Abstract
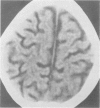
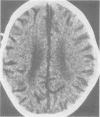
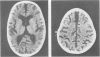
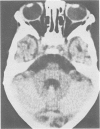
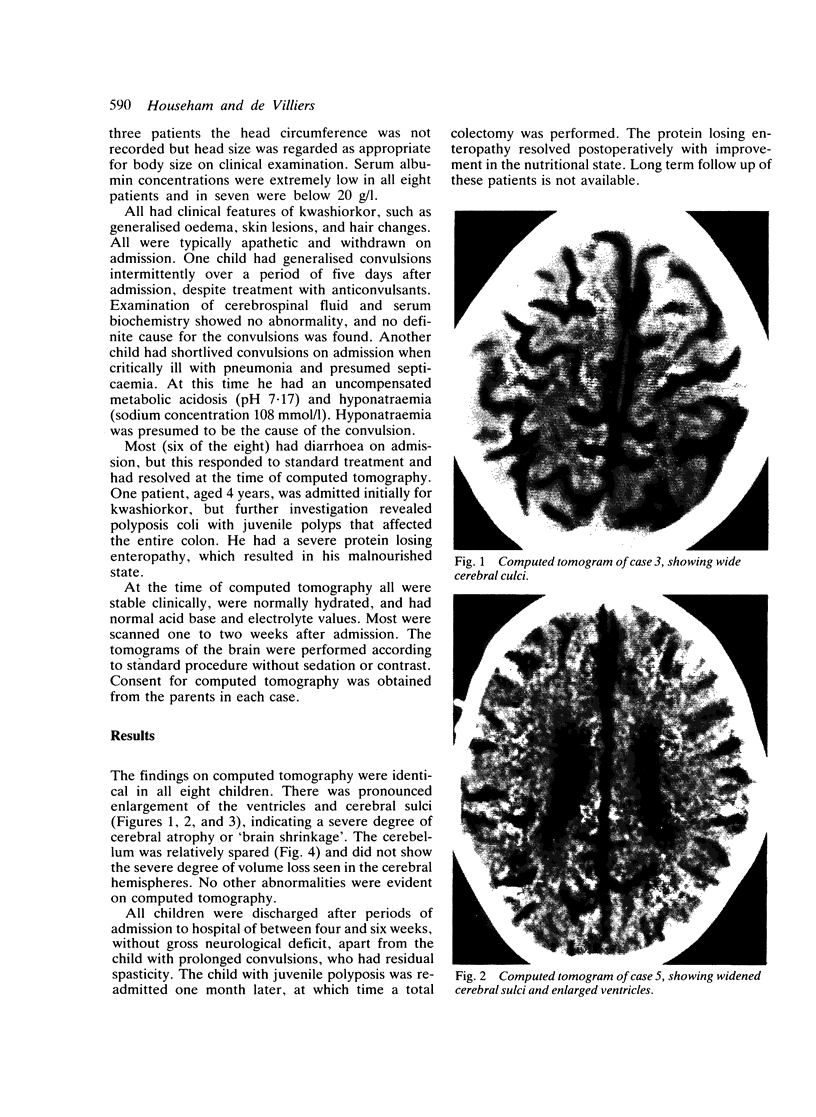
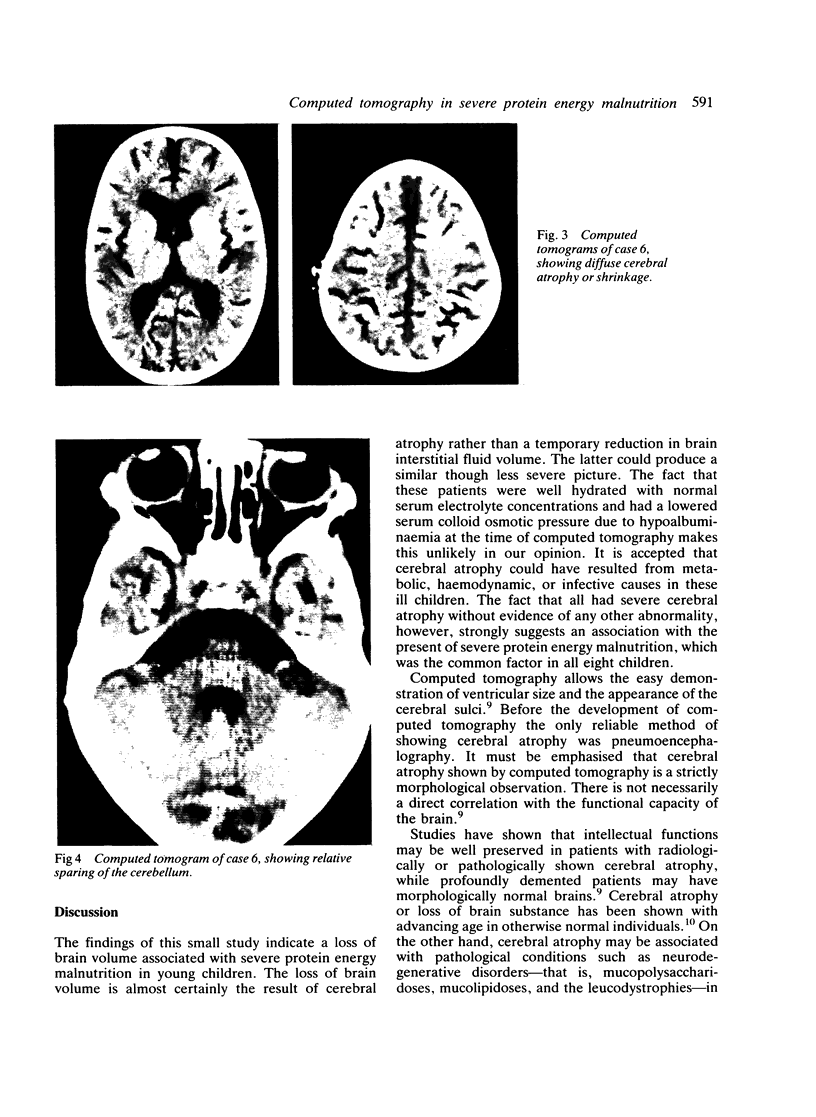
Computed tomography of the brain was performed on eight children aged 1 to 4 years with severe protein energy malnutrition. Clinical features typical of kwashiorkor were present in all the children studied. Severe cerebral atrophy or brain shrinkage according to standard radiological criteria was present in every case. The findings of this study suggest considerable cerebral insult associated with severe protein energy malnutrition.
Full text
PDF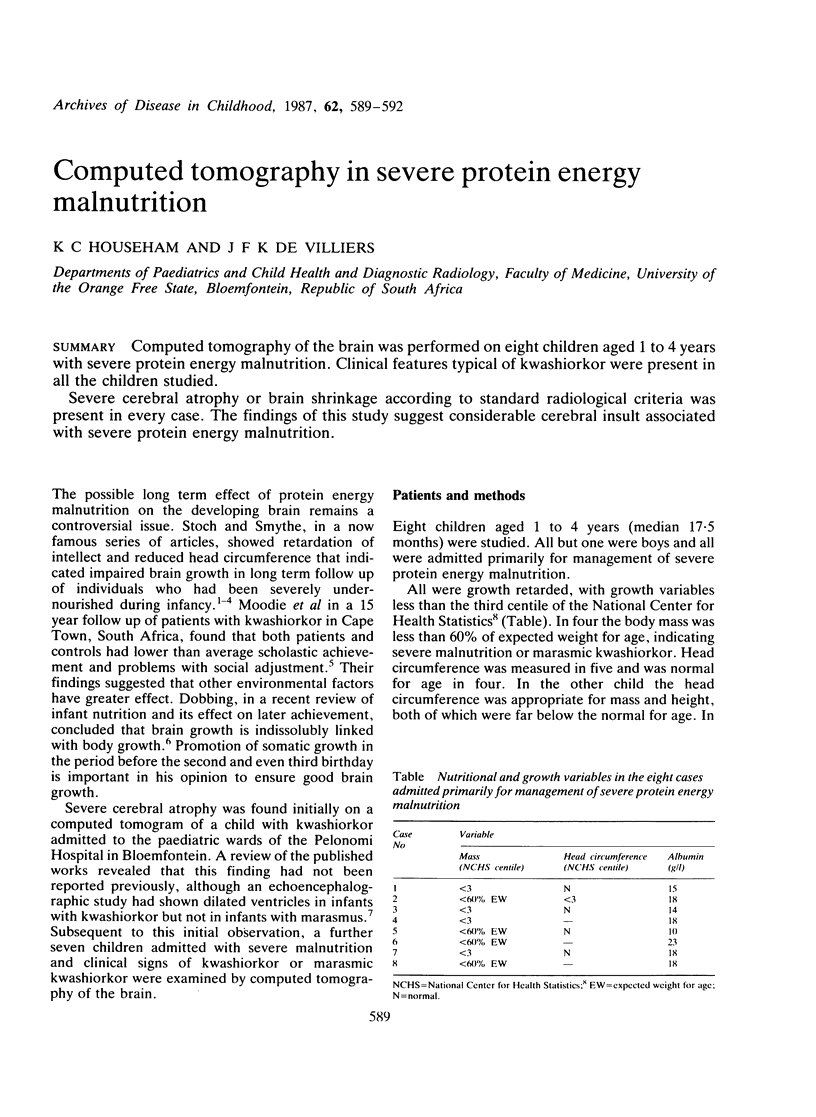

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowie M. D., Moodie A. D., Mann M. D., Hansen J. D. A prospective 15-year follow-up study of kwashiorkor patients. Part I. Physical growth and development. S Afr Med J. 1980 Oct 25;58(17):671–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbing J. Infant nutrition and later achievement. Nutr Rev. 1984 Jan;42(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1984.tb02233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbing J., Sands J. Quantitative growth and development of human brain. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Oct;48(10):757–767. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.10.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill P. V., Drizd T. A., Johnson C. L., Reed R. B., Roche A. F., Moore W. M. Physical growth: National Center for Health Statistics percentiles. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Mar;32(3):607–629. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.3.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handler L. C., Stoch M. B., Smythe P. M. CT brain scans: part of a 20-year development study following gross undernutrition during infancy. Br J Radiol. 1981 Nov;54(647):953–954. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-54-647-953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper C., Kril J. Pathological changes in alcoholic brain shrinkage. Med J Aust. 1986 Jan 6;144(1):3–4. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1986.tb113618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands J., Dobbing J., Gratrix C. A. Cell number and cell size: organ growth and development and the control of catch-up growth in rats. Lancet. 1979 Sep 8;2(8141):503–505. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91556-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner I., Gomori J. M., Melamed E. Progressive brain atrophy during normal aging in man: a quantitative computerized tomography study. Isr J Med Sci. 1985 Mar;21(3):279–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoch M. B., Smythe P. M. 15-Year developmental study on effects of severe undernutrition during infancy on subsequent physical growth and intellectual functioning. Arch Dis Child. 1976 May;51(5):327–336. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.5.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoch M. B., Smythe P. M., Moodie A. D., Bradshaw D. Psychosocial outcome and CT findings after gross undernourishment during infancy: a 20-year developmental study. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1982 Aug;24(4):419–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1982.tb13647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoch M. B., Smythe P. M. The effect of undernutrition during infancy on subsequent brain growth and intellectual development. S Afr Med J. 1967 Oct 28;41(41):1027–1030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vahlquist B., Engsner G., Sjögren I. Malnutrition and size of the cerebral ventricles. Echoencephalographic studies in infants and young children. Preliminary communication. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1971 Sep;60(5):533–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1971.tb06986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wende S., Ludwig B., Kishikawa T., Rochel M., Gehler J. The value of CT in diagnosis and prognosis of different inborn neurodegenerative disorders in childhood. J Neurol. 1984;231(2):57–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00313718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]