Abstract
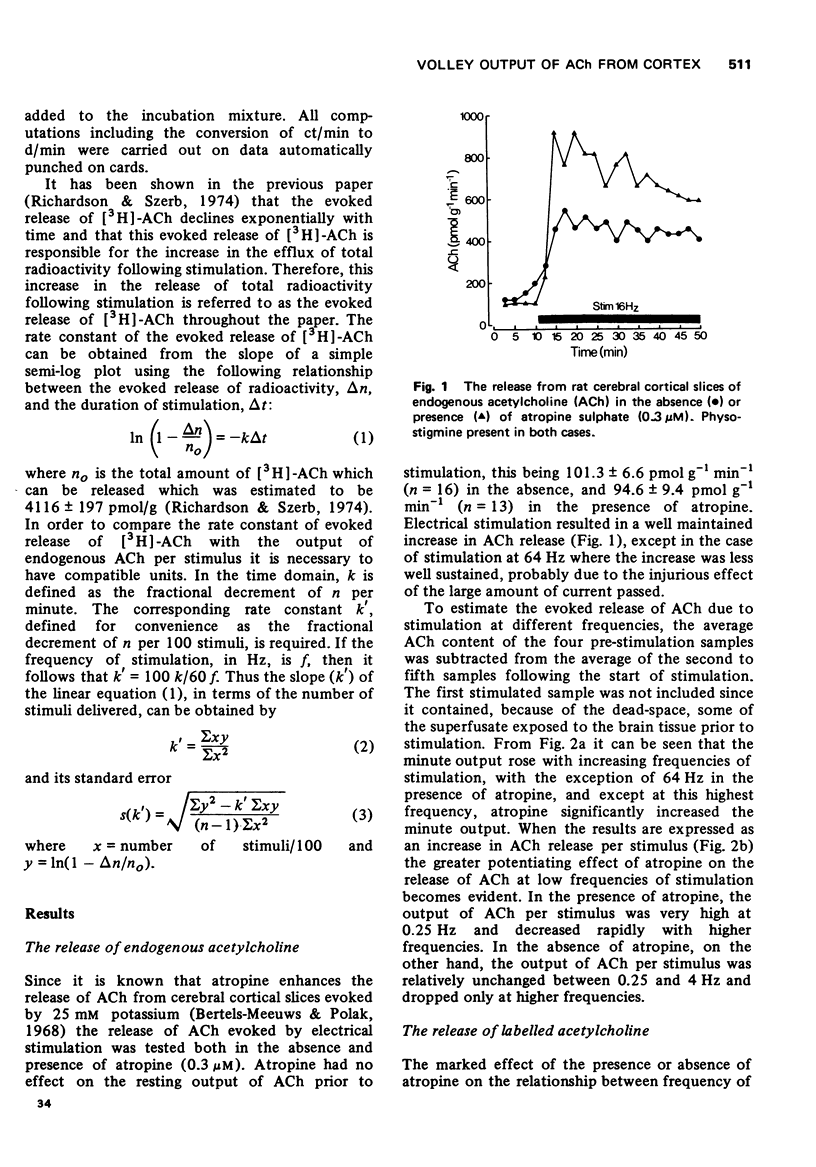
1 The release of endogenous acetylcholine (ACh) from cerebral cortical slices stimulated at 0.25, 1, 4, 16 and 64 Hz was measured in the presence either of physostigmine or of physostigmine and atropine.
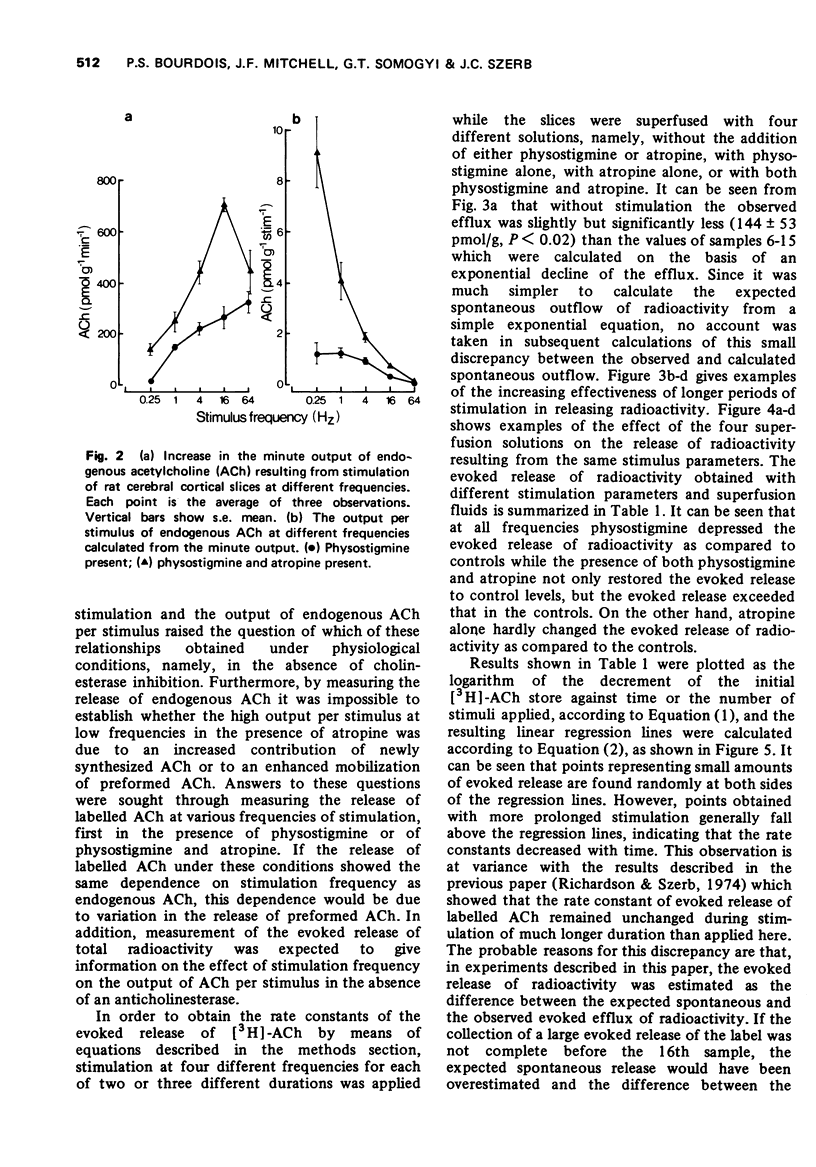
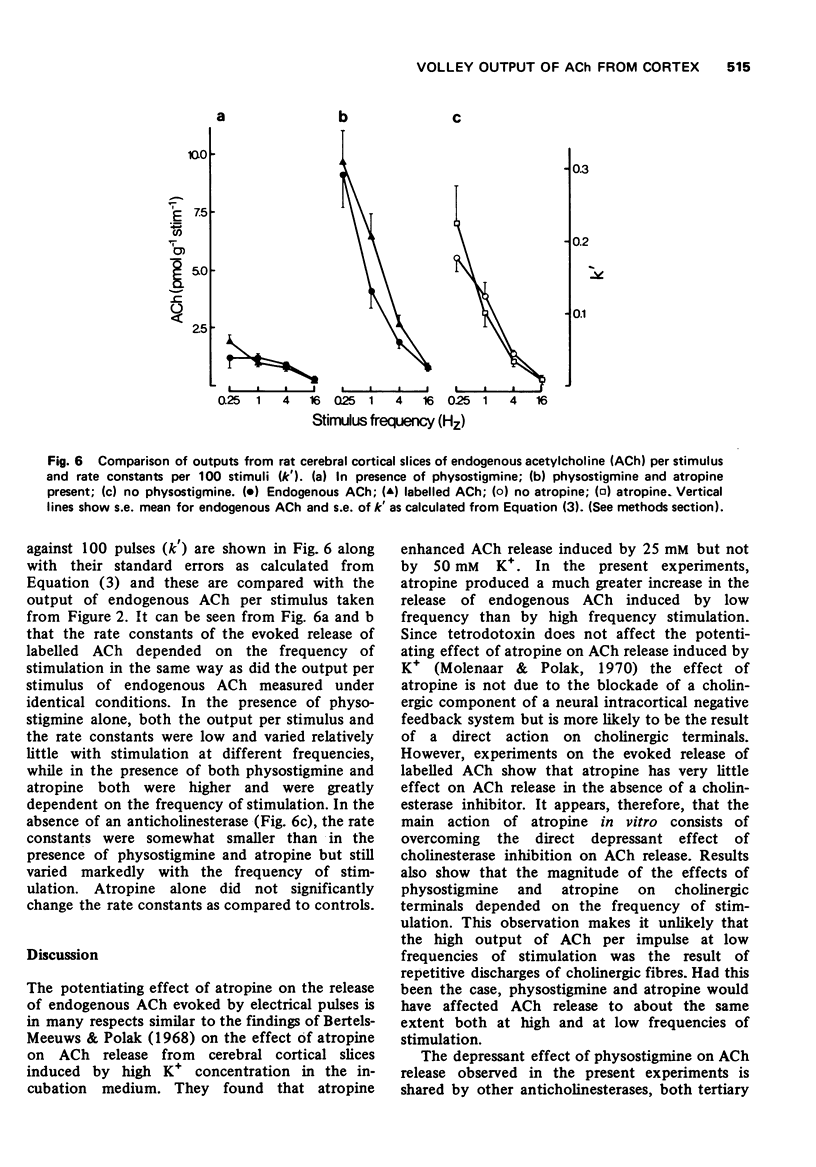
2 Atropine potentiated the evoked release of endogenous ACh especially at low frequencies resulting in an output per stimulus which sharply declined with increasing frequency of stimulation, while in the absence of atropine the output of ACh per stimulus was low and fairly constant.
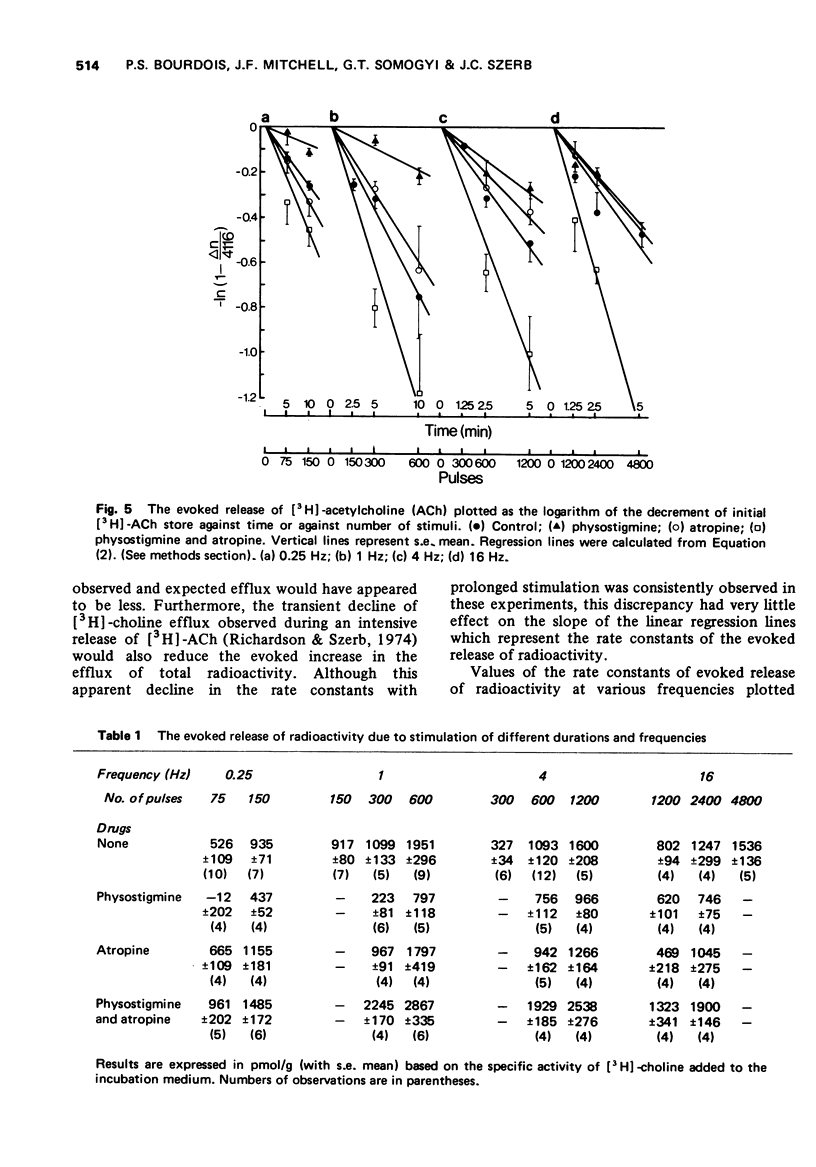
3 The evoked release of [3H]-ACh per stimulus following the incubation of the slices with [3H]-choline, as estimated by means of rate constants of the evoked release of total radioactivity, showed a frequency dependence similar to endogenous ACh when the two were tested under identical conditions.
4 In the absence of an anticholinesterase the evoked release of [3H]-ACh per stimulus was dependent on frequency of stimulation in a similar way to that in the presence of physostigmine and atropine.
5 Results suggest that under physiological conditions, i.e. in the absence of an anti-cholinesterase, the release of ACh per stimulus decreases with increasing frequency of stimulation and that this decrease is due to a lag in the mobilization of stored ACh rather than in the synthesis of new ACh.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen G. S., Glover A. B., Rand M. J., Story D. F. Effects of acetylcholine on vasoconstriction and release of 3 H-noradrenaline in response to sympathetic nerve stimulation in the isolated artery of the rabbit ear. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Nov;46(3):527P–528P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertels-Meeuws M. M., Polak R. L. Influence of antimuscarinic substances on in vitro synthesis of acetylcholine by rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jun;33(2):368–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdois P. S., Mitchell J. F., Szerb J. C. Effect of atropine on acetylcholine release from cerebral cortical slices stimulated at different frequencies. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Aug;42(4):640P–641P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A. L., Kosterlitz H. W., Watt A. J. Mode of action of morphine-like drugs on autonomic neuro-effectors. Nature. 1968 Dec 7;220(5171):1040–1042. doi: 10.1038/2201040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudar J. D., Szerb J. C. The effect of topically applied atropine on resting and evoked cortical acetylcholine release. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(3):741–762. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fozard J. R., Muscholl E. Effects of several muscarinic agonists on cardiac performance and the release of noradrenaline from sympathetic nerves of the perfused rabbit heart. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Aug;45(4):616–629. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb08119.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemsworth B. A., Neal M. J. The effect of central stimulant drugs on acetylcholine release from rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;34(3):543–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb08483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan L. M., Phillis J. W. Acetylcholine inhibition in the intact and chronically isolated cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Aug;45(4):584–595. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb08116.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Acetylcholine-sensitive cells in the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:296–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J., Vizi E. S. Effect of frequency of stimulation on the inhibition by noradrenaline of the acetylcholine output from parasympathetic nerve terminals. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Jun;42(2):263–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann P. J., Tennenbaum M., Quastel J. H. Acetylcholine metabolism in the central nervous system: The effects of potassium and other cations on acetylcholine liberation. Biochem J. 1939 May;33(5):822–835. doi: 10.1042/bj0330822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. F. The spontaneous and evoked release of acetylcholine from the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Jan;165(1):98–116. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar P. C., Polak R. L. Stimulation by atropine of acetylcholine release and synthesis in cortical slices from rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;40(3):406–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10622.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. CHOLINERGIC TRANSMISSION AND ACETYLCHOLINE OUTPUT. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1963 Dec;41:2637–2653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter L. T. Synthesis, storage and release of [14C]acetylcholine in isolated rat diaphragm muscles. J Physiol. 1970 Jan;206(1):145–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWSELL E. V. Applied electrical pulses and the ammonia and acetylcholine of isolated cerebral cortex slices. Biochem J. 1954 Aug;57(4):666–673. doi: 10.1042/bj0570666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson I. W., Szerb J. C. The release of labelled acetylcholine and choline from cerebral cortical slices stimulated electrically. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Dec;52(4):499–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09717.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZERB J. THE EFFECT OF TERTIARY AND QUATERNARY ATROPINE ON CORTICAL ACETYLCHOLINE OUTPUT AND ON THE ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAM IN CATS. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1964 May;42:303–314. doi: 10.1139/y64-036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi G. T., Szerb J. C. Demonstration of acetylcholine release by measuring efflux of labelled choline from cerebral cortical slices. J Neurochem. 1972 Nov;19(11):2667–2677. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01326.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szerb J. C., Malik H., Hunter E. G. Relationship between acetylcholine content and release in the cat's cerebral cortex. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;48(11):780–790. doi: 10.1139/y70-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szerb J. C., Somogyi G. T. Depression of acetylcholine release from cerebral cortical slices by cholinesterase inhibition and by oxotremorine. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 24;241(108):121–122. doi: 10.1038/newbio241121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


