Abstract
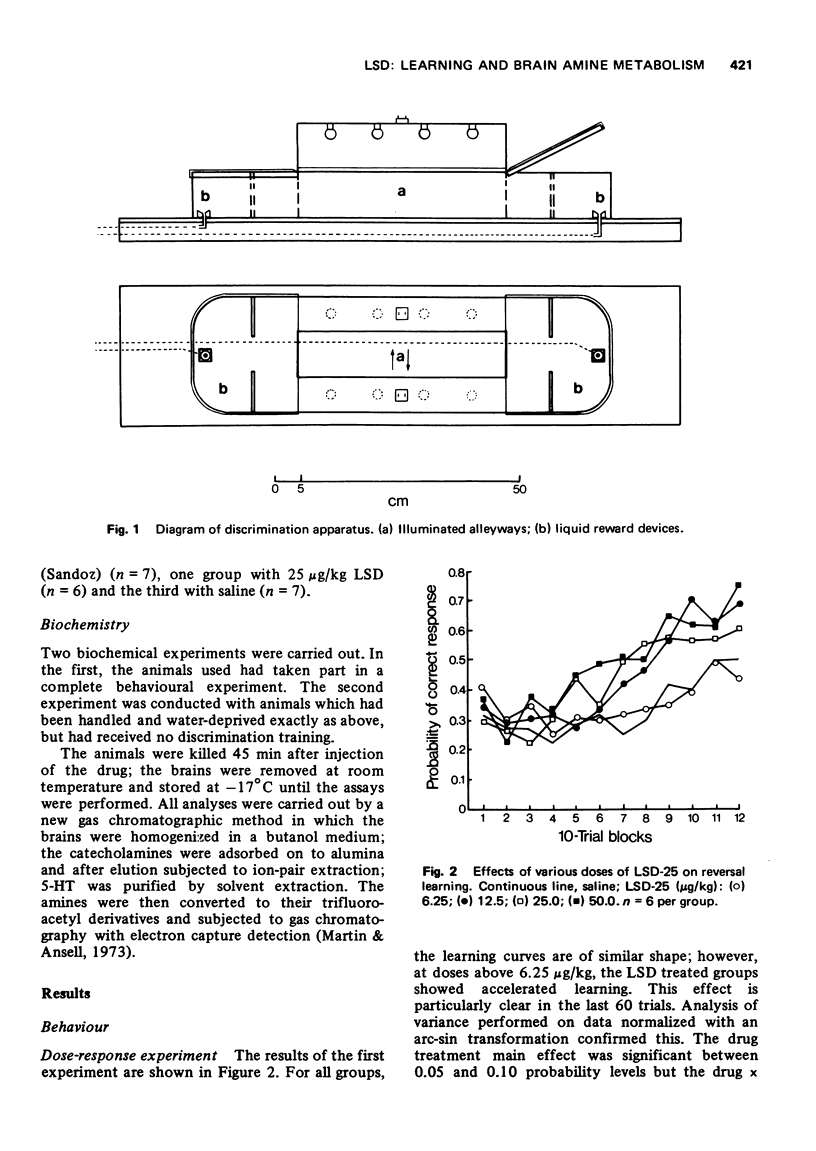
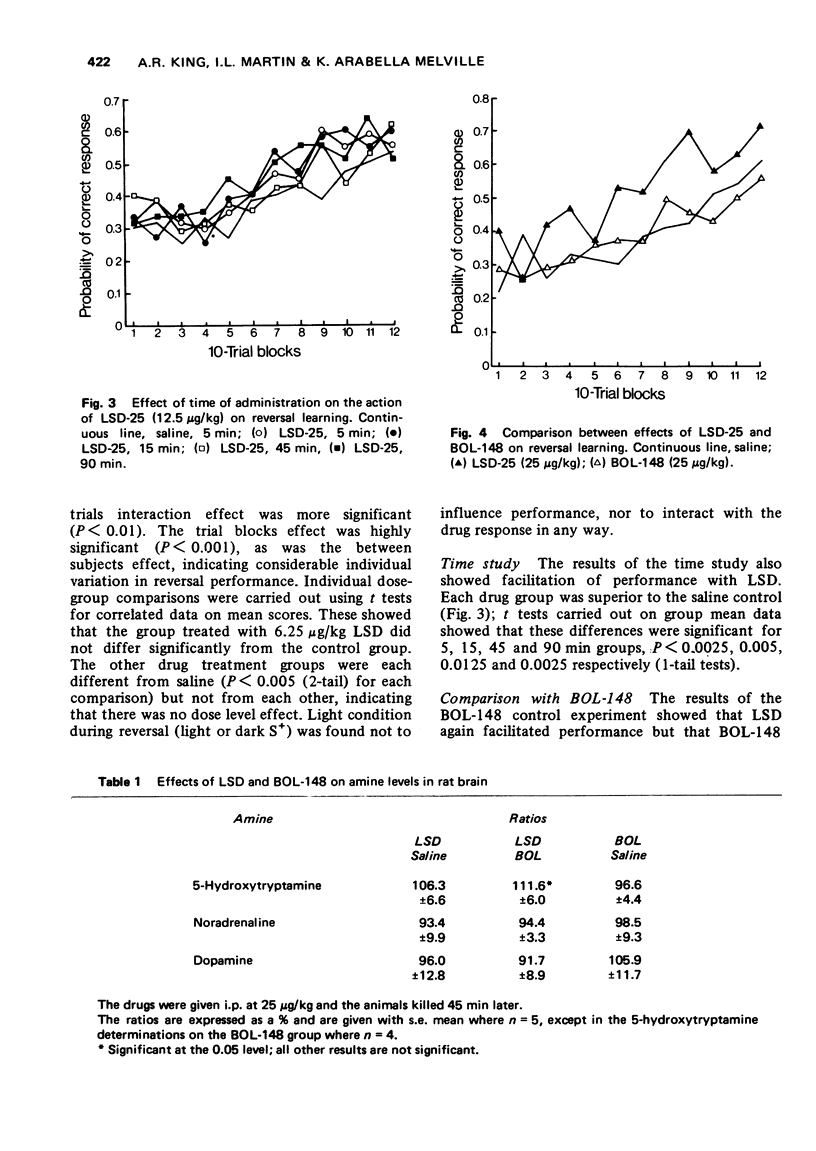
1 Small doses of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) (12.5-50 μg/kg) consistently facilitated learning of a brightness discrimination reversal.
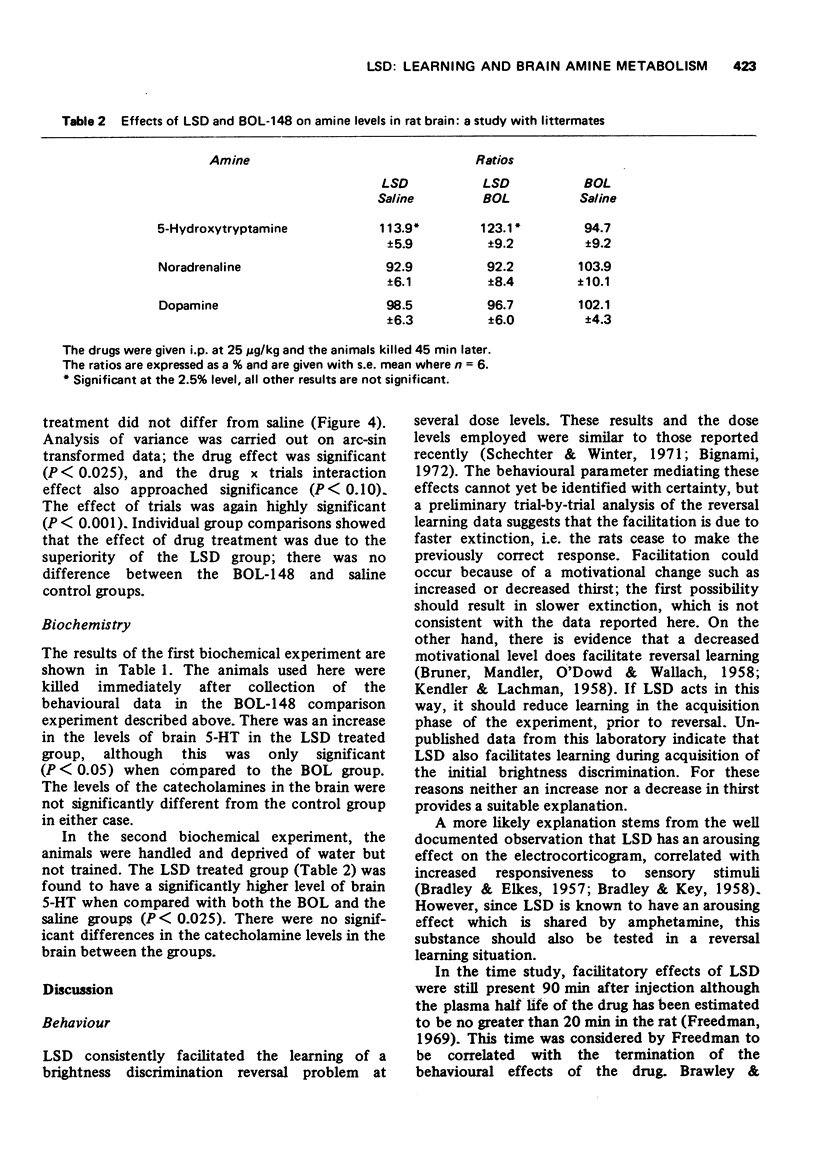
2 2-Bromo-lysergic acid diethylamide (BOL-148), a structural analogue of LSD, with similar peripheral anti-5-hydroxytrypamine activity but no psychotomimetic properties, had no effect in this learning situation at a similar dose (25 μg/kg).
3 LSD, but not BOL-148, caused a small but significant increase in brain 5-hydroxytryptamine levels, but had no effect on the levels of catecholamines in the brain at 25 μg/kg.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APPEL J. B., FREEDMAN D. X. CHEMICALLY-INDUCED ALTERATIONS IN THE BEHAVIORAL EFFECTS OF LSD-25. Biochem Pharmacol. 1964 Jun;13:861–869. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(64)90030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aghajanian G. K., Foote W. E., Sheard M. H. Action of psychotogenic drugs on single midbrain raphe neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Feb;171(2):178–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andén N. E., Corrodi H., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T. Evidence for a central 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor stimulation by lysergic acid diethylamide. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Sep;34(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb07943.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appel J. B. Effects of LSD on time-based schedules of reinforcement. Psychopharmacologia. 1971;21(2):174–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00572275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY P. B., ELKES J. The effects of some drugs on the electrical activity of the brain. Brain. 1957 Mar;80(1):77–117. doi: 10.1093/brain/80.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY P. B., KEY B. J. The effect of drugs on arousal responses produced by electrical stimulation of the reticular formation of the brain. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1958 Feb;10(1):97–110. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(58)90107-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUNER J. S., MANDLER J. M., O'DOWD D., WALLACH M. A. The role of overlearning and drive level in reversal learning. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1958 Oct;51(5):607–613. doi: 10.1037/h0039789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignami G. Facilitation of avoidance acquisition by LSD-25. Possible effects on drive modulating systems. Psychopharmacologia. 1972;25(2):146–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00423191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boakes R. J., Bradley P. B., Briggs I., Dray A. Antagonism of 5-hydroxytryptamine by LSD 25 in the central nervous system: a possible neuronal basis for the actions of LSD 25. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Oct;40(2):202–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09914.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawley P., Duffield J. C. The pharmacology of hallucinogens. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Mar;24(1):31–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellano C. Lysergic acid diethylamide, amphetamine and chlorpromazine on water maze discrimination in mice. Psychopharmacologia. 1971;19(1):16–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00403698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz J. L., Huttunen M. O. Persistent increase in brain serotonin turnover after chronic administration of LSD in the rat. Science. 1971 Oct 1;174(4004):62–64. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4004.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDMAN D. X. Effects of LSD-25 on brain serotonin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 Nov;134:160–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman D. X. The psychopharmacology of hallucinogenic agents. Annu Rev Med. 1969;20:409–418. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.20.020169.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himwich H. E., Alpers H. S. Psychopharmacology. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1970;10:313–334. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.10.040170.001525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENDLER H. H., LACHMAN R. Habit reversal as a function of schedule of reinforcement and drive strength. J Exp Psychol. 1958 Jun;55(6):584–591. doi: 10.1037/h0044114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEY B. J. The effect of drugs on discrimination and sensory generalisation of auditory stimuli in cats. Psychopharmacologia. 1961;2:352–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00404123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key B. J. Alterations in the generalisation of visual stimuli induced by lysergic acid diethylamide in cats. Psychopharmacologia. 1964 Nov 11;6(5):327–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00404243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key B. J. The effect of LSD-25 on the interaction between conditioned and non-conditioned stimuli in a simple avoidance situation. Psychopharmacologia. 1964 Nov 11;6(5):319–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00404242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Roth R. H., Aghajanian G. K. Selective reduction of tryptophan hydroxylase activity in rat forebrain after midbrain raphe lesions. Brain Res. 1971 Dec 10;35(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90602-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard B. E., Tonge S. R. The effects of some hallucinogenic drugs upon the metabolism of noradrenaline. Life Sci. 1969 Aug 1;8(15):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin I. L., Ansell G. B. A sensitive gas chromatographic procedure for the estimation of noradrenaline, dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine in rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Feb 15;22(4):521–533. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90295-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosecrans J. A., Lovell R. A., Freedman D. X. Effects of lysergic acid diethylamide on the metabolism of brain 5-hydroxytryptamine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Oct;16(10):2011–2021. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter M. D., Winter J. C. Effect of BOL on the LSD-induced alteration of flicker discrimination in the rat. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1972 Mar;196(1):64–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter M. D., Winter J. C. Effect of mescaline and lysergic acid diethylamide on flicker discrimination in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 May;177(2):461–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparber S. B., Tilson H. A. Environmental influences upon drug-induced suppression of operant behavior. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Oct;179(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


