Abstract
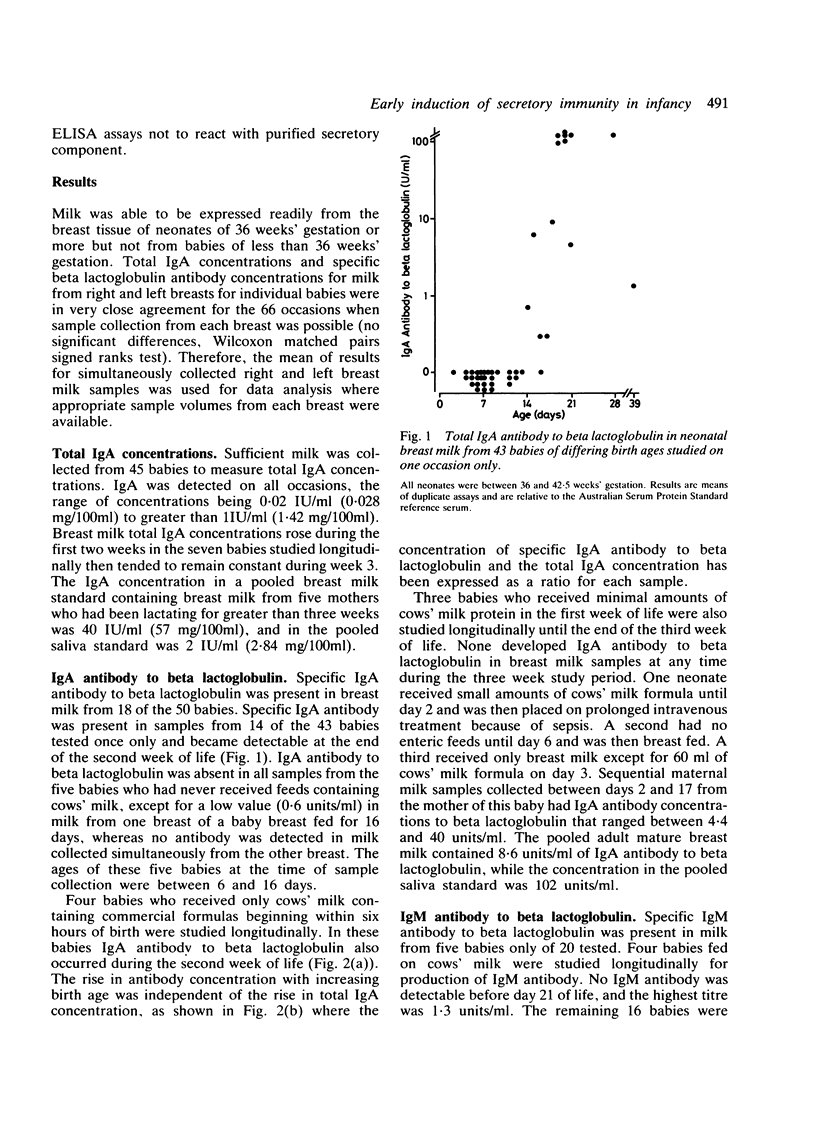
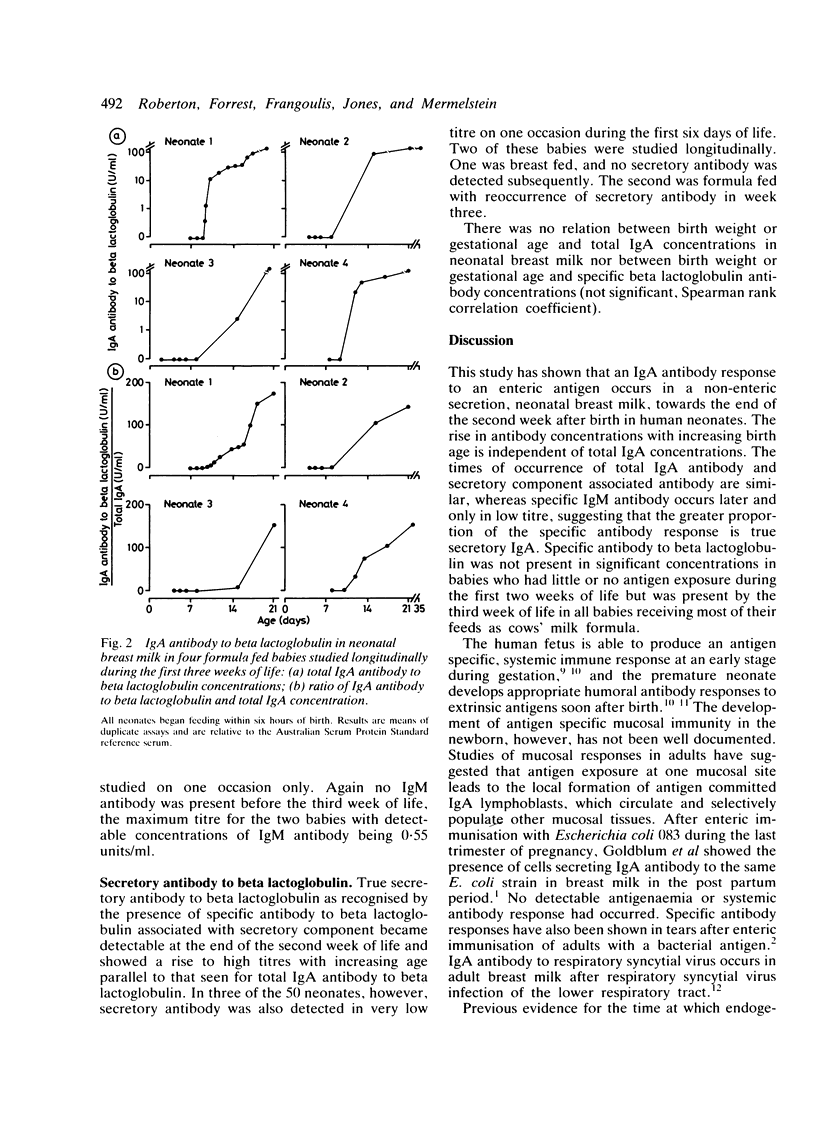
Neonatal breast milk from 50 babies aged between 2 and 39 days was studied for the presence of antibody to the cows' milk protein beta lactoglobulin. Specific IgA antibody and specific secretory antibody to beta lactoglobulin were detectable towards the end of the second week of life in milk secreted by neonates fed cows' milk formula. Specific antibody concentrations were independent of total IgA concentrations. Babies receiving little or no cows' milk protein did not produce antibody in neonatal breast milk. Antigen specific mucosal immune responses develop in tissues distant from the site of primary mucosal exposure by the end of the second week of life in term human neonates, suggesting that prophylactic immunisation against enteric or other mucosal pathogens within a few days of birth may provide antibody responses in secretions, which may protect against mucosal infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beach R. C., Menzies I. S., Clayden G. S., Scopes J. W. Gastrointestinal permeability changes in the preterm neonate. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Feb;57(2):141–145. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernbaum J., Anolik R., Polin R. A., Douglas S. D. Development of the premature infant's host defense system and its relationship to routine immunizations. Clin Perinatol. 1984 Feb;11(1):73–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishaut M., Murphy D., Neifert M., McIntosh K., Ogra P. L. Bronchomammary axis in the immune response to respiratory syncytial virus. J Pediatr. 1981 Aug;99(2):186–191. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80447-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum R. M., Ahlstedt S., Carlsson B., Hanson L. A., Jodal U., Lidin-Janson G., Sohl-Akerlund A. Antibody-forming cells in human colostrum after oral immunisation. Nature. 1975 Oct 30;257(5529):797–798. doi: 10.1038/257797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovar M. G., Serdula M. K., Marks J. S., Fraser D. W. Review of the epidemiologic evidence for an association between infant feeding and infant health. Pediatrics. 1984 Oct;74(4 Pt 2):615–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Lippmann A., Rieger C. H. Oral immunization to milk protein in human infants in the presence of passive antibody. Pediatr Res. 1983 Sep;17(9):724–728. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198309000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogra S. S., Weintraub D., Ogra P. L. Immunologic aspects of human colostrum and milk. III. Fate and absorption of cellular and soluble components in the gastrointestinal tract of the newborn. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):245–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberton D. M., Paganelli R., Dinwiddie R., Levinsky R. J. Milk antigen absorption in the preterm and term neonate. Arch Dis Child. 1982 May;57(5):369–372. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.5.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg R. M. Immunoglobulin and specific antibody synthesis during the first weeks of life of premature infants. J Pediatr. 1969 Sep;75(3):391–399. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80264-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver L. T., Laker M. F., Nelson R. Intestinal permeability in the newborn. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Mar;59(3):236–241. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.3.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap P. L., McKiernan J., Mirtle C. L., McClelland D. B. The development of mammary secretory immunity in the human newborn. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1981 Jul;70(4):459–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1981.tb05723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


