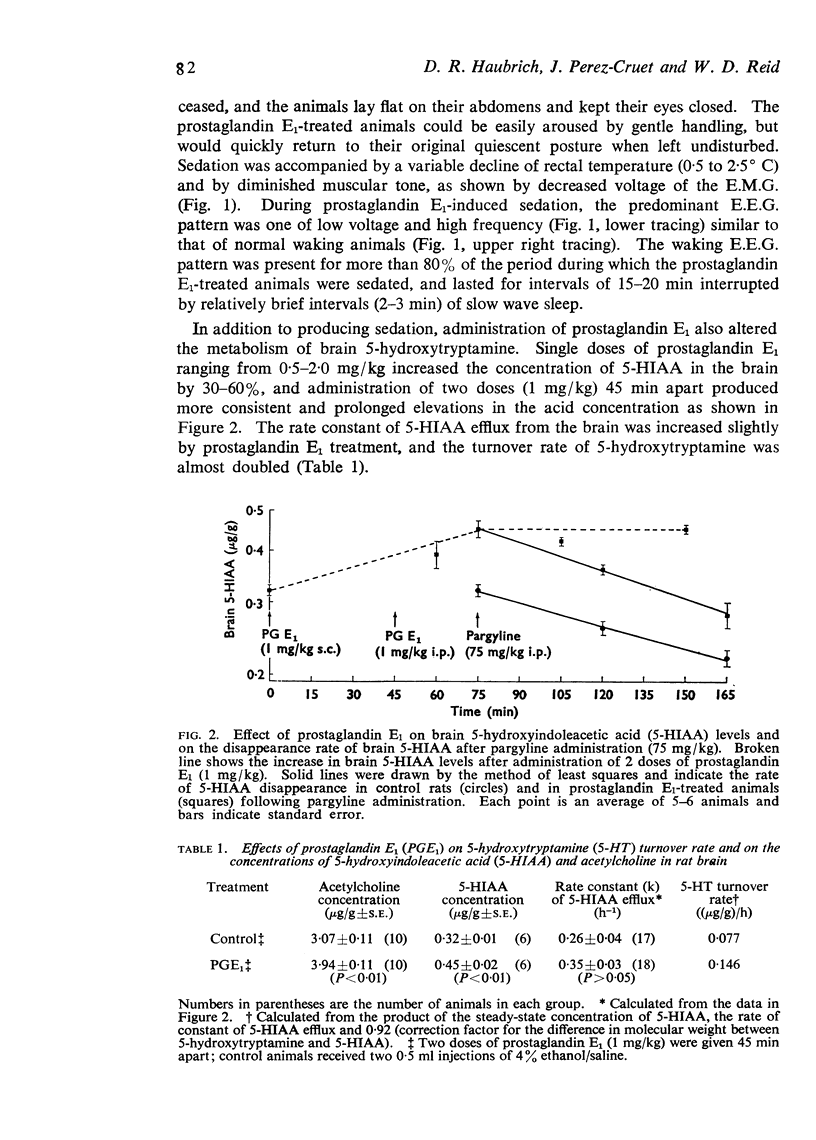
2. Administration of prostaglandin E1 also increased the turnover rate of 5-hydroxytryptamine and raised the concentration of acetylcholine in brain.
3. The behavioural effects of prostaglandin were blocked by prior administration of p-chlorophenylalanine or pargyline, drugs which lowered the brain concentration of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), and was potentiated by pretreatment with probenecid, which elevated the 5-HIAA concentration. Pretreatment with atropine sulphate failed to alter prostaglandin E1-induced sedation.
4. The results are compatible with the possibility that prostaglandin E1 induces a state resembling paradoxical sleep through an action on 5-hydroxytryptamine metabolism in brain.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avanzino G. L., Bradley P. B., Wolstencroft J. H. Actions of prostaglandins E1, E2, and F2-alpha on brain stem neurones. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 May;27(1):157–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01651.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avanzino G. L., Bradley P. B., Wolstencroft J. H. Excitatory action of prostaglandin E-1 on brain-stem neurones. Nature. 1966 Jan 1;209(5018):87–88. doi: 10.1038/209087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOGDANSKI D. F., PLETSCHER A., BRODIE B. B., UNDENFRIEND S. Identification and assay of serotonin in brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1956 May;117(1):82–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Samuels G. M., Shaw J. E. Correlation of prostaglandin release from the cerebral cortex of cats with the electrocorticogram, following stimulation of the reticular formation. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Sep;37(1):151–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb09532.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCEANI F., WOLFE L. S. PROSTAGLANDINS IN BRAIN AND THE RELEASE OF PROSTAGLANDIN-LIKE COMPOUNDS FROM THE CAT CEREBELLAR CORTEX. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1965 May;43:445–450. doi: 10.1139/y65-045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSSLAND J., MERRICK A. J. The effect of anaesthesia on the acetylcholine content of brain. J Physiol. 1954 Jul 28;125(1):56–66. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMENT W. The occurrence of low voltage, fast, electroencephalogram patterns during behavioral sleep in the cat. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1958 May;10(2):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(58)90037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldstein A., Chang F. H., Kucharski J. M. Tryptophol, 5-hydroxytryptophol and 5-methoxytryptophol induced sleep in mice. Life Sci. 1970 Mar 15;9(6):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90220-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins: their disappearance from and release into the circulation. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):868–873. doi: 10.1038/216868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEORGE R., HASLETT W. L., JENDEN D. J. A CHOLINERGIC MECHANISM IN THE BRAINSTEM RETICULAR FORMATION: INDUCTION OF PARADOXICAL SLEEP. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1964 Dec;3:541–552. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(64)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORTON E. W. ACTIONS OF PROSTAGLANDINS E1, E2 AND E3 ON THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Feb;22:189–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01558.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORTON E. W., MAIN I. H. DIFFERENCES IN THE EFFECTS OF PROSTAGLANDIN F2-ALPHA, A CONSTITUENT OF CEREBRAL TISSUE, AND PROSTAGLANDIN E1 ON CONSCIOUS CATS AND CHICKS. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1965 Apr;4:65–69. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(65)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton E. W., Main I. H. Further observations on the central nervous actions of prostaglandins F2a and E1. With an addendum on the effects of prostglandins E1 and F2a on systemic arterial blood pressure in chicks. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Aug;30(3):568–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb02163.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton E. W., Main I. H. Identification of prostaglandins in central nervous tissues of the cat and chicken. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Aug;30(3):582–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb02165.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasper H. H., Tessier J. Acetylcholine liberation from cerebral cortex during paradoxical (REM) sleep. Science. 1971 May 7;172(3983):601–602. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3983.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouvet M. Biogenic amines and the states of sleep. Science. 1969 Jan 3;163(3862):32–41. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3862.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KHAZAN N., SAWYER C. H. MECHANISMS OF PARADOXICAL SLEEP AS REVEALED BY NEUROPHYSIOLOGIC AND PHARMACOLOGIC APPROACHES IN THE RABBIT. Psychopharmacologia. 1964 Jun 8;5:457–466. doi: 10.1007/BF02193483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka K., Ramwell P. W., Jessup S. Prostaglandins: localization in subcellular particles of rat cerebral cortex. Science. 1967 Sep 8;157(3793):1187–1189. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3793.1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khazan N., Bar R., Sulman F. G. The effect of cholinergic drugs on paradoxical sleep in the rat. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1967 Jul;6(4):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(67)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostowski W., Giacalone E., Garattini S., Valzelli L. Studies on behavioural and biochemical changes in rats after lesion of midbrain raphé. Eur J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;4(4):371–376. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(68)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATSUMOTO J., JOUVET M. EFFETS DE R'ESERPINE, DOPA ET 5 HTP SUR LES DEUX 'ETATS DE SOMMEIL. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1964;158:2137–2140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz J., Harwood J. P., Forn J., Krishna G., Rodgers B., Morrow A. Effect of noradrenaline and prostaglandin E1 on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate formation in isolated pericardial fat cells of man. Nat New Biol. 1971 Apr 14;230(15):214–215. doi: 10.1038/newbio230214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouret J., Bobillier P., Jouvet M. Insomnia following parachlorophenylalanine in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1968 Dec;5(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(68)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neef N. H., Tozer T. N., Brodie B. B. Application of seady-state kinetics to studies of the transfer of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid from brain to plasma. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Nov;158(2):214–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. H., Spano P. F., Groppetti A., Wang C. T., Costa E. A simple procedure for calculating the synthesis rate of norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Mar;176(3):701–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid W. D., Haubrich D. R., Krishna G. Enzymic radioassay for acetylcholine and choline in brain. Anal Biochem. 1971 Aug;42(2):390–397. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid W. D., Volicer L., Smookler H., Beaven M. A., Brodie B. B. Brain amines and temperature regulation. Pharmacology. 1968;1(6):329–344. doi: 10.1159/000135983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMUELSSON B. IDENTIFICATION OF A SMOOTH MUSCLE-STIMULATING FACTOR IN BOVINE BRAIN. PROSTAGLANDINS AND RELATED FACTORS 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 20;84:218–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINBERG D., VAUGHAN M., NESTEL P. J., STRAND O., BERGSTROEM S. EFFECTS OF THE PROSTAGLANDINS ON HORMONE-INDUCED MOBILIZATION OF FREE FATTY ACIDS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Aug;43:1533–1540. doi: 10.1172/JCI105030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWISHER J. E. Manifestations of "activated" sleep in the rat. Science. 1962 Dec 7;138(3545):1110–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.138.3545.1110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UDENFRIEND S., WEISSBACH H., BRODIE B. B. Assay of serotonin and related metabolites, enzymes, and drugs. Methods Biochem Anal. 1958;6:95–130. doi: 10.1002/9780470110225.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


