Abstract
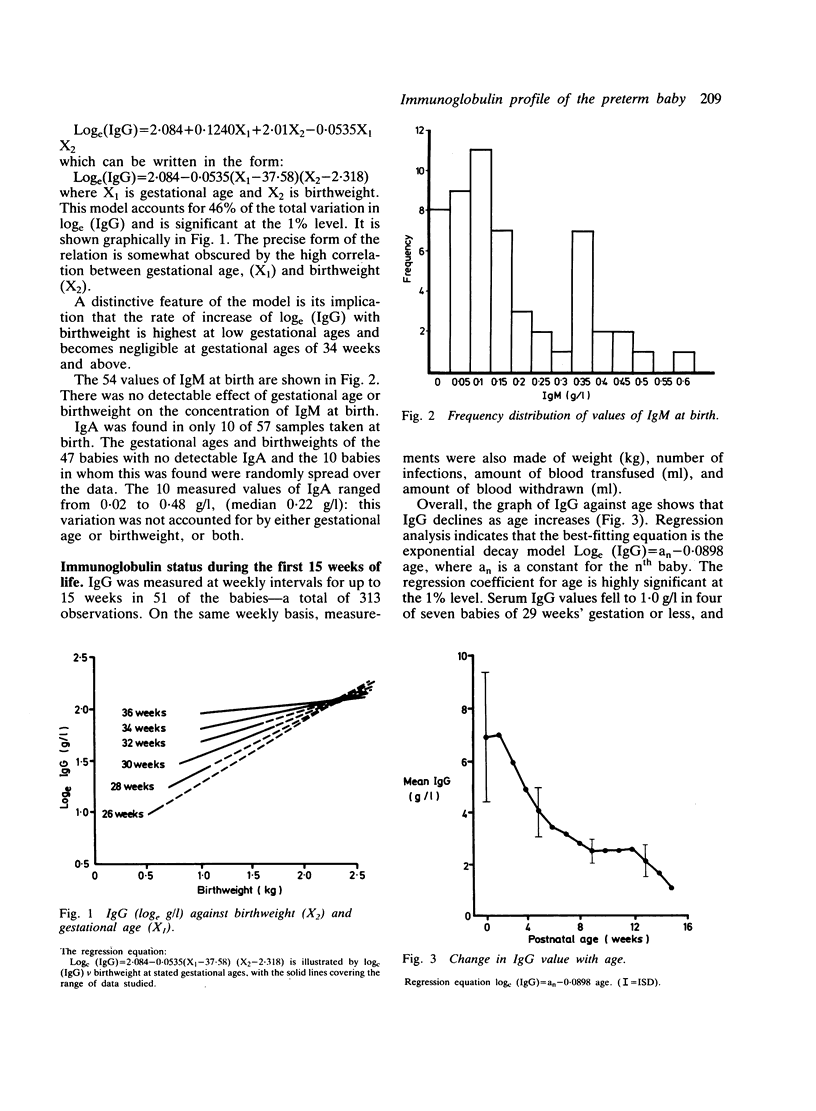
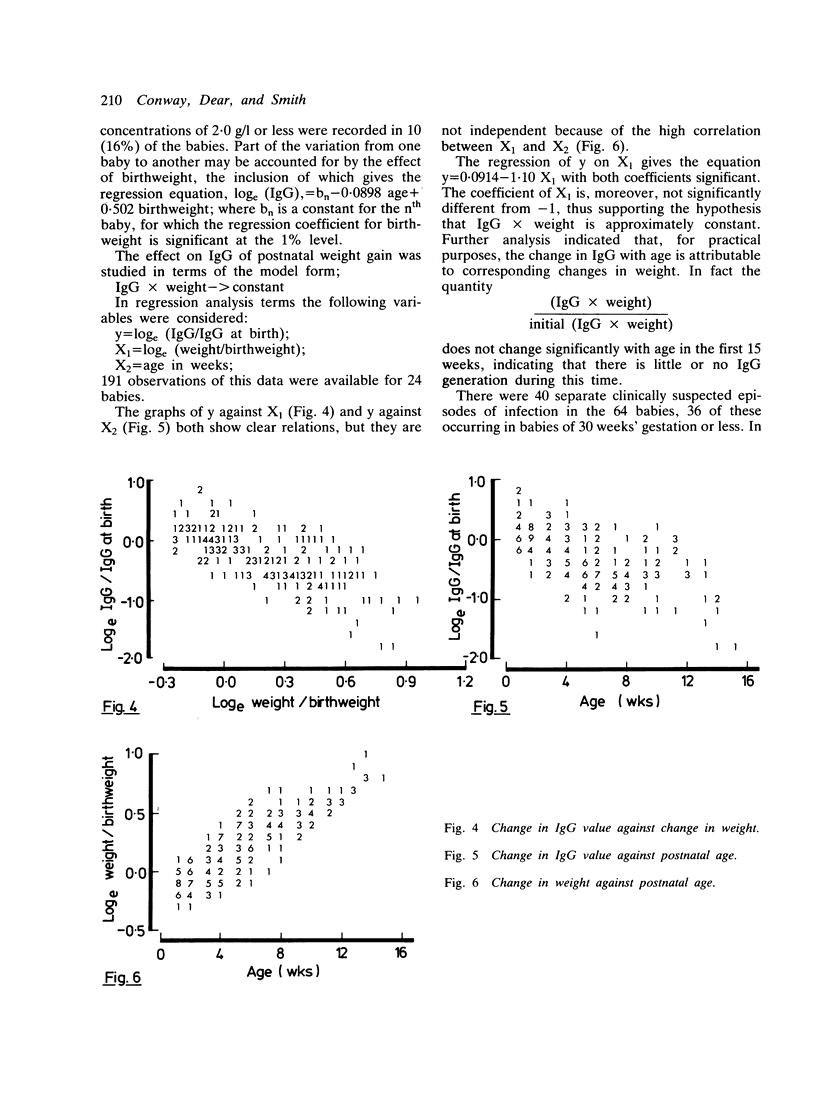
Immunoglobulin concentrations were determined in 64 consecutively born preterm babies at birth and serially throughout each baby's stay in the neonatal unit. No significant IgG generation was found during the first 15 weeks of life, regression analysis giving an exponential decay model. Concentrations fell to 2 g/l or less in 10 (16%) babies (gestational age 25 to 32 weeks), and were as low as 1 g/l in four babies (gestational age 25 to 29 weeks). The effects of gestational age and birthweight on the concentration of IgG at birth were highly interdependent and significant. Most babies had no detectable IgA at birth, and no effect of gestational age or birthweight, or both, on either initial IgA or IgM concentrations could be shown.
Full text
PDF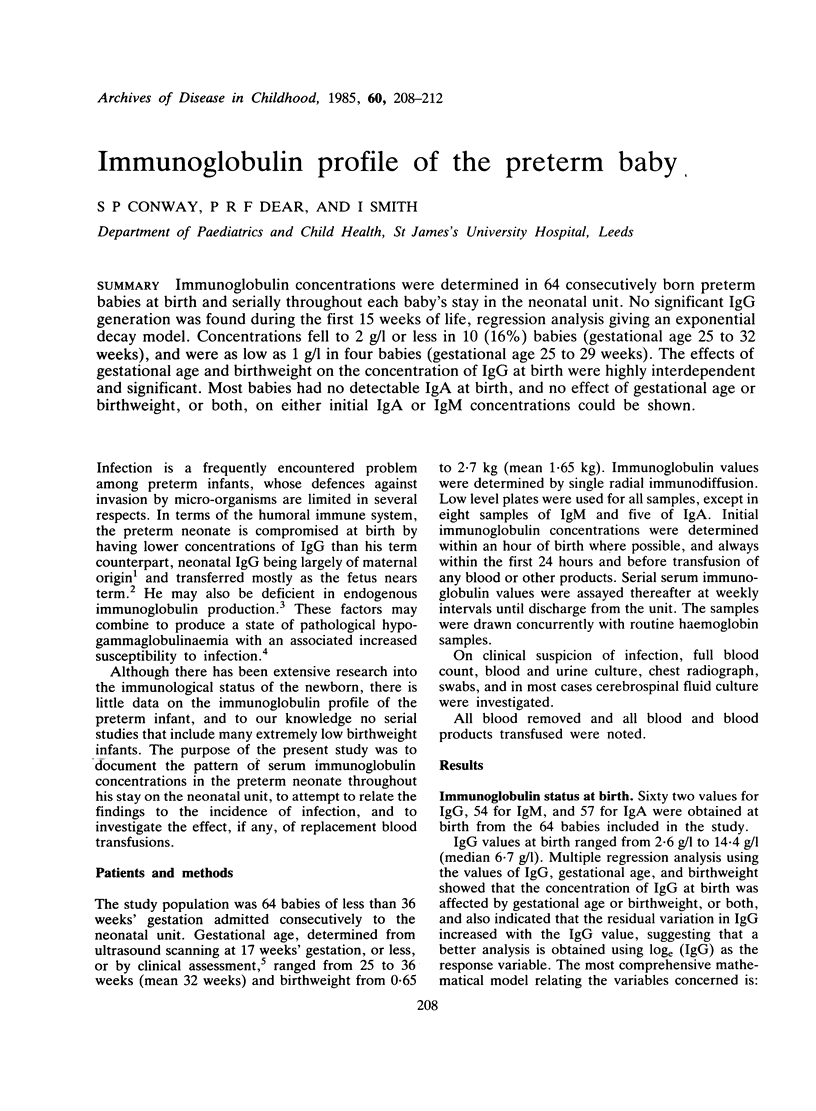


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMER J., OTT E., IBBOTT F. A., O'BRIEN D., KEMPE C. H. The effect of monthly gamma-globulin administration on morbidity and mortality from infection in premature infants during the first year of life. Pediatrics. 1963 Jul;32:4–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIDGES R. A., CONDIE R. M., ZAK S. J., GOOD R. A. The morphologic basis of antibody formation development during the neonatal period. J Lab Clin Med. 1959 Mar;53(3):331–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederqvist L. L., Ewool L. C., Litwin S. D. The effect of fetal age, birth weight, and sex on cord blood immunoglobulin values. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1978 Jul 1;131(5):520–525. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(78)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowitz L. M., Dubowitz V., Goldberg C. Clinical assessment of gestational age in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1970 Jul;77(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. E., Akpata S. O., Glass L. Serum immunoglobulin levels in premature and full-term infants. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Sep;56(3):416–418. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/56.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. J., Buckley R. H., Wakil S. S., McAllister D. C., David R. J., Faix R. G. Elevated IgA concentration in milk produced by mothers delivered of preterm infants. J Pediatr. 1981 Sep;99(3):389–393. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80323-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusdon J. P., Jr Fetal and maternal immunoglobulin levels during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1969 Apr 1;103(7):895–900. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)34434-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson L. A., Winberg J. Breast milk and defence against infection in the newborn. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Dec;47(256):845–848. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.256.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs J. R., Davis J. A. Serum gamma-G-globulin levels and gestational age in premature babies. Lancet. 1967 Apr 8;1(7493):757–759. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91369-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs D., Altman D. G., Tidmarsh C. E., Valman H. B., Webster A. D. Serum immunoglobulin concentrations in preschool children measured by laser nephelometry: reference ranges for IgG, IgA, IgM. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Oct;36(10):1193–1196. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.10.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahambare A. P., Iyer Y. S., Joshi M. K., Irani S. F., Kandoth P. W. Neonatal immunoglobulins. Indian Pediatr. 1978 Jul;15(7):577–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadatos C., Papaevangelou G. J., Alexiou D., Mendris J. Serum immunoglobulin G levels in small-for-dates newborn babies. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Aug;45(242):570–572. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.242.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadatos C., Papaevangelou G., Alexiou D., Mendris J. Immunoglobulin levels and gestational age. Biol Neonat. 1969;14(5):365–373. doi: 10.1159/000240202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravivarma K. R., Babar S. T., Master J., Bapat J. P., Baxi A. J. Immunoglobulins in newborns: differential study of premature and full term infants. J Postgrad Med. 1979 Apr;25(2):97–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salimonu L. S., Ladipo O. A., Adeniran S. O., Osukoya B. O. Serum immunoglobulin levels in normal, premature and postmature newborns and their mothers. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 1978;16(2):119–123. doi: 10.1002/j.1879-3479.1978.tb00410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Fudenberg H. H. Serum levels of immune globulins in health and disease: a survey. Pediatrics. 1966 May;37(5):715–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster A. D., Latif A. A., Brenner M. K., Bird D. Evaluation of test immunisation in the assessment of antibody deficiency syndromes. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Jun 23;288(6434):1864–1866. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6434.1864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung C. Y., Hobbs J. R. Serum-gamma-G-globulin levels in normal premature, post-mature, and "small-for-dates" newborn babies. Lancet. 1968 Jun 1;1(7553):1167–1170. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91865-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yodfat Y., Silvian I. A prospective study of acute respiratory tract infections among children in a kibbutz: the role of secretory IgA and serum immunoglobulins. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):26–30. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


