Abstract
1. Cat isolated spleens release prostaglandins into the venous effluent in response to stimuli such as nerve stimulation, noradrenaline and angiotensin II.
2. The release of prostaglandins is abolished by pre-treatment of the spleen with indomethacin (0·3-5 μg/ml).
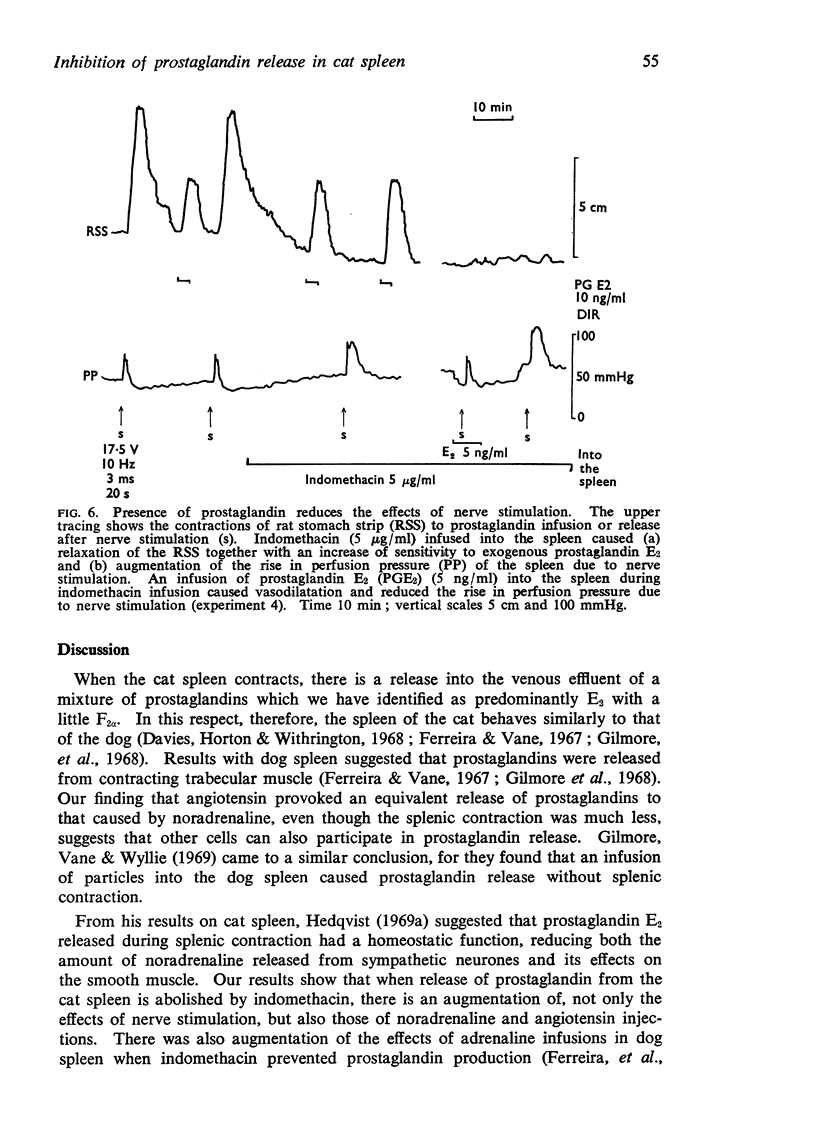
3. The capsular and vascular responses to the different stimuli are augmented after inhibition of prostaglandin release.
4. The prevention of prostaglandin release, as well as the augmentation of vascular and capsular responses, are reversible after indomethacin treatment is stopped.
5. The role of prostaglandins as modulators of the responses to several stimuli is discussed.
Full text
PDF
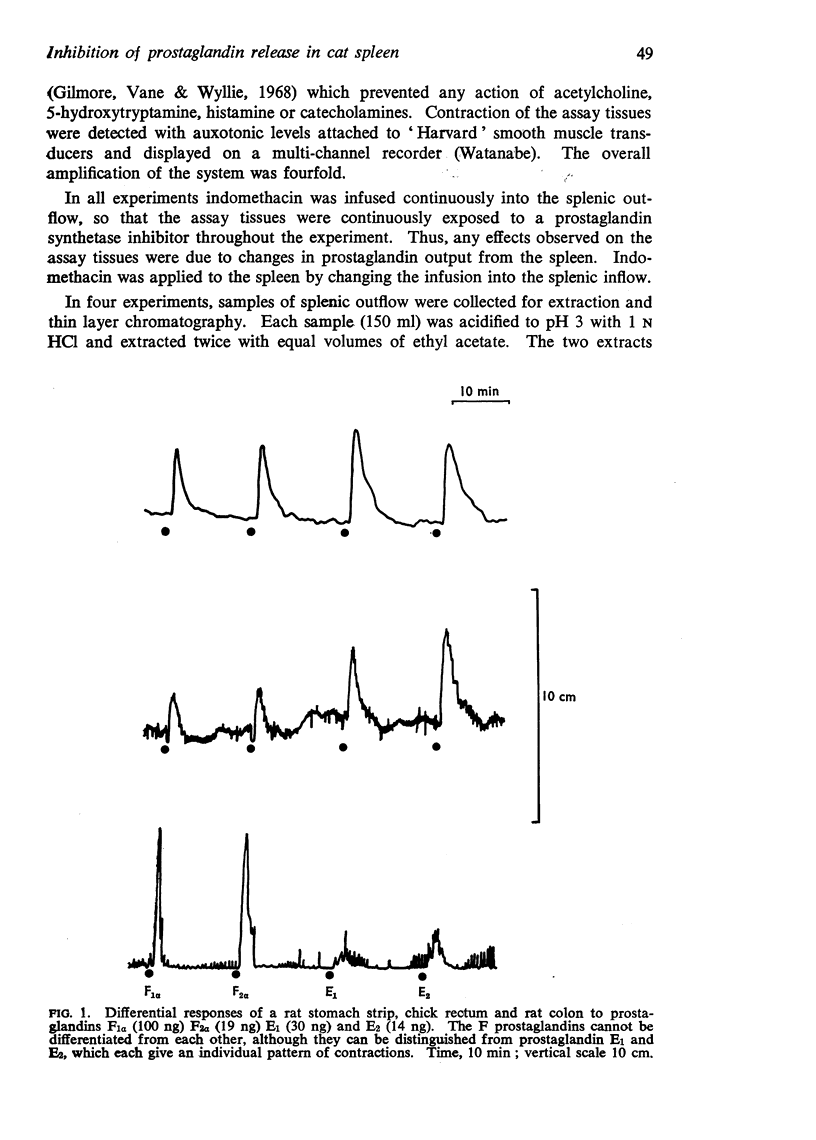

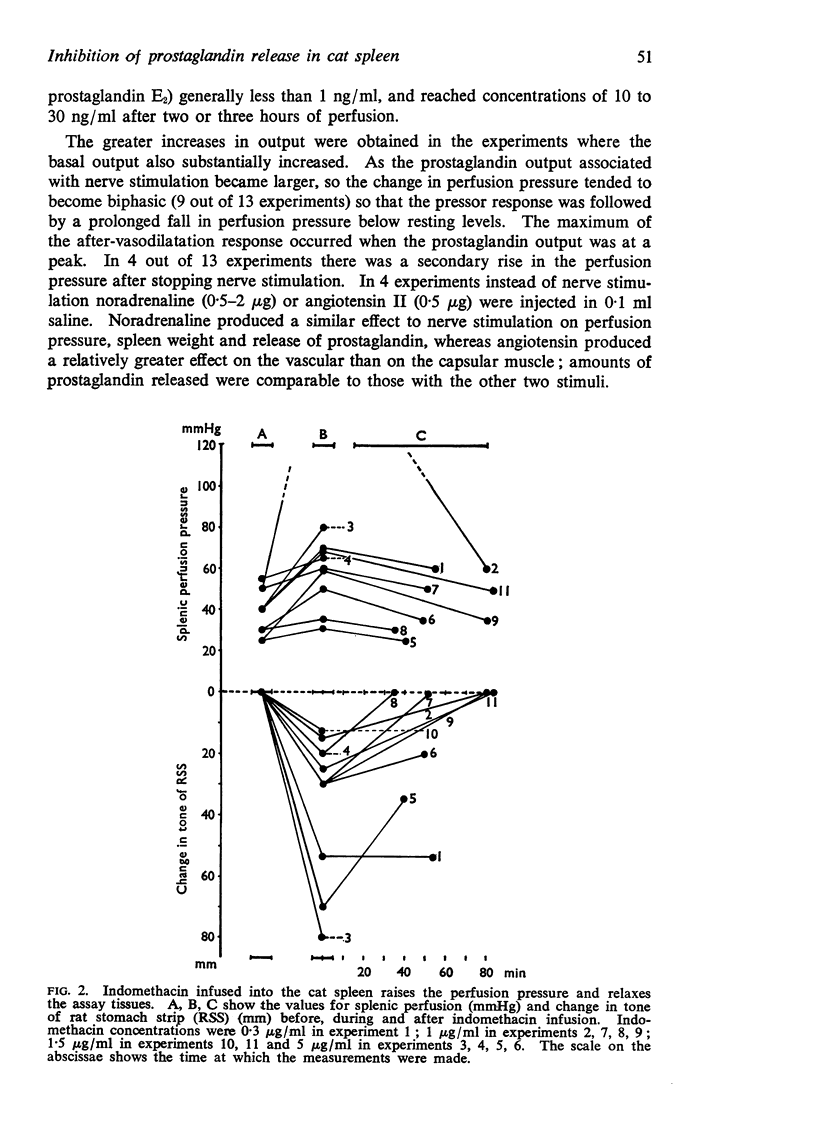
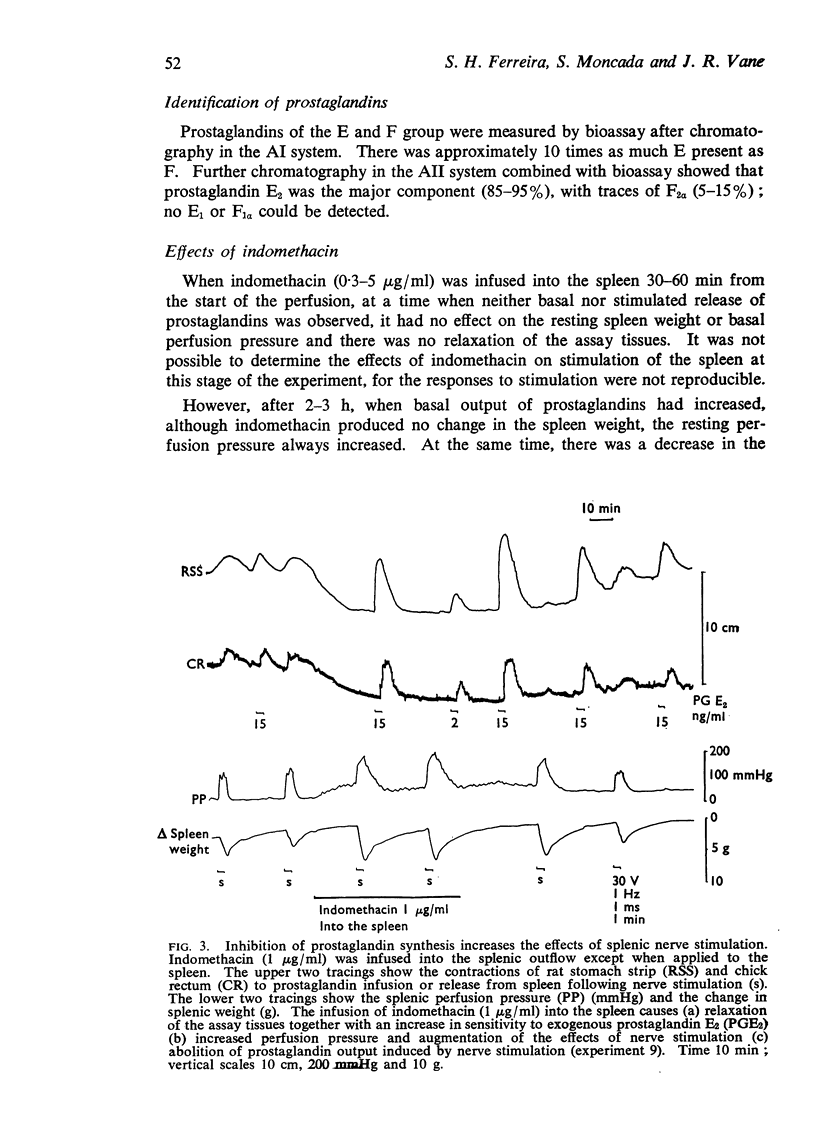

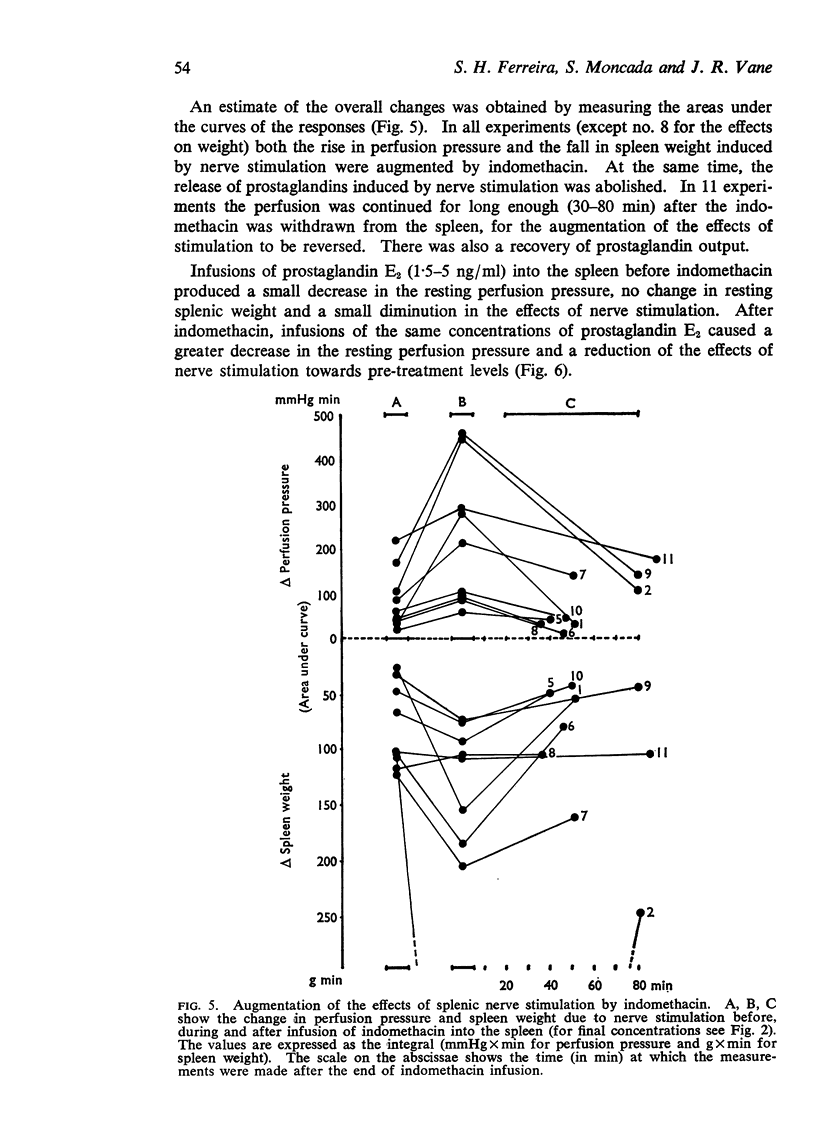



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergström S. Prostaglandins: members of a new hormonal system. These physiologically very potent compounds of ubiquitous occurrence are formed from essential fatty acids. Science. 1967 Jul 28;157(3787):382–391. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3787.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O. Prostaglandins and aspirin. Nature. 1971 Jul 2;232(5305):17–19. doi: 10.1038/232017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies B. N., Horton E. W., Withrington P. G. The occurrence of prostaglandin E2 in splenic venous blood of the dog following splenic nerve stimulation. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jan;32(1):127–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00436.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Indomethacin and aspirin abolish prostaglandin release from the spleen. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):237–239. doi: 10.1038/newbio231237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins: their disappearance from and release into the circulation. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):868–873. doi: 10.1038/216868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN K., SAMUELSSON B. PROSTAGLANDINS AND RELATED FACTORS: XIX. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF PROSTAGLANDINS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:117–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore N., Vane J. R., Wyllie J. H. Prostaglandins released by the spleen. Nature. 1968 Jun 22;218(5147):1135–1140. doi: 10.1038/2181135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES S. W., HORTON E. W., MAIN I. H. THE EFFECT OF PROSTAGLANDIN E1 ON RESPONSES OF SMOOTH MUSCLE TO CATECHOL AMINES, ANGIOTENSIN AND VASOPRESSIN. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Dec;21:538–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb02021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P. Antagonism between prostaglandin E2 and phenoxybenzamine on noradrenaline release from the cat spleen. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Jul;76(3):383–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P. Control by prostaglandin E2 of sympathetic neurotrans-mission in the spleen. Life Sci. 1970 Mar 1;9(5):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P. Modulating effect of prostaglandin E2 on noradrenaline release from the isolated cat spleen. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Mar;75(3):511–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P., Stjärne L., Wennmalm A. Inhibition by prostaglandin E2 of sympathetic neurotransmission in the rabbit heart. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 May;79(1):139–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04712.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P., von Euler U. S. Prostaglandin controls neuromuscular transmission in guinea-pig vas deferens. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 29;236(65):113–115. doi: 10.1038/newbio236113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton E. W. Hypotheses on physiological roles of prostaglandins. Physiol Rev. 1969 Jan;49(1):122–161. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1969.49.1.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANN M., WEST G. B. The nature of hepatic and splenic sympathin. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1950 Jun;5(2):173–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1950.tb01004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P., Vane J. The release of prostaglandins from lung and other tissues. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Apr 30;180:363–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb53205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REGOLI D., VANE J. R. A SENSITIVE METHOD FOR THE ASSAY OF ANGIOTENSIN. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Oct;23:351–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Willis A. L. Aspirin selectively inhibits prostaglandin production in human platelets. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):235–237. doi: 10.1038/newbio231235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swedin G. Endogenous inhibition of the mechanical response of the isolated rat and guinea-pig vas deferens to pre- and postganglionic nerve stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Dec;83(4):473–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb05105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANE J. R. A sensitive method for the assay of 5-hydroxytryptamine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Sep;12(3):344–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb00146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner R., Kaley G. Influence of prostaglandin E1 on the terminal vascular bed. Am J Physiol. 1969 Aug;217(2):563–566. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.2.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennmalm A., Hedqvist P. Prostaglandin E1 as inhibitor of the sympathetic neuroffector system in the rabbit heart. Life Sci I. 1970 Aug 15;9(16):931–937. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennmalm A., Stjärne L. Inhibition of the release of adrenergic transmitter by a fatty acid in the perfusate from sympathetically stimulated rabbit heart. Life Sci I. 1971 Apr 15;10(8):471–479. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(71)90113-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


