Abstract
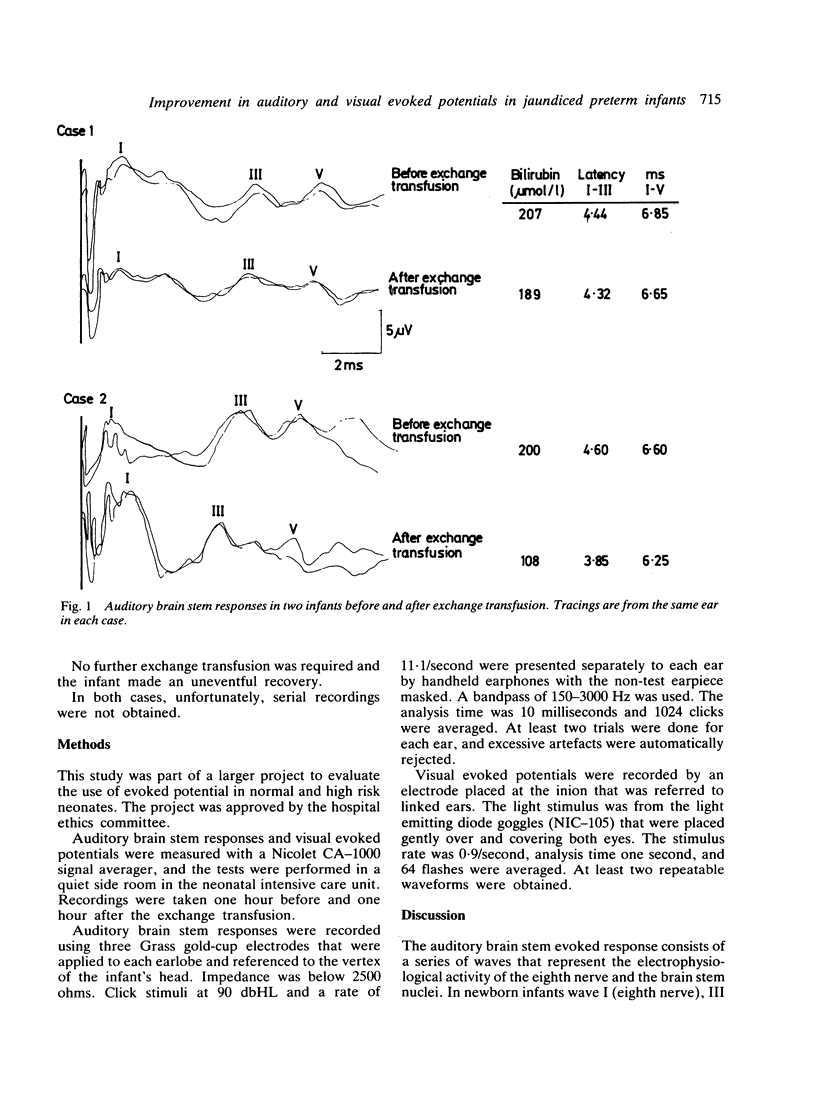
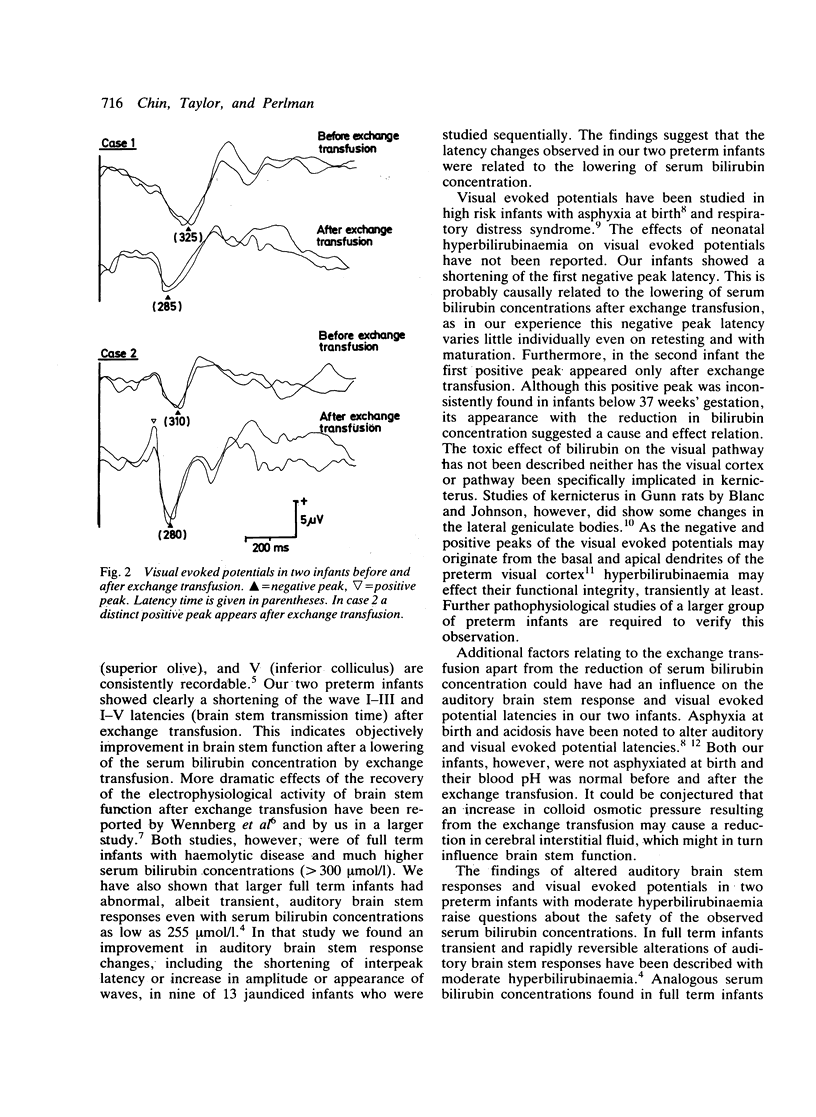
Two preterm infants with peak serum bilirubin concentrations of 270 mumol/l and 200 mumol/l, respectively showed improvement in the wave peak latencies of the auditory and visual evoked potentials after exchange transfusion. The implications of this observation and the use of evoked potential recording in neonatal jaundice are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLANC W. A., JOHNSON L. Studies on kernicterus; relationship with sulfonamide intoxication, report on kernicterus in rats with glucuronyl transferase deficiency and review of pathogenesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1959 Jan;18(1):165–189. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195901000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culley P., Powell J., Waterhouse J., Wood B. Sequelae of neonatal jaundice. Br Med J. 1970 Aug 15;3(5719):383–386. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5719.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner L. M., Snyder R. N., Chabon R. S., Bernstein J. Kernicterus: high incidence in premature infants with low serum bilirubin concentrations. Pediatrics. 1970 Jun;45(6):906–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani L. J., Weitzman E. D., Pineda G. Visual evoked responses during neonatal respiratory disorders in low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res. 1972 Apr;6(4):203–210. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197204000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrbek A., Karlberg P., Kjellmer I., Olsson T., Riha M. Clinical application of evoked electroencephalographic responses in newborn infants. I: Perinatal asphyxia. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1977 Feb;19(1):34–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1977.tb08017.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucey J. F. The unsolved problem of kernicterus in the susceptible low birth weight infant. Pediatrics. 1972 May;49(5):646–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nwaesei C. G., Van Aerde J., Boyden M., Perlman M. Changes in auditory brainstem responses in hyperbilirubinemic infants before and after exchange transfusion. Pediatrics. 1984 Nov;74(5):800–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman M., Fainmesser P., Sohmer H., Tamari H., Wax Y., Pevsmer B. Auditory nerve-brainstem evoked responses in hyperbilirubinemic neonates. Pediatrics. 1983 Nov;72(5):658–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. A., Balow B., Fisch R. O. Neonatal serum bilirubin levels related to cognitive development at ages 4 through 7 years. J Pediatr. 1979 Apr;94(4):601–604. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr A., Amlie R. N., Martin W. H., Sanders S. Development of auditory function in newborn infants revealed by auditory brainstem potentials. Pediatrics. 1977 Dec;60(6):831–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennberg R. P., Ahlfors C. E., Bickers R., McMurtry C. A., Shetter J. L. Abnormal auditory brainstem response in a newborn infant with hyperbilirubinemia: improvement with exchange transfusion. J Pediatr. 1982 Apr;100(4):624–626. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80771-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods J. R., Jr, Coppes V., Brooks D. E., Freeman M., Knowles P. J., Parisi V., O'Mara P., McCarty G. E. Measurement of visual evoked potential in the asphyctic fetus and during neonatal survival. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982 Aug 15;143(8):944–951. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(82)90479-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


